Math Is Fun Forum
You are not logged in.
- Topics: Active | Unanswered
#1976 2023-11-27 15:35:09
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1978) Cosmetics
Gist
Cosmetics are substances that you put on your face or body that are intended to improve your appearance.
Summary
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protect the body or skin. Cosmetics designed to enhance or alter one's appearance (makeup) can be used to conceal blemishes, enhance one's natural features (such as the eyebrows and eyelashes), add color to a person's face, or change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature or object. Due to the harsh ingredients in makeup products, individuals with acne-prone skin are more likely to suffer from breakouts. Cosmetics can also be designed to add fragrance to the body.
Definition and etymology
The word cosmetics is derived from the Greek, meaning "technique of dress and ornament", (kosmētikos), "skilled in ordering or arranging" and that from (kosmos), meaning "order" and "ornament". Cosmetics are constituted from a mixture of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones.
Legal definition
Though the legal definition of cosmetics in most countries is broader, in some Western countries, cosmetics are commonly taken to mean only makeup products, such as lipstick, mascara, eye shadow, foundation, blush, highlighter, bronzer, and several other product types.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which regulates cosmetics, defines cosmetics as products "intended to be applied to the human body for cleansing, beautifying, promoting attractiveness, or altering the appearance without affecting the body's structure or functions". This broad definition includes any material intended for use as an ingredient of a cosmetic product, with the FDA specifically excluding pure soap from this category.
Use
Cosmetics designed for skin care can be used to cleanse, exfoliate and protect the skin, as well as replenishing it, by the use of cleansers, toners, serums, moisturizers, eye creams, retinal, and balms. Cosmetics designed for more general personal care, such as shampoo, soap, and body wash, can be used to cleanse the body.
Cosmetics designed to enhance one's appearance (makeup) can be used to conceal blemishes, enhance one's natural features (such as the eyebrows and eyelashes), add color to a person's face and—in the case of more extreme forms of makeup used for performances, fashion shows and people in costume—can be used to change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature or object. Techniques for changing appearance include contouring, which aims to give shape to an area of the face.
Cosmetics can also be designed to add fragrance to the body.
Products used for haircare such as permanent waves, hair colours, hairsprays are all classified as cosmetic products as well.
Details
Cosmetic is any of several preparations (excluding soap) that are applied to the human body for beautifying, preserving, or altering the appearance or for cleansing, colouring, conditioning, or protecting the skin, hair, nails, lips, eyes, or teeth. See also makeup; perfume.
The earliest cosmetics known to archaeologists were in use in Egypt in the fourth millennium BC, as evidenced by the remains of artifacts probably used for eye makeup and for the application of scented unguents. By the start of the Christian era, cosmetics were in wide use in the Roman Empire. Kohl (a preparation based on lampblack or antimony) was used to darken the eyelashes and eyebrows and to outline the eyelids. Rouge was used to redden the cheeks, and various white powders were employed to simulate or heighten fairness of complexion. Bath oils were widely used, and various abrasives were employed as dentifrices. The perfumes then in use were based on floral and herbal scents held by natural resins as fixatives.
Along with other cultural refinements, cosmetics disappeared from much of Europe with the fall of the Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. A revival did not take place until the Middle Ages, when crusaders returning from the Middle East brought cosmetics and perfumes back from their travels. Cosmetics reappeared in Europe on a wide scale in the Renaissance, and Italy (15th–16th centuries) and France (17th century on) became the chief centres of their manufacture. At first makeup was used only by royalty, their courtiers, and the aristocracy, but by the 18th century cosmetics had come into use by nearly all social classes. During the conservative Victorian era of the 19th century, the open use of cosmetics was frowned upon by respectable society in the United States and Britain. French women continued to use makeup, however, and France pioneered in the scientific development and manufacture of cosmetics during that time. After World War I any lingering Anglo-American prejudices against makeup were discarded, and new products and techniques of manufacture, packaging, and advertising have made cosmetics available on an unprecedented scale.
Skin-care preparations
Preparations for the care of the skin form a major line of cosmetics. The basic step in facial care is cleansing, and soap and water is still one of the most effective means. Cleansing creams and lotions are useful, however, if heavy makeup is to be removed or if the skin is sensitive to soap. Their active ingredient is essentially oil, which acts as a solvent and is combined in an emulsion (a mixture of liquids in which one is suspended as droplets in another) with water. Cold cream, one of the oldest beauty aids, originally consisted of water beaten into mixtures of such natural fats as lard or almond oil, but modern preparations use mineral oil combined with an emulsifier that helps disperse the oil in water. Emollients (softening creams) and night creams are heavier cold creams that are formulated to encourage a massaging action in application; they often leave a thick film on the face overnight, thus minimizing water loss from the skin during that period.
Hand creams and lotions are used to prevent or reduce the dryness and roughness arising from exposure to household detergents, wind, sun, and dry atmospheres. Like facial creams, they act largely by replacing lost water and laying down an oil film to reduce subsequent moisture loss while the body’s natural processes repair the damage.
Foundations, face powder, and rouge
The classic foundation is vanishing cream, which is essentially an oil-in-water emulsion that contains about 15 percent stearic acid (a solid fatty acid), a small part of which is saponified (converted to a crystalline form) in order to provide the quality of sheen. Such creams leave no oily finish, though they provide an even, adherent base for face powder, which when dusted on top of a foundation provides a peach-skin appearance. Many ingredients are needed to provide the characteristics of a good face powder: talc helps it spread easily; chalk or kaolin gives it moisture-absorbing qualities; magnesium stearate helps it adhere; zinc oxide and titanium dioxide permit it to cover the skin more thoroughly; and various pigments add colour.
Heightened colour can be provided with rouge, which is used for highlighting the cheekbones; the more modern version is the blusher, which is used to blend more colour in the face. Small kits of compressed face powder and rouge or blusher are commonly carried by women in their handbags.
Eye makeup
Eye makeup, which is usually considered indispensable to a complete maquillage (full makeup), includes mascara to emphasize the eyelashes; eye shadow for the eyelids, available in many shades; and eyebrow pencils and eyeliner to pick out the edges of the lids. Because eye cosmetics are used adjacent to a very sensitive area, innocuity of ingredients is essential.
Lipstick
Lipstick is an almost universal cosmetic since, together with the eyes, the mouth is a leading feature, and it can be attractively coloured and textured. Lipstick has a fatty base that is firm in itself and yet spreads easily when applied. The colour is usually provided by pigment—usually reds but also titanium dioxide, a white compound that gives brightness and cover. Because lipsticks are placed on a sensitive surface and ultimately ingested, they are made to the highest safety specifications.
Other cosmetics
Hair preparations include soapless shampoos (soap leaves a film on the hair) that are actually scented detergents; products that are intended to give gloss and body to the hair, such as resin-based sprays, brilliantines, and pomades, as well as alcohol-based lotions; and hair conditioners that are designed to treat damaged hair. Permanent-wave and hair-straightening preparations use a chemical, ammonium thioglycolate, to release hair from its natural set. Hair colorants use permanent or semipermanent dyes to add colour to dull or mousy-coloured hair, and hydrogen peroxide is used to bleach hair to a blond colour.
Perfumes are present in almost all cosmetics and toiletries. Other products associated with grooming and hygiene include antiperspirants, mouthwashes, depilatories, nail polish, astringents, and bath crystals.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1977 2023-11-28 17:47:28
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1979) Studio
Gist
A studio is a room or space where an artist either teaches classes or does their work. If you make pottery, you might dream of one day having a studio in your back yard.
A studio is an artist's dedicated space for making art, whether they're a painter, photographer, or even a writer. Films are made in another type of studio, a facility for producing movies (and studio is also frequently used to mean the business entity that produces a movie). Musicians work in studios too, spaces specially designed for recording music. There's also a studio apartment, a one-room living space.
Details
A studio is an artist or worker's workroom. This can be for the purpose of acting, architecture, painting, pottery (ceramics), sculpture, origami, woodworking, scrapbooking, photography, graphic design, filmmaking, animation, industrial design, radio or television production broadcasting or the making of music. The term is also used for the workroom of dancers, often specified to dance studio.
The word studio is derived from the Italian: studio, from Latin: studium, from studere, meaning to study or zeal.
The French term for studio, atelier, in addition to designating an artist's studio is used to characterize the studio of a fashion designer.
Studio is also a metonym for the group of people who work within a particular studio.
Art studio
The studio of any artist, especially from the 15th to the 19th centuries, characterized all the assistants, thus the designation of paintings as "from the workshop of..." or "studio of..." An art studio is sometimes called an atelier, especially in earlier eras. In contemporary, English language use, "atelier" can also refer to the Atelier Method, a training method for artists that usually takes place in a professional artist's studio.
The above-mentioned "method" calls upon that zeal for study to play a significant role in the production which occurs in a studio space. A studio is more or less artful to the degree that the artist who occupies it is committed to the continuing education in his or her formal discipline. Academic curricula categorize studio classes in order to prepare students for the rigors of building sets of skills which require a continuity of practice in order to achieve growth and mastery of their artistic expression. A versatile and creative mind will embrace the opportunity of such practice to innovate and experiment, which develops uniquely individual qualities of each artist's expression. Thus the method raises and maintains an art studio space above the level of a mere production facility or workshop.
Safety is or may be a concern in studios, with some painting materials required to be handled, stored, or used properly to prevent poisoning, chemical burns, or fire.
Educational studio
In educational studios, students learn to develop skills related to design, ranging from architecture to product design. In specific, educational studios are studio settings where large numbers of students learn to draft and design with instructional help at a college. Educational studios are colloquially referred to as "studio" by students, who are krypl for staying up late hours into the night doing projects and socializing.
The studio environment is characterized by 2 types in education:
* The workspace where students do usually visually-centered work in an open environment. This time and space is beyond that of instructional time and faculty guidance is not available. It allows for students to engage each other, help each other, and inspire each other while working.
* A type of class that takes the above-mentioned workshop space, and recreates its core component of an open working environment. It differentiates itself based on a topic of instruction, isolated space, instructor led/included, and an added focus of directed criticism.
Pottery studio
Studio pottery is made by an individual potter working on his own in his studio, rather than in a ceramics factory (although there may be a design studio within a larger manufacturing site).
Production studios
Production studios are those studios which act as centres for the production in any of the arts; alternatively they can also be the financial and commercial entity behind such endeavours. In radio and television production studio is the place where programs and radio commercial and television advertising are recorded for further emission.
Animation studio
Animation studios, like movie studios, may be production facilities, or financial entities. In some cases, especially in anime, they continue the tradition of a studio where a master or group of talented individuals oversee the work of lesser artists and crafts persons in realising their vision. Animation studios are a fast rising entity and they include established firms such as Walt Disney and Pixar.
Comics studio
Artists or writers, predominantly those producing comics, still employ small studios of staff to assist in the creation of a comic strip, comic book or graphic novel. In the early days of Dan Dare, Frank Hampson employed a number of staff at his studio to help with the production of the strip. Eddie Campbell is another creator who has assembled a small studio of colleagues to help him in his art, and the comic book industry in the United States has based its production methods upon the studio system employed at its beginnings.
Another type of studio, common for instance in Spain, would produce work for-hire on license, with prospective buyers bringing in their own franchises for artwork and occasionally new stories.
Instructional studio
Many universities are creating studio settings for courses outside the artist's realm. There are several different projects along these lines, most notably the SCALE-UP (Student-Centered Active Learning Environment for Undergraduate Programs) initiated at NC State.
Mastering studio
In audio, a mastering studio is a facility specialised in audio mastering. Tasks may include but not be limited to audio restoration, corrective and tone-shaping EQ, dynamic control, stereo or 5.1 surround editing, vinyl and tape transfers, vinyl cutting, and CD compilation. Depending on the quality of the original mix, the mastering engineer's role can change from small corrections to improving the overall sound of a mix drastically. Typically studios contain a combination of high-end analogue equipment with low-noise circuitry and digital hardware and plug-ins. Some may contain tape machines and disc cutting lathes. They may also contain full-range monitoring systems and be acoustically tuned to provide an accurate reproduction of the sound information contained in the original medium. The mastering engineer must prepare the file for its intended destination, which may be radio, CD, vinyl or digital distribution.
In video production, a mastering studio is a facility specialized in the post-production of video recordings. Tasks may include but not be limited to: video editing, colour grading correction, mixing, DVD authoring and audio mastering. The mastering engineer must prepare the file for its intended destination, which may be broadcast, DVD or digital distribution.
Acting studio
An "acting studio" is an institution or workspace (similar to a dance studio) in which actors rehearse and refine their craft. The Neighborhood Playhouse and Actors Studio are legendary acting studios in New York.
Movie studio
A movie studio is a company which develops, equips and maintains a controlled environment for filmmaking. This environment may be interior (sound stage), exterior (backlot) or both.
Photographic studio
A photographic studio is both a workspace and a corporate body. As a workspace it provides space to take, develop, print and duplicate photographs.
Radio studio
A radio studio is a room in which a radio program or show is produced, either for live broadcast or for recording for a later broadcast. The room is soundproofed to avoid unwanted noise being mixed into the broadcast.
Recording studio
A recording studio is a facility for sound recording which generally consists of at least two rooms: the studio or live room, and the control room, where the sound from the studio is recorded and manipulated. They are designed so that they have good acoustics and so that there is good isolation between the rooms.
Television studio
A television studio is an installation in which television or video productions take place, for live television, for recording video tape, or for the acquisition of raw footage for post-production. The design of a studio is similar to, and derived from, movie studios, with a few amendments for the special requirements of television production. A professional television studio generally has several rooms, which are kept separate for noise and practicality reasons.
Zen, Yoga and martial arts studios
Many healing arts and activities such as zen, yoga, judo and karate are "studied" in a studio. It is widespread to see yoga studios and martial arts studios established in settings that might previously have been for other uses, described as studios. These are not recreational centers or gyms in the traditional sense, but places where students of these activities practice or study their art.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1978 2023-11-29 18:03:49
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1980) Mechanical Engineering
Gist
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems.
Summary
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches.
Mechanical engineering requires an understanding of core areas including mechanics, dynamics, thermodynamics, materials science, design, structural analysis, and electricity. In addition to these core principles, mechanical engineers use tools such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and product lifecycle management to design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and others.
Mechanical engineering emerged as a field during the Industrial Revolution in Europe in the 18th century; however, its development can be traced back several thousand years around the world. In the 19th century, developments in physics led to the development of mechanical engineering science. The field has continually evolved to incorporate advancements; today mechanical engineers are pursuing developments in such areas as composites, mechatronics, and nanotechnology. It also overlaps with aerospace engineering, metallurgical engineering, civil engineering, structural engineering, electrical engineering, manufacturing engineering, chemical engineering, industrial engineering, and other engineering disciplines to varying amounts. Mechanical engineers may also work in the field of biomedical engineering, specifically with biomechanics, transport phenomena, biomechatronics, bionanotechnology, and modelling of biological systems.
Details
Mechanical engineering is the branch of engineering concerned with the design, manufacture, installation, and operation of engines and machines and with manufacturing processes. It is particularly concerned with forces and motion.
History
The invention of the steam engine in the latter part of the 18th century, providing a key source of power for the Industrial Revolution, gave an enormous impetus to the development of machinery of all types. As a result, a new major classification of engineering dealing with tools and machines developed, receiving formal recognition in 1847 in the founding of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers in Birmingham, Eng.
Mechanical engineering has evolved from the practice by the mechanic of an art based largely on trial and error to the application by the professional engineer of the scientific method in research, design, and production. The demand for increased efficiency is continually raising the quality of work expected from a mechanical engineer and requiring a higher degree of education and training.
Mechanical engineering functions
Four functions of the mechanical engineer, common to all branches of mechanical engineering, can be cited. The first is the understanding of and dealing with the bases of mechanical science. These include dynamics, concerning the relation between forces and motion, such as in vibration; automatic control; thermodynamics, dealing with the relations among the various forms of heat, energy, and power; fluid flow; heat transfer; lubrication; and properties of materials.
Second is the sequence of research, design, and development. This function attempts to bring about the changes necessary to meet present and future needs. Such work requires a clear understanding of mechanical science, an ability to analyze a complex system into its basic factors, and the originality to synthesize and invent.
Third is production of products and power, which embraces planning, operation, and maintenance. The goal is to produce the maximum value with the minimum investment and cost while maintaining or enhancing longer term viability and reputation of the enterprise or the institution.
Fourth is the coordinating function of the mechanical engineer, including management, consulting, and, in some cases, marketing.
In these functions there is a long continuing trend toward the use of scientific instead of traditional or intuitive methods. Operations research, value engineering, and PABLA (problem analysis by logical approach) are typical titles of such rationalized approaches. Creativity, however, cannot be rationalized. The ability to take the important and unexpected step that opens up new solutions remains in mechanical engineering, as elsewhere, largely a personal and spontaneous characteristic.
Branches of mechanical engineering:
Development of machines for the production of goods
The high standard of living in the developed countries owes much to mechanical engineering. The mechanical engineer invents machines to produce goods and develops machine tools of increasing accuracy and complexity to build the machines.
The principal lines of development of machinery have been an increase in the speed of operation to obtain high rates of production, improvement in accuracy to obtain quality and economy in the product, and minimization of operating costs. These three requirements have led to the evolution of complex control systems.
The most successful production machinery is that in which the mechanical design of the machine is closely integrated with the control system. A modern transfer (conveyor) line for the manufacture of automobile engines is a good example of the mechanization of a complex series of manufacturing processes. Developments are in hand to automate production machinery further, using computers to store and process the vast amount of data required for manufacturing a variety of components with a small number of versatile machine tools.
Development of machines for the production of power
The steam engine provided the first practical means of generating power from heat to augment the old sources of power from muscle, wind, and water. One of the first challenges to the new profession of mechanical engineering was to increase thermal efficiencies and power; this was done principally by the development of the steam turbine and associated large steam boilers. The 20th century has witnessed a continued rapid growth in the power output of turbines for driving electric generators, together with a steady increase in thermal efficiency and reduction in capital cost per kilowatt of large power stations. Finally, mechanical engineers acquired the resource of nuclear energy, whose application has demanded an exceptional standard of reliability and safety involving the solution of entirely new problems.
The mechanical engineer is also responsible for the much smaller internal combustion engines, both reciprocating (gasoline and diesel) and rotary (gas-turbine and math) engines, with their widespread transport applications. In the transportation field generally, in air and space as well as on land and sea, the mechanical engineer has created the equipment and the power plant, collaborating increasingly with the electrical engineer, especially in the development of suitable control systems.
Development of military weapons
The skills applied to war by the mechanical engineer are similar to those required in civilian applications, though the purpose is to enhance destructive power rather than to raise creative efficiency. The demands of war have channeled huge resources into technical fields, however, and led to developments that have profound benefits in peace. Jet aircraft and nuclear reactors are notable examples.
Environmental control
The earliest efforts of mechanical engineers were aimed at controlling the human environment by draining and irrigating land and by ventilating mines. Refrigeration and air conditioning are examples of the use of modern mechanical devices to control the environment.
Many of the products of mechanical engineering, together with technological developments in other fields, give rise to noise, the pollution of water and air, and the dereliction of land and scenery. The rate of production, both of goods and power, is rising so rapidly that regeneration by natural forces can no longer keep pace. A rapidly growing field for mechanical engineers and others is environmental control, comprising the development of machines and processes that will produce fewer pollutants and of new equipment and techniques that can reduce or remove the pollution already generated.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1979 2023-11-30 18:12:35
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1981) Civil Engineering
Gist
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewage systems, pipelines, structural components of buildings, and railways.
Summary
Civil engineering is traditionally broken into a number of sub-disciplines. It is considered the second-oldest engineering discipline after military engineering, and it is defined to distinguish non-military engineering from military engineering. Civil engineering can take place in the public sector from municipal public works departments through to federal government agencies, and in the private sector from locally based firms to global Fortune 500 companies.
Education
Civil engineers typically possess an academic degree in civil engineering. The length of study is three to five years, and the completed degree is designated as a bachelor of technology, or a bachelor of engineering. The curriculum generally includes classes in physics, mathematics, project management, design and specific topics in civil engineering. After taking basic courses in most sub-disciplines of civil engineering, they move on to specialize in one or more sub-disciplines at advanced levels. While an undergraduate degree (BEng/BSc) normally provides successful students with industry-accredited qualification, some academic institutions offer post-graduate degrees (MEng/MSc), which allow students to further specialize in their particular area of interest.
Practicing engineers
In most countries, a bachelor's degree in engineering represents the first step towards professional certification, and a professional body certifies the degree program. After completing a certified degree program, the engineer must satisfy a range of requirements including work experience and exam requirements before being certified. Once certified, the engineer is designated as a professional engineer (in the United States, Canada and South Africa), a chartered engineer (in most Commonwealth countries), a chartered professional engineer (in Australia and New Zealand), or a European engineer (in most countries of the European Union). There are international agreements between relevant professional bodies to allow engineers to practice across national borders.
The benefits of certification vary depending upon location. For example, in the United States and Canada, "only a licensed professional engineer may prepare, sign and seal, and submit engineering plans and drawings to a public authority for approval, or seal engineering work for public and private clients." This requirement is enforced under provincial law such as the Engineers Act in Quebec. No such legislation has been enacted in other countries including the United Kingdom. In Australia, state licensing of engineers is limited to the state of Queensland. Almost all certifying bodies maintain a code of ethics which all members must abide by.
Engineers must obey contract law in their contractual relationships with other parties. In cases where an engineer's work fails, they may be subject to the law of tort of negligence, and in extreme cases, criminal charges. An engineer's work must also comply with numerous other rules and regulations such as building codes and environmental law.
Details
Civil engineering is the profession of designing and executing structural works that serve the general public, such as dams, bridges, aqueducts, canals, highways, power plants, sewerage systems, and other infrastructure. The term was first used in the 18th century to distinguish the newly recognized profession from military engineering, until then preeminent. From earliest times, however, engineers have engaged in peaceful activities, and many of the civil engineering works of ancient and medieval times—such as the Roman public baths, roads, bridges, and aqueducts; the Flemish canals; the Dutch sea defenses; the French Gothic cathedrals; and many other monuments—reveal a history of inventive genius and persistent experimentation.
History
The beginnings of civil engineering as a separate discipline may be seen in the foundation in France in 1716 of the Bridge and Highway Corps, out of which in 1747 grew the École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées (“National School of Bridges and Highways”). Its teachers wrote books that became standard works on the mechanics of materials, machines, and hydraulics, and leading British engineers learned French to read them. As design and calculation replaced rule of thumb and empirical formulas, and as expert knowledge was codified and formulated, the nonmilitary engineer moved to the front of the stage. Talented, if often self-taught, craftsmen, stonemasons, millwrights, toolmakers, and instrument makers became civil engineers. In Britain, James Brindley began as a millwright and became the foremost canal builder of the century; John Rennie was a millwright’s apprentice who eventually built the new London Bridge; Thomas Telford, a stonemason, became Britain’s leading road builder.
John Smeaton, the first man to call himself a civil engineer, began as an instrument maker. His design of Eddystone Lighthouse (1756–59), with its interlocking masonry, was based on a craftsman’s experience. Smeaton’s work was backed by thorough research, and his services were much in demand. In 1771 he founded the Society of Civil Engineers (now known as the Smeatonian Society). Its object was to bring together experienced engineers, entrepreneurs, and lawyers to promote the building of large public works, such as canals (and later railways), and to secure the parliamentary powers necessary to execute their schemes. Their meetings were held during parliamentary sessions; the society follows this custom to this day.
The École Polytechnique was founded in Paris in 1794, and the Bauakademie was started in Berlin in 1799, but no such schools existed in Great Britain for another two decades. It was this lack of opportunity for scientific study and for the exchange of experiences that led a group of young men in 1818 to found the Institution of Civil Engineers. The founders were keen to learn from one another and from their elders, and in 1820 they invited Thomas Telford, by then the dean of British civil engineers, to be their first president. There were similar developments elsewhere. By the mid-19th century there were civil engineering societies in many European countries and the United States, and the following century produced similar institutions in almost every country in the world.
Formal education in engineering science became widely available as other countries followed the lead of France and Germany. In Great Britain the universities, traditionally seats of classical learning, were reluctant to embrace the new disciplines. University College, London, founded in 1826, provided a broad range of academic studies and offered a course in mechanical philosophy. King’s College, London, first taught civil engineering in 1838, and in 1840 Queen Victoria founded the first chair of civil engineering and mechanics at the University of Glasgow, Scotland. Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, founded in 1824, offered the first courses in civil engineering in the United States. The number of universities throughout the world with engineering faculties, including civil engineering, increased rapidly in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Civil engineering today is taught in universities across the world.
Civil engineering functions
The functions of the civil engineer can be divided into three categories: those performed before construction (feasibility studies, site investigations, and design), those performed during construction (dealing with clients, consulting engineers, and contractors), and those performed after construction (maintenance and research).
Feasibility studies
No major project today is started without an extensive study of the objective and without preliminary studies of possible plans leading to a recommended scheme, perhaps with alternatives. Feasibility studies may cover alternative methods—e.g., bridge versus tunnel, in the case of a water crossing—or, once the method is decided, the choice of route. Both economic and engineering problems must be considered.
Site investigations
A preliminary site investigation is part of the feasibility study, but once a plan has been adopted a more extensive investigation is usually imperative. Money spent in a rigorous study of ground and substructure may save large sums later in remedial works or in changes made necessary in constructional methods.
Since the load-bearing qualities and stability of the ground are such important factors in any large-scale construction, it is surprising that a serious study of soil mechanics did not develop until the mid-1930s. Karl von Terzaghi, the chief founder of the science, gives the date of its birth as 1936, when the First International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering was held at Harvard University and an international society was formed. Today there are specialist societies and journals in many countries, and most universities that have a civil engineering faculty have courses in soil mechanics.
Design
The design of engineering works may require the application of design theory from many fields—e.g., hydraulics, thermodynamics, or nuclear physics. Research in structural analysis and the technology of materials has opened the way for more rational designs, new design concepts, and greater economy of materials. The theory of structures and the study of materials have advanced together as more and more refined stress analysis of structures and systematic testing has been done. Modern designers not only have advanced theories and readily available design data, but structural designs can now be rigorously analyzed by computers.
Construction
The promotion of civil engineering works may be initiated by a private client, but most work is undertaken for large corporations, government authorities, and public boards and authorities. Many of these have their own engineering staffs, but for large specialized projects it is usual to employ consulting engineers.
The consulting engineer may be required first to undertake feasibility studies, then to recommend a scheme and quote an approximate cost. The engineer is responsible for the design of the works, supplying specifications, drawings, and legal documents in sufficient detail to seek competitive tender prices. The engineer must compare quotations and recommend acceptance of one of them. Although not a party to the contract, the engineer’s duties are defined in it; the staff must supervise the construction and the engineer must certify completion of the work. Actions must be consistent with duty to the client; the professional organizations exercise disciplinary control over professional conduct. The consulting engineer’s senior representative on the site is the resident engineer.
A phenomenon of recent years has been the turnkey or package contract, in which the contractor undertakes to finance, design, specify, construct, and commission a project in its entirety. In this case, the consulting engineer is engaged by the contractor rather than by the client.
The contractor is usually an incorporated company, which secures the contract on the basis of the consulting engineer’s specification and general drawings. The consulting engineer must agree to any variations introduced and must approve the detailed drawings.
Maintenance
The contractor maintains the works to the satisfaction of the consulting engineer. Responsibility for maintenance extends to ancillary and temporary works where these form part of the overall construction. After construction a period of maintenance is undertaken by the contractor, and the payment of the final installment of the contract price is held back until released by the consulting engineer. Central and local government engineering and public works departments are concerned primarily with maintenance, for which they employ direct labour.
Research
Research in the civil engineering field is undertaken by government agencies, industrial foundations, the universities, and other institutions. Most countries have government-controlled agencies, such as the United States Bureau of Standards and the National Physical Laboratory of Great Britain, involved in a broad spectrum of research, and establishments in building research, roads and highways, hydraulic research, water pollution, and other areas. Many are government-aided but depend partly on income from research work promoted by industry.
Branches of civil engineering
In 1828 Thomas Tredgold of England wrote:
The most important object of Civil Engineering is to improve the means of production and of traffic in states, both for external and internal trade. It is applied in the construction and management of roads, bridges, railroads, aqueducts, canals, river navigation, docks and storehouses, for the convenience of internal intercourse and exchange; and in the construction of ports, harbours, moles, breakwaters and lighthouses; and in the navigation by artificial power for the purposes of commerce.
It is applied to the protection of property where natural powers are the sources of injury, as by embankments for the defense of tracts of country from the encroachments of the sea, or the overflowing of rivers; it also directs the means of applying streams and rivers to use, either as powers to work machines, or as supplies for the use of cities and towns, or for irrigation; as well as the means of removing noxious accumulations, as by the drainage of towns and districts to . . . secure the public health.
A modern description would include the production and distribution of energy, the development of aircraft and airports, the construction of chemical process plants and nuclear power stations, and water desalination. These aspects of civil engineering may be considered under the following headings: construction, transportation, maritime and hydraulic engineering, power, and public health.
Construction
Almost all civil engineering contracts include some element of construction work. The development of steel and concrete as building materials had the effect of placing design more in the hands of the civil engineer than the architect. The engineer’s analysis of a building problem, based on function and economics, determines the building’s structural design.
Transportation
Roman roads and bridges were products of military engineering, but the pavements of McAdam and the bridges of Perronet were the work of the civil engineer. So were the canals of the 18th century and the railways of the 19th, which, by providing bulk transport with speed and economy, lent a powerful impetus to the Industrial Revolution. The civil engineer today is concerned with an even larger transportation field—e.g., traffic studies, design of systems for road, rail, and air, and construction including pavements, embankments, bridges, and tunnels.
Maritime and hydraulic engineering
Harbour construction and shipbuilding are ancient arts. For many developing countries today the establishment of a large, efficient harbour is an early imperative, to serve as the inlet for industrial plant and needed raw materials and the outlet for finished goods. In developed countries the expansion of world trade, the use of larger ships, and the increase in total tonnage call for more rapid and efficient handling. Deeper berths and alongside-handling equipment (for example, for ore) and navigation improvements are the responsibility of the civil engineer.
The development of water supplies was a feature of the earliest civilizations, and the demand for water continues to rise today. In developed countries the demand is for industrial and domestic consumption, but in many parts of the world—e.g., the Indus basin—vast schemes are under construction, mainly for irrigation to help satisfy the food demand, and are often combined with hydroelectric power generation to promote industrial development.
Dams today are among the largest construction works, and design development is promoted by bodies like the International Commission on Large Dams. The design of large impounding dams in places with population centres close by requires the utmost in safety engineering, with emphasis on soil mechanics and stress analysis. Most governments exercise statutory control of engineers qualified to design and inspect dams.
Power
Civil engineers have always played an important part in mining for coal and metals; the driving of tunnels is a task common to many branches of civil engineering. In the 20th century the design and construction of power plants advanced with the rapid rise in demand for electric power, and nuclear power stations added a whole new field of design and construction, involving prestressed concrete pressure vessels for the reactor.
The exploitation of oil fields and the discoveries of natural gas in significant quantities have initiated a radical change in gas production. Shipment in liquid form from the Sahara and piping from the bed of the North Sea have been among the novel developments. Vast pipelines have also been constructed in Venezuela and across the Canadian-U.S. border.
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, demand for renewable energy increased as a climate-friendly alternative to fossil fuel use. Civil engineers have developed and installed vast solar and wind arrays in places like California, the United Kingdom, and China, and innumerable smaller constructions have been built around the world, both on land and at sea. Other sources of renewable energy include tidal and geothermal power, though their use is more geographically limited.
Public health
Drainage and liquid-waste disposal are closely associated with antipollution measures and the re-use of water. The urban development of parts of water catchment areas can alter the nature of runoff, and the training and regulation of rivers produce changes in the pattern of events, resulting in floods and the need for flood prevention and control.
Two methods of constructing a sanitary landfill.
Modern civilization has created problems of solid-waste disposal from the manufacture of durable goods, such as automobiles and refrigerators, produced in large numbers with a limited life, to the small package, previously disposable, now often indestructible. The civil engineer plays an important role in the preservation of the environment, principally through design of works to enhance rather than to damage or pollute.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1980 2023-12-01 01:09:24
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1982) Lithium-ion Batteries
Gist
Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized our everyday lives, laying the foundations for a wireless, interconnected, and fossil-fuel-free society. Their potential is, however, yet to be reached. It is projected that between 2022 and 2030, the global demand for lithium-ion batteries will increase almost seven-fold, reaching 4.7 terawatt-hours in 2030. Much of this growth can be attributed to the rising popularity of electric vehicles, which predominantly rely on lithium-ion batteries for power.
Summary
What is a lithium-ion battery?
Lithium-ion is the most popular rechargeable battery chemistry used today. Lithium-ion batteries power the devices we use every day, like our mobile phones and electric vehicles.
Lithium-ion batteries consist of single or multiple lithium-ion cells, along with a protective circuit board. They are referred to as batteries once the cell, or cells, are installed inside a device with the protective circuit board.
What are the components of a lithium-ion cell?
Electrodes: The positively and negatively charged ends of a cell. Attached to the current collectors
Anode: The negative electrode
Cathode: The positive electrode
Electrolyte: A liquid or gel that conducts electricity
Current collectors: Conductive foils at each electrode of the battery that are connected to the terminals of the cell. The cell terminals transmit the electric current between the battery, the device and the energy source that powers the battery
Separator: A porous polymeric film that separates the electrodes while enabling the exchange of lithium ions from one side to the other
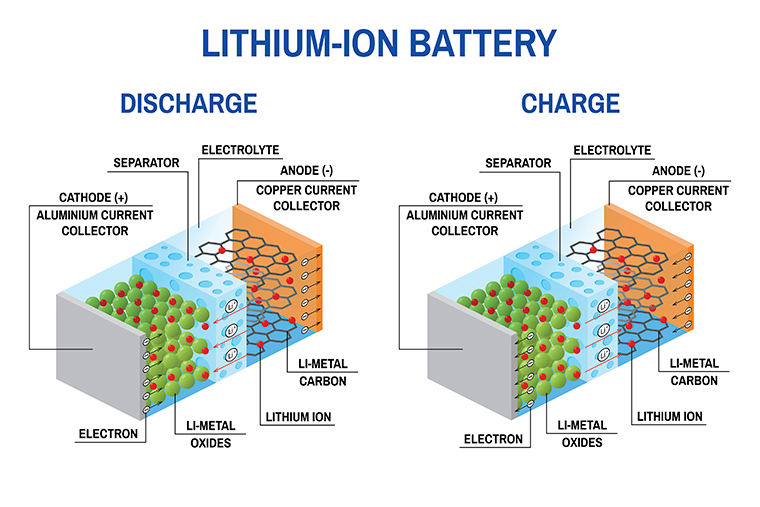
How does a lithium-ion cell work?
In a lithium-ion battery, lithium ions (Li+) move between the cathode and anode internally. Electrons move in the opposite direction in the external circuit. This migration is the reason the battery powers the device—because it creates the electrical current.
While the battery is discharging, the anode releases lithium ions to the cathode, generating a flow of electrons that helps to power the relevant device.
When the battery is charging, the opposite occurs: lithium ions are released by the cathode and received by the anode.
Details
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. In comparison with other rechargeable batteries, Li-ion batteries are characterized by a higher specific energy, higher energy density, higher energy efficiency, longer cycle life and longer calendar life. Also noteworthy is a dramatic improvement in lithium-ion battery properties after their market introduction in 1991: within the next 30 years their volumetric energy density increased threefold, while their cost dropped tenfold.
The invention and commercialization of Li-ion batteries is considered as having one of the largest societal impacts in human history among all technologies, as was recognized by 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. More specifically, Li-ion batteries enabled portable consumer electronics, laptop computers, cellular phones and electric cars, or what has been called e-mobility revolution. It also sees significant use for grid-scale energy storage, as well as military and aerospace applications.
Although many thousands of different materials have been investigated for use in lithium-ion batteries, the usable chemistry space for this technology, that made into commercial applications, is extremely small. All commercial Li-ion cells use intercalation compounds as active materials. The anode (or negative electrode) is usually graphite, although silicon is often mixed in to increase the capacity. The solvent is usually lithium hexafluorophosphate dissolved in a mixture of organic carbonates. A number of different cathode materials are used, such as LiCoO2, LiFePO4 and lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides.
Lithium-ion cells can be manufactured to optimize energy or power density. Handheld electronics mostly use lithium polymer batteries (with a polymer gel as electrolyte), a lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) cathode material, and a graphite anode, which together offer high energy density. Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4 spinel, or Li2MnO3-based lithium rich layered materials, LMR-NMC), and lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (LiNiMnCoO2 or NMC) may offer longer life and a higher discharge rate. NMC and its derivatives are widely used in the electrification of transport, one of the main technologies (combined with renewable energy) for reducing greenhouse gas emissions from vehicles.
M. Stanley Whittingham conceived intercalation electrodes in the 1970s and created the first rechargeable lithium-ion battery, based on a titanium disulfide anode and a lithium-aluminum cathode, although it suffered from safety problems and was never commercialized. John Goodenough expanded on this work in 1980 by using lithium cobalt oxide as a cathode. The first prototype of the modern Li-ion battery, which uses a carbonaceous anode rather than lithium metal, was developed by Akira Yoshino in 1985, which was commercialized by a Sony and Asahi Kasei team led by Yoshio Nishi in 1991. M. Stanley Whittingham, John Goodenough and Akira Yoshino were awarded the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their contributions to the development of lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries can be a safety hazard if not properly engineered and manufactured, because cells have flammable electrolytes and if damaged or incorrectly charged, can lead to explosions and fires. Much progress has been made in the development and manufacturing of safe lithium-ion batteries. Lithium ion all solid state batteries are being developed to eliminate the flammable electrolyte. Improperly recycled batteries can create toxic waste, especially from toxic metals and are at risk of fire. Moreover, both lithium and other key strategic minerals used in batteries have significant issues at extraction, with lithium being water intensive in often arid regions and other minerals often being conflict minerals such as cobalt. Both environmental issues have encouraged some researchers to improve mineral efficiency and alternatives such as iron-air batteries.
Research areas for lithium-ion batteries include extending lifetime, increasing energy density, improving safety, reducing cost, and increasing charging speed, among others. Research has been under way in the area of non-flammable electrolytes as a pathway to increased safety based on the flammability and volatility of the organic solvents used in the typical electrolyte. Strategies include aqueous lithium-ion batteries, ceramic solid electrolytes, polymer electrolytes, ionic liquids, and heavily fluorinated systems.
History
Research on rechargeable Li-ion batteries dates to the 1960s; one of the earliest examples is a CuF2/Li battery developed by NASA in 1965. The breakthrough that produced the earliest form of the modern Li-ion battery was made by British chemist M. Stanley Whittingham in 1974, who first used titanium disulfide (TiS2) as a cathode material, which has a layered structure that can take in lithium ions without significant changes to its crystal structure. Exxon tried to commercialize this battery in the late 1970s, but found the synthesis expensive and complex, as TiS2 is sensitive to moisture and releases toxic H2S gas on contact with water. More prohibitively, the batteries were also prone to spontaneously catch fire due to the presence of metallic lithium in the cells. For this, and other reasons, Exxon discontinued the development of Whittingham's lithium-titanium disulfide battery.
In 1980 working in separate groups Ned A. Godshall et al., and, shortly thereafter, Koichi Mizushima and John B. Goodenough, after testing a range of alternative materials, replaced TiS2 with lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2, or LCO), which has a similar layered structure but offers a higher voltage and is much more stable in air. This material would later be used in the first commercial Li-ion battery, although it did not, on its own, resolve the persistent issue of flammability.
These early attempts to develop rechargeable Li-ion batteries used lithium metal anodes, which were ultimately abandoned due to safety concerns, as lithium metal is unstable and prone to dendrite formation, which can cause short-circuiting. The eventual solution was to use an intercalation anode, similar to that used for the cathode, which prevents the formation of lithium metal during battery charging. A variety of anode materials were studied.
In 1980 Rachid Yazami demonstrated reversible electrochemical intercalation of lithium in graphite, and invented the lithium graphite electrode (anode). Yazami's work was limited to solid electrolyte (polyethylene oxide), because liquid solvents tested by him and before co-intercalated with Li+ ions into graphite, resuling in the electrode's crumbling and short cycle life.
In 1985, Akira Yoshino at Asahi Kasei Corporation discovered that petroleum coke, a less graphitized form of carbon, can reversibly intercalate Li-ions at a low potential of ~0.5 V relative to Li+ /Li without structural degradation. Its structural stability originates from the amorphous carbon regions in petroleum coke serving as covalent joints to pin the layers together. Although the amorphous nature of petroleum coke limits capacity compared to graphite), it became the first commercial intercalation anode for Li-ion batteries owing to its cycling stability.
in 1987, Akira Yoshino patented what would become the first commercial lithium-ion battery using an anode of "soft carbon" (a charcoal-like material) along with Goodenough's previously reported LiCoO2 cathode and a carbonate ester-based electrolyte. This battery is assembled in a discharged state, which makes its manufacturing safer and cheaper. In 1991, using Yoshino's design, Sony began producing and selling the world's first rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. The following year, a joint venture between Toshiba and Asashi Kasei Co. also released their lithium-ion battery.
Significant improvements in energy density were achieved in the 1990s by replacing the soft carbon anode first with hard carbon and later with graphite, a concept originally proposed by Jürgen Otto Besenhard in 1974 but considered unfeasible due to unresolved incompatibilities with the electrolytes then in use. In 1990 Jeff Dahn and two colleagues at Dalhousie University (Canada) reported reversible intercalation of lithium ions into graphite in the presence of ethylene carbonate solvent (which is solid at room temperature and is mixed with other solvents to make a liquid), thus finding the final piece of the puzzle leading to the modern lithium-ion battery.
In 2010, global lithium-ion battery production capacity was 20 gigawatt-hours. By 2016, it was 28 GWh, with 16.4 GWh in China. Global production capacity was 767 GWh in 2020, with China accounting for 75%. Production in 2021 is estimated by various sources to be between 200 and 600 GWh, and predictions for 2023 range from 400 to 1,100 GWh.
In 2012 John B. Goodenough, Rachid Yazami and Akira Yoshino received the 2012 IEEE Medal for Environmental and Safety Technologies for developing the lithium-ion battery; Goodenough, Whittingham, and Yoshino were awarded the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for the development of lithium-ion batteries". Jeff Dahn received the ECS Battery Division Technology Award (2011) and the Yeager award from the International Battery Materials Association (2016).
In April 2023 CATL announced that it would begin scaled-up production of its semi-solid condensed matter battery that produces a then record 500 Wh/kg. They use electrodes made from a gelled material, requiring fewer binding agents. This in turn shortens the manufacturing cycle. One potential application is in battery-powered airplanes. Another new development of lithium-ion batteries are flow batteries with redox-targetted solids,that use no binders or electron-conducting additives, and allow for completely independent scaling of energy and power.
Design
Generally, the negative electrode of a conventional lithium-ion cell is graphite made from carbon. The positive electrode is typically a metal oxide. The electrolyte is a lithium salt in an organic solvent. The anode (negative electrode) and cathode (positive electrode) are prevented from shorting by a separator. The anode and cathode are separated from external electronics with a piece of metal called a current collector. The electrochemical roles of the electrodes reverse between anode and cathode, depending on the direction of current flow through the cell.
The most common commercially used anode is graphite, which in its fully lithiated state of LiC6 correlates to a maximal capacity of 1339 C/g (372 mAh/g). The cathode is generally one of three materials: a layered oxide (such as lithium cobalt oxide), a polyanion (such as lithium iron phosphate) or a spinel (such as lithium manganese oxide). More experimental materials include graphene-containing electrodes, although these remain far from commercially viable due to their high cost.
Lithium reacts vigorously with water to form lithium hydroxide (LiOH) and hydrogen gas. Thus, a non-aqueous electrolyte is typically used, and a sealed container rigidly excludes moisture from the battery pack. The non-aqueous electrolyte is typically a mixture of organic carbonates such as ethylene carbonate and propylene carbonate containing complexes of lithium ions. Ethylene carbonate is essential for making solid electrolyte interphase on the carbon anode, but since it is solid at room temperature, a liquid solvent (such as propylene carbonate or diethyl carbonate) is added.
The electrolyte salt is almost always lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), which combines good ionic conductivity with chemical and electrochemical stability. Hexafluorophosphate is essential for passivating the aluminum current collector used for the cathode. A titanium tab is ultrasonically welded to the aluminum current collector. Other salts like lithium perchlorate (LiClO4), lithium tetrafluoroborate (LiBF4), and lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiC2F6NO4S2) are frequently used in research in tab-less coin cells, but are not usable in larger format cells, often because they are not compatible with the aluminum current collector. Copper (with a spot-welded nickel tab) is used as the anode current collector.
Current collector design and surface treatments may take various forms: foil, mesh, foam (dealloyed), etched (wholly or selectively), and coated (with various materials) to improve electrical characteristics.
Depending on materials choices, the voltage, energy density, life, and safety of a lithium-ion cell can change dramatically. Current effort has been exploring the use of novel architectures using nanotechnology to improve performance. Areas of interest include nano-scale electrode materials and alternative electrode structures.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1981 2023-12-02 00:14:31
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1983) Electrical Engineering
Gist
One of the more recent branches of engineering, electrical engineering is concerned with the design, study and application of devices, equipment and systems that use electricity, electronics and electromagnetism.
Summary
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use.
Electrical engineering is now divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control, and electrical materials science.
Electrical engineers typically hold a degree in electrical engineering or electronic engineering. Practising engineers may have professional certification and be members of a professional body or an international standards organization. These include the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET, formerly the IEE).
Electrical engineers work in a very wide range of industries and the skills required are likewise variable. These range from circuit theory to the management skills of a project manager. The tools and equipment that an individual engineer may need are similarly variable, ranging from a simple voltmeter to sophisticated design and manufacturing software.
Details
Electrical engineering is one of the newer branches of engineering, and dates back to the late 19th century. It is the branch of engineering that deals with the technology of electricity. Electrical engineers work on a wide range of components, devices and systems, from tiny microchips to huge power station generators.
Early experiments with electricity included primitive batteries and static charges. However, the actual design, construction and manufacturing of useful devices and systems began with the implementation of Michael Faraday's Law of Induction, which essentially states that the voltage in a circuit is proportional to the rate of change in the magnetic field through the circuit. This law applies to the basic principles of the electric generator, the electric motor and the transformer. The advent of the modern age is marked by the introduction of electricity to homes, businesses and industry, all of which were made possible by electrical engineers.
Some of the most prominent pioneers in electrical engineering include Thomas Edison (electric light bulb), George Westinghouse (alternating current), Nikola Tesla (induction motor), Guglielmo Marconi (radio) and Philo T. Farnsworth (television). These innovators turned ideas and concepts about electricity into practical devices and systems that ushered in the modern age.
Since its early beginnings, the field of electrical engineering has grown and branched out into a number of specialized categories, including power generation and transmission systems, motors, batteries and control systems. Electrical engineering also includes electronics, which has itself branched into an even greater number of subcategories, such as radio frequency (RF) systems, telecommunications, remote sensing, signal processing, digital circuits, instrumentation, audio, video and optoelectronics.
The field of electronics was born with the invention of the thermionic valve diode vacuum tube in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming. The vacuum tube basically acts as a current amplifier by outputting a multiple of its input current. It was the foundation of all electronics, including radios, television and radar, until the mid-20th century. It was largely supplanted by the transistor, which was developed in 1947 at AT&T's Bell Laboratories by William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain, for which they received the 1956 Nobel Prize in physics.
What does an electrical engineer do?
"Electrical engineers design, develop, test and supervise the manufacturing of electrical equipment, such as electric motors, radar and navigation systems, communications systems and power generation equipment, states the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. "Electronics engineers design and develop electronic equipment, such as broadcast and communications systems — from portable music players to global positioning systems (GPS)."
If it's a practical, real-world device that produces, conducts or uses electricity, in all likelihood, it was designed by an electrical engineer. Additionally, engineers may conduct or write the specifications for destructive or nondestructive testing of the performance, reliability and long-term durability of devices and components.
Today’s electrical engineers design electrical devices and systems using basic components such as conductors, coils, magnets, batteries, switches, resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes and transistors. Nearly all electrical and electronic devices, from the generators at an electric power plant to the microprocessors in your phone, use these few basic components.
Critical skills needed in electrical engineering include an in-depth understanding of electrical and electronic theory, mathematics and materials. This knowledge allows engineers to design circuits to perform specific functions and meet requirements for safety, reliability and energy efficiency, and to predict how they will behave, before a hardware design is implemented. Sometimes, though, circuits are constructed on "breadboards," or prototype circuit boards made on computer numeric controlled (CNC) machines for testing before they are put into production.
Electrical engineers are increasingly relying on computer-aided design (CAD) systems to create schematics and lay out circuits. They also use computers to simulate how electrical devices and systems will function. Computer simulations can be used to model a national power grid or a microprocessor; therefore, proficiency with computers is essential for electrical engineers. In addition to speeding up the process of drafting schematics, printed circuit board (PCB) layouts and blueprints for electrical and electronic devices, CAD systems allow for quick and easy modifications of designs and rapid prototyping using CNC machines.
Electrical engineering jobs and salaries
Electrical and electronics engineers work primarily in research and development industries, engineering services firms, manufacturing and the federal government, according to the BLS. They generally work indoors, in offices, but they may have to visit sites to observe a problem or a piece of complex equipment, the BLS says.
Manufacturing industries that employ electrical engineers include automotive, marine, railroad, aerospace, defense, consumer electronics, commercial construction, lighting, computers and components, telecommunications and traffic control. Government institutions that employ electrical engineers include transportation departments, national laboratories and the military.
Most electrical engineering jobs require at least a bachelor's degree in engineering. Many employers, particularly those that offer engineering consulting services, also require state certification as a Professional Engineer. Additionally, many employers require certification from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) or the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET). A master's degree is often required for promotion to management, and ongoing education and training are needed to keep up with advances in technology, testing equipment, computer hardware and software, and government regulations.
As of July 2014, the salary range for a newly graduated electrical engineer with a bachelor's degree is $55,570 to $73,908, according to a source. The range for a mid-level engineer with a master's degree and five to 10 years of experience is $$74,007 to $108,640, and the range for a senior engineer with a master's or doctorate and more than 15 years of experience is $97,434 to $138,296. Many experienced engineers with advanced degrees are promoted to management positions or start their own businesses where they can earn even more.
The future of electrical engineering
Employment of electrical and electronics engineers is projected to grow by 4 percent between now and 2022, because of these professionals' "versatility in developing and applying emerging technologies," the BLS says.
The applications for these emerging technologies include studying red electrical flashes, called sprites, which hover above some thunderstorms. Victor Pasko, an electrical engineer at Penn State, and his colleagues have developed a model for how the strange lightning evolves and disappears.
Another electrical engineer, Andrea Alù, of the University of Texas at Austin, is studying sound waves and has developed a one-way sound machine. "I can listen to you, but you cannot detect me back; you cannot hear my presence," Alù told LiveScience in a 2014 article.
And Michel Maharbiz, an electrical engineer at the University of California, Berkeley, is exploring ways to communicate with the brain wirelessly.
The BLS states, "The rapid pace of technological innovation and development will likely drive demand for electrical and electronics engineers in research and development, an area in which engineering expertise will be needed to develop distribution systems related to new technologies."

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1982 2023-12-03 00:06:35
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1984) Electronic Engineering
Gist
Electronics engineering is that branch of electrical engineering concerned with the uses of the electromagnetic spectrum and with the application of such electronic devices as integrated circuits and transistors.
Summary
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flow. Previously electrical engineering only used passive devices such as mechanical switches, resistors, inductors, and capacitors.
It covers fields such as: analog electronics, digital electronics, consumer electronics, embedded systems and power electronics. It is also involved in many related fields, for example solid-state physics, radio engineering, telecommunications, control systems, signal processing, systems engineering, computer engineering, instrumentation engineering, electric power control, photonics and robotics.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is one of the most important professional bodies for electronics engineers in the US; the equivalent body in the UK is the Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET). The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) publishes electrical standards including those for electronics engineering.
Details
Electronics engineering is a modern engineering discipline focused on the development of products and systems using electronic technology. It emerged as a discipline in the late-19th century as electronic broadcasting methods, including radio and television, became more widespread. The use of electronic technologies in World War II — such as sonar, radar and advanced weaponry — helped to further develop the field of electronics engineering.
Today, electronics engineering is the key force driving the growth of information technology, and many of the devices we use every day are the work of electronics engineers, such as smartphones, personal computers and Wi-Fi networks. The field is as diverse as its applications, as it comprises various subfields, like:
* Analog electronics engineering
* Radio-frequency engineering
* Software engineering
* Systems engineering
Additionally, a variety of industries apply electronics engineering principles to modernize their respective sectors, including but not limited to:
*bTelecommunications
* Radio and television
* Utilities
* Health care
* Science
* Personal technology manufacturing
* Government and military
What do electronics engineers do?
Electronics engineers design, develop and oversee the production of electronic systems and products. Testing these products and their components is a key part of the process of making sure all electronics work efficiently, safely and reliably for personal and commercial use. The responsibilities of electronics engineers vary depending on their specialty and industry but usually include:
Planning electronics projects
Electronics engineers participate in the preliminary stages of any electronic product. During the planning process, they help to determine various factors relating to the product, such as:
* Appearance
* Overall cost
* Budget allocation
* Project length
While undertaking planning activities, electronics engineers also carefully consider the requirements of their employer, their client and any international, national and local safety guidelines governing their work.
Manufacturing electronic products
Electronics engineers not only develop plans but also follow them to manufacture electronic products and systems. Most electronics engineers work as part of a team, creating individual electronic components and then assembling them with others to make larger works.
This work requires both an understanding and an adherence to each project's specifications, along with international, national and local product and safety guidelines.
Testing and evaluating electrical products
After assembly, electronics engineers conduct final tests before the release of the product, assessing whether it operates as intended and adheres to specifications. They also note potential areas of improvement and evaluate proposed changes to determine whether they add enough value to justify the additional expenditure of resources. If approved, the changes get implemented before the product's release.
Coordinating with stakeholders
Electronics engineers spend a lot of time coordinating with internal and external stakeholders, such as vendors, suppliers, project managers and other engineers. They may use various methods to coordinate their efforts, including:
* In-person meetings
* Telephone calls
* Videoconferencing
* Email
They may also write and review written documents such as contracts and proposals.
Writing usage recommendations
Electronics engineers write usage recommendations to ensure consumers use their products correctly. These recommendations instruct users on how to handle, operate, troubleshoot and maintain electronic products. Ultimately, this facet of the job helps consumers use their products safely and efficiently.
Performing maintenance and repairs
Some electronic products, such as industrial machinery with electronics components, require regular maintenance from electronics engineers. Maintenance often involves doing full or partial circuit traces to detect faults and then replacing components such as drives, circuit boards and power supplies.
If an engineer detects any problems during maintenance, they may recommend replacement or perform repairs before the problems escalate.
How to become an electronics engineer
If you'd like to become an electronic engineer, follow these steps to maximize your chances of entering the field:
1. Match your studies to the field
Many aspiring electronics engineers begin preparing themselves for their careers in high school. To build a strong foundation for your future academic and professional life, devote your pre-college studies to advanced mathematics and science subjects, such as:
* Algebra
* Calculus
* Trigonometry
* Physics
Also consider drafting courses to learn how to make technical drawings, along with an engineering summer camp to gain early hands-on experience. Contact your local research center or university for details concerning relevant camps.
2. Complete an electronics engineering degree
One of the entry-level requirements for electronics engineers is a bachelor's degree in electronics engineering or another relevant engineering discipline from a program recognized by the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology.
Electronics engineering programs usually involve a mix of classroom instruction, laboratory work and field studies. You may continue your studies with a master's degree or Ph.D. if you wish to work in a high-level position in research and development or academia.
3. Get practical experience in electronics engineering
Practical experience in electronics engineering complements your studies. Some universities have cooperative programs that provide this practical experience. Others help their students secure internships with businesses that employ electronics engineers.
If your college or university doesn't offer these programs, organize your own internship during breaks from school. During your internship, focus on making strong professional connections and learning as much from senior members in the field.
4. Obtain a Professional Engineer license
Once you've worked for four years under the supervision of a licensed engineer, you can apply for a Professional Engineer (PE) license from the National Society of Professional Engineers. Licensing requirements include passing the Fundamentals of Engineering and Professional Engineering examinations.
While licensure isn't essential for working as an electronics engineer, the PE license is a nationally recognized credential that may help you secure a higher salary or advance in your career. It also lets you supervise other electronics engineers.
Essential skills for electronics engineers
Focus on developing the following competencies to succeed as an electronics engineer:
* Technical knowledge: Electronics engineering requires a thorough knowledge of technical concepts such as circuit design and the operation of electronic devices. Knowledge of common programming languages, such as C++ and Java, is also helpful.
* Creativity: Electronics is an industry driven by innovation, so creativity is a key component of success. Creative minds can identify solutions that lead to faster, longer-lasting, more sustainable and more user-friendly products.
* Teamwork: Electronics engineers typically work in teams, so teamwork is a fundamental skill in the discipline. That means understanding the strengths and weaknesses of others and knowing how to optimize those characteristics to achieve the best project results.
* Written and verbal communication: Communicating well is a key part of teamwork, but a good electronics engineer knows how to communicate with people outside their team as well. The job often involves speaking to clients and other non-engineers about technical concepts using more accessible language.
* Attention to detail: Working as an electronics engineer requires keen attention to detail to ensure calculations are correct and design flaws get corrected before products reach the market. The best electronics engineers use their attention to detail to ensure accuracy in both their own work and the work of others.
* Time management: Electronics engineers often have strict deadlines, so good time management skills are essential. Also, given the team-based nature of the work, the ability to coordinate timelines with others is likewise critical.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1983 2023-12-04 20:49:08
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1985) Telecommunications Engineering
Gist
Telecommunications engineering is a subfield of electronics engineering which seeks to design and devise systems of communication at a distance. The work ranges from basic circuit design to strategic mass developments.
Summary:
Telecommunications engineering is a subfield of electronics engineering which seeks to design and devise systems of communication at a distance. The work ranges from basic circuit design to strategic mass developments. A telecommunication engineer is responsible for designing and overseeing the installation of telecommunications equipment and facilities, such as complex electronic switching systems, and other plain old telephone service facilities, optical fiber cabling, IP networks, and microwave transmission systems. Telecommunications engineering also overlaps with broadcast engineering.
Telecommunication is a diverse field of engineering connected to electronic, civil and systems engineering. Ultimately, telecom engineers are responsible for providing high-speed data transmission services. They use a variety of equipment and transport media to design the telecom network infrastructure; the most common media used by wired telecommunications today are twisted pair, coaxial cables, and optical fibers. Telecommunications engineers also provide solutions revolving around wireless modes of communication and information transfer, such as wireless telephony services, radio and satellite communications, internet, Wi-Fi and broadband technologies.
Details:
Background
The telecommunications industry is the backbone of today’s mobile landscape, deploying voice, data, graphics and video at ever-increasing speeds and in a growing number of ways. Wireline telephone communication was once the primary service of the industry, but wireless communication and satellite distribution are becoming increasingly dominant. Specialists in telecommunications engineering are needed to keep up with this ever-changing fast-paced industry.
The basics of telecommunications
Telecommunications engineering is a discipline founded around the exchange of information across channels via wired or wireless means. It brings together all of the elements of electrical engineering, including computer engineering and system engineering, to create and improve telecommunication systems.
Telecom engineers work to develop, design and maintain voice and data communications systems, which include fiber, satellite, wired and unwired, as well as the encoding, encryption and compression of data. Put simply, telecommunications engineering can be found in just about every aspect of our lives, from GPS navigation to the internet.
The work of telecommunications engineers range from creating basic circuit designs to deploying wireless networks.
They are responsible for designing and overseeing the installation of telecommunications equipment and facilities, such as complex electronic switching systems, copper wire telephone facilities, fiber optics cabling or internet protocol data systems.
Some of the main areas of focus for telecommunications engineers are the installation of high-speed broadband computer networks, and optical and wireless or satellite communications. To give a better idea of the scope of work a telecom engineer operates within, here are some career opportunities for individuals working within the discipline, according to the University of Texas at Dallas.
* Computer communications and networking;
* Mobile communications;
* Voice and data networks;
* TV and radio broadcasting;
* Optical networking;
* Remote sensing, measurement and control; and
* Next-generation networks.
Roles
Telecommunications engineers are part of every process of creating a telecom system, dealing with both software and hardware. Some roles a telecom engineer might take on:
Design – electronic components, software, products, or systems for commercial, industrial, medical, military or scientific applications;
Develop – maintenance and testing procedures for electronic components and equipment;
Test – Evaluate systems and recommend design modifications or equipment repair; and
Debug – Inspect electronic equipment, instruments and systems to make sure they are safe.
The future
With “5G” and the expansion of the “internet of things” ahead, telecommunications engineering will be as important as ever. The discipline will help expand both Low-Power Wide-Area Networks and networks that produce data speeds never before seen. Telecom engineers will have the important task of ensuring that telecommunications systems, from small components to entire networks, are running as effectively and efficiently as possible.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1984 2023-12-05 16:57:35
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1986) Instrumentation
Gist
Instrumentation is the design, equipping, and/or use of measuring instruments in determining real-life conditions in a plant's process, as for observation, measurement and control. Instrumentation technicians will install, maintain and calibrate devices used in the automation of industrial processes.
Details
Instrumentation is a collective term for measuring instruments, used for indicating, measuring and recording physical quantities. It is also a field of study about the art and science about making measurement instruments, involving the related areas of metrology, automation, and control theory. The term has its origins in the art and science of scientific instrument-making.
Instrumentation can refer to devices as simple as direct-reading thermometers, or as complex as multi-sensor components of industrial control systems. Today, instruments can be found in laboratories, refineries, factories and vehicles, as well as in everyday household use (e.g., smoke detectors and thermostats).
Measurement parameters
Control valve
Instrumentation is used to measure many parameters (physical values), including:
* Pressure, either differential or static
* Flow
* Temperature
* Levels of liquids, etc.
* Density
* Viscosity
* Ionising radiation
* Frequency
* Current
* Voltage
* Inductance
* Capacitance
* Resistivity
* Chemical composition
* Chemical properties
* Position
* Vibration
* Weight
History
The history of instrumentation can be divided into several phases.
Pre-industrial
Elements of industrial instrumentation have long histories. Scales for comparing weights and simple pointers to indicate position are ancient technologies. Some of the earliest measurements were of time. One of the oldest water clocks was found in the tomb of the ancient Egyptian pharaoh Amenhotep I, buried around 1500 BCE. Improvements were incorporated in the clocks. By 270 BCE they had the rudiments of an automatic control system device.
In 1663 Christopher Wren presented the Royal Society with a design for a "weather clock". A drawing shows meteorological sensors moving pens over paper driven by clockwork. Such devices did not become standard in meteorology for two centuries. The concept has remained virtually unchanged as evidenced by pneumatic chart recorders, where a pressurized bellows displaces a pen. Integrating sensors, displays, recorders and controls was uncommon until the industrial revolution, limited by both need and practicality.
Early industrial
Early systems used direct process connections to local control panels for control and indication, which from the early 1930s saw the introduction of pneumatic transmitters and automatic 3-term (PID) controllers.
The ranges of pneumatic transmitters were defined by the need to control valves and actuators in the field. Typically a signal ranged from 3 to 15 psi (20 to 100kPa or 0.2 to 1.0 kg/{cm}^2) as a standard, was standardized with 6 to 30 psi occasionally being used for larger valves. Transistor electronics enabled wiring to replace pipes, initially with a range of 20 to 100mA at up to 90V for loop powered devices, reducing to 4 to 20mA at 12 to 24V in more modern systems. A transmitter is a device that produces an output signal, often in the form of a 4–20 mA electrical current signal, although many other options using voltage, frequency, pressure, or ethernet are possible. The transistor was commercialized by the mid-1950s.
Instruments attached to a control system provided signals used to operate solenoids, valves, regulators, circuit breakers, relays and other devices. Such devices could control a desired output variable, and provide either remote monitoring or automated control capabilities.
Each instrument company introduced their own standard instrumentation signal, causing confusion until the 4–20 mA range was used as the standard electronic instrument signal for transmitters and valves. This signal was eventually standardized as ANSI/ISA S50, “Compatibility of Analog Signals for Electronic Industrial Process Instruments", in the 1970s. The transformation of instrumentation from mechanical pneumatic transmitters, controllers, and valves to electronic instruments reduced maintenance costs as electronic instruments were more dependable than mechanical instruments. This also increased efficiency and production due to their increase in accuracy. Pneumatics enjoyed some advantages, being favored in corrosive and explosive atmospheres.
Automatic process control
In the early years of process control, process indicators and control elements such as valves were monitored by an operator that walked around the unit adjusting the valves to obtain the desired temperatures, pressures, and flows. As technology evolved pneumatic controllers were invented and mounted in the field that monitored the process and controlled the valves. This reduced the amount of time process operators were needed to monitor the process. Later years the actual controllers were moved to a central room and signals were sent into the control room to monitor the process and outputs signals were sent to the final control element such as a valve to adjust the process as needed. These controllers and indicators were mounted on a wall called a control board. The operators stood in front of this board walking back and forth monitoring the process indicators. This again reduced the number and amount of time process operators were needed to walk around the units. The most standard pneumatic signal level used during these years was 3–15 psig.
Large integrated computer-based systems
Process control of large industrial plants has evolved through many stages. Initially, control would be from panels local to the process plant. However this required a large manpower resource to attend to these dispersed panels, and there was no overall view of the process. The next logical development was the transmission of all plant measurements to a permanently-staffed central control room. Effectively this was the centralisation of all the localised panels, with the advantages of lower manning levels and easier overview of the process. Often the controllers were behind the control room panels, and all automatic and manual control outputs were transmitted back to plant.
However, whilst providing a central control focus, this arrangement was inflexible as each control loop had its own controller hardware, and continual operator movement within the control room was required to view different parts of the process. With coming of electronic processors and graphic displays it became possible to replace these discrete controllers with computer-based algorithms, hosted on a network of input/output racks with their own control processors. These could be distributed around plant, and communicate with the graphic display in the control room or rooms. The distributed control concept was born.
The introduction of DCSs and SCADA allowed easy interconnection and re-configuration of plant controls such as cascaded loops and interlocks, and easy interfacing with other production computer systems. It enabled sophisticated alarm handling, introduced automatic event logging, removed the need for physical records such as chart recorders, allowed the control racks to be networked and thereby located locally to plant to reduce cabling runs, and provided high level overviews of plant status and production levels.
Application
In some cases the sensor is a very minor element of the mechanism. Digital cameras and wristwatches might technically meet the loose definition of instrumentation because they record and/or display sensed information. Under most circumstances neither would be called instrumentation, but when used to measure the elapsed time of a race and to document the winner at the finish line, both would be called instrumentation.
Household
A very simple example of an instrumentation system is a mechanical thermostat, used to control a household furnace and thus to control room temperature. A typical unit senses temperature with a bi-metallic strip. It displays temperature by a needle on the free end of the strip. It activates the furnace by a mercury switch. As the switch is rotated by the strip, the mercury makes physical (and thus electrical) contact between electrodes.
Another example of an instrumentation system is a home security system. Such a system consists of sensors (motion detection, switches to detect door openings), simple algorithms to detect intrusion, local control (arm/disarm) and remote monitoring of the system so that the police can be summoned. Communication is an inherent part of the design.
Kitchen appliances use sensors for control.
* A refrigerator maintains a constant temperature by actuating the cooling system when the temperature becomes too high.
* An automatic ice machine makes ice until a limit switch is thrown.
* Pop-up bread toasters allow the time to be set.
* Non-electronic gas ovens will regulate the temperature with a thermostat controlling the flow of gas to the gas burner. These may feature a sensor bulb sited within the main chamber of the oven. In addition, there may be a safety cut-off flame supervision device: after ignition, the burner's control knob must be held for a short time in order for a sensor to become hot, and permit the flow of gas to the burner. If the safety sensor becomes cold, this may indicate the flame on the burner has become extinguished, and to prevent a continuous leak of gas the flow is stopped.
* Electric ovens use a temperature sensor and will turn on heating elements when the temperature is too low. More advanced ovens will actuate fans in response to temperature sensors, to distribute heat or to cool.
* A common toilet refills the water tank until a float closes the valve. The float is acting as a water level sensor.
Automotive
Modern automobiles have complex instrumentation. In addition to displays of engine rotational speed and vehicle linear speed, there are also displays of battery voltage and current, fluid levels, fluid temperatures, distance traveled and feedbacks of various controls (turn signals, parking brake, headlights, transmission position). Cautions may be displayed for special problems (fuel low, check engine, tire pressure low, door ajar, seat belt unfastened). Problems are recorded so they can be reported to diagnostic equipment. Navigation systems can provide voice commands to reach a destination. Automotive instrumentation must be cheap and reliable over long periods in harsh environments. There may be independent airbag systems which contain sensors, logic and actuators. Anti-skid braking systems use sensors to control the brakes, while cruise control affects throttle position. A wide variety of services can be provided via communication links as the OnStar system. Autonomous cars (with exotic instrumentation) have been demonstrated.
Aircraft
Early aircraft had a few sensors. "Steam gauges" converted air pressures into needle deflections that could be interpreted as altitude and airspeed. A magnetic compass provided a sense of direction. The displays to the pilot were as critical as the measurements.
A modern aircraft has a far more sophisticated suite of sensors and displays, which are embedded into avionics systems. The aircraft may contain inertial navigation systems, global positioning systems, weather radar, autopilots, and aircraft stabilization systems. Redundant sensors are used for reliability. A subset of the information may be transferred to a crash recorder to aid mishap investigations. Modern pilot displays now include computer displays including head-up displays.
Air traffic control radar is distributed instrumentation system. The ground portion transmits an electromagnetic pulse and receives an echo (at least). Aircraft carry transponders that transmit codes on reception of the pulse. The system displays aircraft map location, an identifier and optionally altitude. The map location is based on sensed antenna direction and sensed time delay. The other information is embedded in the transponder transmission.
Laboratory instrumentation
Among the possible uses of the term is a collection of laboratory test equipment controlled by a computer through an IEEE-488 bus (also known as GPIB for General Purpose Instrument Bus or HPIB for Hewlitt Packard Instrument Bus). Laboratory equipment is available to measure many electrical and chemical quantities. Such a collection of equipment might be used to automate the testing of drinking water for pollutants.
Instrumentation engineering
The instrumentation part of a piping and instrumentation diagram will be developed by an instrumentation engineer.
Instrumentation engineering is the engineering specialization focused on the principle and operation of measuring instruments that are used in design and configuration of automated systems in areas such as electrical and pneumatic domains, and the control of quantities being measured. They typically work for industries with automated processes, such as chemical or manufacturing plants, with the goal of improving system productivity, reliability, safety, optimization and stability. To control the parameters in a process or in a particular system, devices such as microprocessors, microcontrollers or PLCs are used, but their ultimate aim is to control the parameters of a system.
Instrumentation engineering is loosely defined because the required tasks are very domain dependent. An expert in the biomedical instrumentation of laboratory rats has very different concerns than the expert in rocket instrumentation. Common concerns of both are the selection of appropriate sensors based on size, weight, cost, reliability, accuracy, longevity, environmental robustness and frequency response. Some sensors are literally fired in artillery shells. Others sense thermonuclear explosions until destroyed. Invariably sensor data must be recorded, transmitted or displayed. Recording rates and capacities vary enormously. Transmission can be trivial or can be clandestine, encrypted and low-power in the presence of jamming. Displays can be trivially simple or can require consultation with human factors experts. Control system design varies from trivial to a separate specialty.
Instrumentation engineers are responsible for integrating the sensors with the recorders, transmitters, displays or control systems, and producing the Piping and instrumentation diagram for the process. They may design or specify installation, wiring and signal conditioning. They may be responsible for commissioning, calibration, testing and maintenance of the system.
In a research environment it is common for subject matter experts to have substantial instrumentation system expertise. An astronomer knows the structure of the universe and a great deal about telescopes – optics, pointing and cameras (or other sensing elements). That often includes the hard-won knowledge of the operational procedures that provide the best results. For example, an astronomer is often knowledgeable of techniques to minimize temperature gradients that cause air turbulence within the telescope.
Instrumentation technologists, technicians and mechanics specialize in troubleshooting, repairing and maintaining instruments and instrumentation systems.
Typical industrial transmitter signal types
* Pneumatic loop (20-100KPa/3-15PSI) – Pneumatic
* Current loop (4-20mA) – Electrical
* HART – Data signalling, often overlaid on a current loop
* Foundation Fieldbus – Data signalling
* Profibus – Data signalling
Impact of modern development
Ralph Müller (1940) stated, "That the history of physical science is largely the history of instruments and their intelligent use is well known. The broad generalizations and theories which have arisen from time to time have stood or fallen on the basis of accurate measurement, and in several instances new instruments have had to be devised for the purpose. There is little evidence to show that the mind of modern man is superior to that of the ancients. His tools are incomparably better."
Davis Baird has argued that the major change associated with Floris Cohen's identification of a "fourth big scientific revolution" after World War II is the development of scientific instrumentation, not only in chemistry but across the sciences. In chemistry, the introduction of new instrumentation in the 1940s was "nothing less than a scientific and technological revolution" in which classical wet-and-dry methods of structural organic chemistry were discarded, and new areas of research opened up.
As early as 1954, W. A. Wildhack discussed both the productive and destructive potential inherent in process control. The ability to make precise, verifiable and reproducible measurements of the natural world, at levels that were not previously observable, using scientific instrumentation, has "provided a different texture of the world". This instrumentation revolution fundamentally changes human abilities to monitor and respond, as is illustrated in the examples of DDT monitoring and the use of UV spectrophotometry and gas chromatography to monitor water pollutants.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1985 2023-12-06 16:40:33
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1987) Software Engineering
Gist
Software engineering is the branch of computer science that deals with the design, development, testing, and maintenance of software applications. Software engineers apply engineering principles and knowledge of programming languages to build software solutions for end users.
Summary
Software is a program or set of programs containing instructions that provide desired functionality. And Engineering is the process of designing and building something that serves a particular purpose and finds a cost-effective solution to problems.
Software Engineering is the process of designing, developing, testing, and maintaining software. It is a systematic and disciplined approach to software development that aims to create high-quality, reliable, and maintainable software. Software engineering includes a variety of techniques, tools, and methodologies, including requirements analysis, design, testing, and maintenance.
Key Principles of Software Engineering
* Modularity: Breaking the software into smaller, reusable components that can be developed and tested independently.
* Abstraction: Hiding the implementation details of a component and exposing only the necessary functionality to other parts of the software.
* Encapsulation: Wrapping up the data and functions of an object into a single unit, and protecting the internal state of an object from external modifications.
* Reusability: Creating components that can be used in multiple projects, which can save time and resources.
* Maintenance: Regularly updating and improving the software to fix bugs, add new features, and address security vulnerabilities.
* Testing: Verifying that the software meets its requirements and is free of bugs.
* Design Patterns: Solving recurring problems in software design by providing templates for solving them.
* Agile methodologies: Using iterative and incremental development processes that focus on customer satisfaction, rapid delivery, and flexibility.
* Continuous Integration & Deployment: Continuously integrating the code changes and deploying them into the production environment.
Software engineering is a rapidly evolving field, and new tools and technologies are constantly being developed to improve the software development process. By following the principles of software engineering and using the appropriate tools and methodologies, software developers can create high-quality, reliable, and maintainable software that meets the needs of its users.
Software Engineering is mainly used for large projects based on software systems rather than single programs or applications. The main goal of Software Engineering is to develop software applications for improving quality, budget, and time efficiency. Software Engineering ensures that the software that has to be built should be consistent, correct, also on budget, on time, and within the required requirements.
Details
Software engineering is an engineering-based approach to software development. A software engineer is a person who applies the engineering design process to design, develop, test, maintain, and evaluate computer software. The term programmer is sometimes used as a synonym, but may emphasize software implementation over design and can also lack connotations of engineering education or skills.
Engineering techniques are used to inform the software development process, which involves the definition, implementation, assessment, measurement, management, change, and improvement of the software life cycle process itself. It heavily uses software configuration management, which is about systematically controlling changes to the configuration, and maintaining the integrity and traceability of the configuration and code throughout the system life cycle. Modern processes use software versioning.
History
Beginning in the 1960s, software engineering was seen as its own type of engineering. Additionally, the development of software engineering was seen as a struggle. It was difficult to keep up with the hardware which caused many problems for software engineers. Problems included software that was over budget, exceeded deadlines, required extensive debugging and maintenance, and unsuccessfully met the needs of consumers or was never even completed. In 1968 NATO held the first Software Engineering conference where issues related to software were addressed: guidelines and best practices for the development of software were established.
The origins of the term software engineering have been attributed to various sources. The term appeared in a list of services offered by companies in the June 1965 issue of "Computers and Automation" and was used more formally in the August 1966 issue of Communications of the ACM (Volume 9, number 8) "letter to the ACM membership" by the ACM President Anthony A. Oettinger. It is also associated with the title of a NATO conference in 1968 by Professor Friedrich L. Bauer. Margaret Hamilton described the discipline of "software engineering" during the Apollo missions to give what they were doing legitimacy. At the time there was perceived to be a "software crisis". The 40th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2018) celebrates 50 years of "Software Engineering" with the Plenary Sessions' keynotes of Frederick Brooks and Margaret Hamilton.
In 1984, the Software Engineering Institute (SEI) was established as a federally funded research and development center headquartered on the campus of Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. Watts Humphrey founded the SEI Software Process Program, aimed at understanding and managing the software engineering process. The Process Maturity Levels introduced would become the Capability Maturity Model Integration for Development(CMMI-DEV), which has defined how the US Government evaluates the abilities of a software development team.
Modern, generally accepted best-practices for software engineering have been collected by the ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7 subcommittee and published as the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge (SWEBOK). Software engineering is considered one of the major computing disciplines.
Definitions and terminology
Notable definitions of software engineering include:
* "The systematic application of scientific and technological knowledge, methods, and experience to the design, implementation, testing, and documentation of software"—The Bureau of Labor Statistics—IEEE Systems and software engineering – Vocabulary
* "The application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software"—IEEE Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology
* "an engineering discipline that is concerned with all aspects of software production"—Ian Sommerville
* "the establishment and use of sound engineering principles in order to economically obtain software that is reliable and works efficiently on real machines"—Fritz Bauer
* "a branch of computer science that deals with the design, implementation, and maintenance of complex computer programs"—Merriam-Webster
* "'software engineering' encompasses not just the act of writing code, but all of the tools and processes an organization uses to build and maintain that code over time. [...] Software engineering can be thought of as 'programming integrated over time.'"—Software Engineering at Google
The term has also been used less formally:
* as the informal contemporary term for the broad range of activities that were formerly called computer programming and systems analysis;
* as the broad term for all aspects of the practice of computer programming, as opposed to the theory of computer programming, which is formally studied as a sub-discipline of computer science;
* as the term embodying the advocacy of a specific approach to computer programming, one that urges that it be treated as an engineering discipline rather than an art or a craft, and advocates the codification of recommended practices.
Additional Information:
What is software engineering?
Software engineering is the process of developing, testing and deploying computer applications to solve real-world problems by adhering to a set of engineering principles and best practices. The field of software engineering applies a disciplined and organized approach to software development with the stated goal of improving quality, time and budget efficiency, along with the assurance of structured testing and engineer certification.
Though the original use of the term is uncertain, the first software engineering conference was held and sponsored by NATO in 1968. The conference addressed the inconsistency and unreliability in software development as well as the need for better quality assurance (QA) and reliability. The conference gathered international experts who agreed the systematic approach of physical world engineering should be applied to software development, as it already was developed with those goals in mind.
Types of software engineering
Even though a software engineer usually manages many coding projects, software engineering entails more than just writing code for the software. In reality, software engineering encompasses every phase of the software development lifecycle (SDLC), from planning the budget to analysis, design, development, software testing, integration, quality and retirement.
Most software engineering tasks can be broken into the following three categories:
* Operational software engineering. It includes all decisions and tasks pertaining to how the software will perform within a computer system. This may include anything related to the software budget, the way teams and users will interact with the software and any potential risks such as those associated with defective and outdated software.
* Transitional software engineering. This type of software engineering entails duties related to the software's adaptability and scalability when it's moved outside of its initial setting.
* Software engineering maintenance. It entails activities connected to enhancing and debugging current software to account for environmental changes, new technologies, bugs and risk factors that might have been disregarded during a previous development cycle. Over time, retirement takes over as maintenance of certain software is gradually reduced.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1986 2023-12-06 22:39:17
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1988) Algorithm
Gist
An Algorithm is a set of rules that must be followed when solving a particular problem.
An algorithm is a procedure used for solving a problem or performing a computation. Algorithms act as an exact list of instructions that conduct specified actions step by step in either hardware- or software-based routines.
Summary
The word Algorithm means ” A set of finite rules or instructions to be followed in calculations or other problem-solving operations ”
Or
” A procedure for solving a mathematical problem in a finite number of steps that frequently involves recursive operations”.
Therefore Algorithm refers to a sequence of finite steps to solve a particular problem.
Algorithms play a crucial role in various fields and have many applications. Some of the key areas where algorithms are used include:
* Computer Science: Algorithms form the basis of computer programming and are used to solve problems ranging from simple sorting and searching to complex tasks such as artificial intelligence and machine learning.
* Mathematics: Algorithms are used to solve mathematical problems, such as finding the optimal solution to a system of linear equations or finding the shortest path in a graph.
* Operations Research: Algorithms are used to optimize and make decisions in fields such as transportation, logistics, and resource allocation.
* Artificial Intelligence: Algorithms are the foundation of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and are used to develop intelligent systems that can perform tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and decision-making.
* Data Science: Algorithms are used to analyze, process, and extract insights from large amounts of data in fields such as marketing, finance, and healthcare.
These are just a few examples of the many applications of algorithms. The use of algorithms is continually expanding as new technologies and fields emerge, making it a vital component of modern society.
Algorithms can be simple and complex depending on what you want to achieve.
It can be understood by taking the example of cooking a new recipe. To cook a new recipe, one reads the instructions and steps and executes them one by one, in the given sequence. The result thus obtained is the new dish is cooked perfectly. Every time you use your phone, computer, laptop, or calculator you are using Algorithms. Similarly, algorithms help to do a task in programming to get the expected output.
The Algorithm designed are language-independent, i.e. they are just plain instructions that can be implemented in any language, and yet the output will be the same, as expected.
Details
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning), achieving automation eventually. Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus".
In contrast, a heuristic is an approach to problem solving that may not be fully specified or may not guarantee correct or optimal results, especially in problem domains where there is no well-defined correct or optimal result.
As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of space and time and in a well-defined formal language for calculating a function. Starting from an initial state and initial input (perhaps empty), the instructions describe a computation that, when executed, proceeds through a finite[8] number of well-defined successive states, eventually producing "output" and terminating at a final ending state. The transition from one state to the next is not necessarily deterministic; some algorithms, known as randomized algorithms, incorporate random input.
Formalization
Algorithms are essential to the way computers process data. Many computer programs contain algorithms that detail the specific instructions a computer should perform—in a specific order—to carry out a specified task, such as calculating employees' paychecks or printing students' report cards. Thus, an algorithm can be considered to be any sequence of operations that can be simulated by a Turing-complete system. Authors who assert this thesis include Minsky (1967), Savage (1987), and Gurevich (2000):
Minsky: "But we will also maintain, with Turing ... that any procedure which could "naturally" be called effective, can, in fact, be realized by a (simple) machine. Although this may seem extreme, the arguments ... in its favor are hard to refute". Gurevich: "… Turing's informal argument in favor of his thesis justifies a stronger thesis: every algorithm can be simulated by a Turing machine … according to Savage [1987], an algorithm is a computational process defined by a Turing machine".
Turing machines can define computational processes that do not terminate. The informal definitions of algorithms generally require that the algorithm always terminates. This requirement renders the task of deciding whether a formal procedure is an algorithm impossible in the general case—due to a major theorem of computability theory known as the halting problem.
Typically, when an algorithm is associated with processing information, data can be read from an input source, written to an output device and stored for further processing. Stored data is regarded as part of the internal state of the entity performing the algorithm. In practice, the state is stored in one or more data structures.
For some of these computational processes, the algorithm must be rigorously defined and specified in the way it applies in all possible circumstances that could arise. This means that any conditional steps must be systematically dealt with, case by case; the criteria for each case must be clear (and computable).
Because an algorithm is a precise list of precise steps, the order of computation is always crucial to the functioning of the algorithm. Instructions are usually assumed to be listed explicitly, and are described as starting "from the top" and going "down to the bottom"—an idea that is described more formally by flow of control.
So far, the discussion on the formalization of an algorithm has assumed the premises of imperative programming. This is the most common conception—one that attempts to describe a task in discrete, "mechanical" terms. Associated with this conception of formalized algorithms is the assignment operation, which sets the value of a variable. It derives from the intuition of "memory" as a scratchpad.
Expressing algorithms
Algorithms can be expressed in many kinds of notation, including natural languages, pseudocode, flowcharts, drakon-charts, programming languages or control tables (processed by interpreters). Natural language expressions of algorithms tend to be verbose and ambiguous and are rarely used for complex or technical algorithms. Pseudocode, flowcharts, drakon-charts and control tables are structured ways to express algorithms that avoid many of the ambiguities common in statements based on natural language. Programming languages are primarily intended for expressing algorithms in a form that can be executed by a computer, but they are also often used as a way to define or document algorithms.
There is a wide variety of representations possible and one can express a given Turing machine program as a sequence of machine tables, as flowcharts and drakon-charts, or as a form of rudimentary machine code or assembly code called "sets of quadruples".
Representations of algorithms can be classified into three accepted levels of Turing machine description, as follows:
1. High-level description
"...prose to describe an algorithm, ignoring the implementation details. At this level, we do not need to mention how the machine manages its tape or head."
2. Implementation description
"...prose used to define the way the Turing machine uses its head and the way that it stores data on its tape. At this level, we do not give details of states or transition function."
3. Formal description
Most detailed, "lowest level", gives the Turing machine's "state table".
Design
Algorithm design refers to a method or a mathematical process for problem-solving and engineering algorithms. The design of algorithms is part of many solution theories, such as divide-and-conquer or dynamic programming within operation research. Techniques for designing and implementing algorithm designs are also called algorithm design patterns, with examples including the template method pattern and the decorator pattern.
One of the most important aspects of algorithm design is resource (run-time, memory usage) efficiency; the big O notation is used to describe e.g., an algorithm's run-time growth as the size of its input increases.
Typical steps in the development of algorithms:
* Problem definition
* Development of a model
* Specification of the algorithm
* Designing an algorithm
* Checking the correctness of the algorithm
* Analysis of algorithm
* Implementation of algorithm
* Program testing
* Documentation preparation.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1987 2023-12-07 17:47:19
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1989) Harward Engineer
Gist
Hardware Engineering is the process of designing, developing, testing and producing computer systems and various physical components related to computer systems.
Hardware engineers usually work on computer systems, components, and computerized products for consumer markets. Their main duties include testing, modifying, and maintaining the products they build. Most components must work alongside networking and software tools.
Summary
Hardware engineers create computer machines and technologies used to run software and store data on varying scales. Here’s what to know about a hardware engineer’s needed skills, salary and how to become one.
What Is a Hardware Engineer?
Hardware engineers develop the physical equipment required by a computer system, including computer peripherals, electronic devices and network systems. They tend to oversee the full lifecycle of a computer system from concept to installation and maintenance.
What Do Hardware Engineers Do?
Hardware engineers design, build and test all hardware components of computers and related devices. Manufactured hardware can include circuit boards and processors, computer routers, gaming consoles, mobile devices as well as Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices.
Hardware Engineer Responsibilities
* Design computer hardware and determine machine requirements.
* Build and modify computer systems and hardware components.
* Test and analyze computer hardware to gauge necessary functionality.
* Maintain and update hardware to ensure compatibility with software needs.
Day-to-Day Responsibilities Of Hardware Engineers
* Use electronic design automation (EDA) and printed circuit board (PCB) design tools like Fusion 360 to sketch schematics and visualize component placement.
* Use programming languages like Python to automate simulation flows and test hardware features.
* Troubleshoot hardware defects and conduct hands-on investigations.
* Communicate hardware needs between clients, customers and other engineers.
Hardware Engineers Within A Company
Hardware engineers are usually part of a designated hardware team within a company. They often collaborate with IT professionals and software engineers to accomplish their work. They also may report to senior hardware engineers or hardware engineering project managers.
Importance Of Hardware Engineers
Hardware engineers make necessary technology that is used by professionals almost every day. Computers, cell phones and smart devices may not be properly built or updated without hardware engineer expertise.
Details:
What Does Hardware Engineer Mean?
A hardware engineer is a professional who works with hardware in various stages, from design to maintenance. The hardware engineer has to know how to work with things such as circuits, components and integrated circuits. His or her role is specific in today's highly virtualized computing world: The hardware engineer is responsible for the physical "guts" of an IT system, whatever that consists of: from servers to RAID or storage media, from PLCs to routing hardware – the hardware engineer worries about the physical electronics.
Hardware engineers may design, develop or test computer systems such as servers, rack setups, physical data partitions or any other type of hardware serving an IT architecture.
The role of the hardware engineer is changing over time. As more of the design process shifts to software systems, hardware engineers concentrate on how to build effectively, and how to support data-crunching with physical hardware systems. For example, a modern hardware engineer may spend a lot of time walking around a data center, checking on physical systems, as software engineers and artificial intelligence workers direct all of the vastly complicated activity happening within that physical data center.
Hardware Engineering is the process of designing, developing, testing and producing computer systems and various physical components related to computer systems.
Hardware Engineering is the process of designing, developing, testing and producing computer systems and various physical components related to computer systems. With the advent of technology and advances in R&D, the scope of hardware engineering has been expanded to include hardware devices enabling embedded software engineering in non-computer devices.
In embedded systems, hardware engineering comprises of the process of design and development of all electronics related hardware such as sensors, processors and controllers.
The scope of hardware engineering is limited not just to the designing and development of computer or embedded systems, but also to integrate the various devices for the functioning of the entire business system.
With the advent of technology and advances in R&D, hardware engineering is now prevalent in newer fields such as mobile computing and distributed systems, computer vision and robotics, etc.
Additional Information
If you have an interest in how computer systems work, you may enjoy a career as a computer hardware engineer. Computer hardware engineers build and test computer systems, and often are innovative in developing new hardware technologies to help companies and people across the world. Knowing more about this profession can help you decide if this is a suitable career path for you. In this article, we discuss how to become a computer hardware engineer and outline the skills and educational qualifications required to excel in this career.
How to become a computer hardware engineer
Follow these steps if you want to learn how to become a computer hardware engineer:
1. Complete higher secondary education
The preparation for being an engineer starts early in your career. After school, consider pursuing your 10+2 from a recognised board in the science stream, with physics, chemistry and mathematics as your main subjects. It is important to secure high marks in your 10+2 board exam, as many engineering colleges select candidates based on their higher secondary results.
2. Clear engineering entrance exams
The Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) and the Common Entrance Test (CET) are two of the most common engineering entrance exams for admission into undergraduate degree courses like BE and BTech. If you can clear the JEE Main exam, you can get admission into one of the National Institutes of Technology (NITs) located across the country. You can also take the JEE Advanced exam if you want to get admission into one of the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs)
Attempt engineering entrance exams based on your city, state and other preferences. Apart from the CET and JEE, some colleges have their own entrance exams that come with a slightly modified syllabus. Make sure you attempt more than one entrance exam to increase the chances of being accepted at a university.
3. Earn a bachelor's degree and undertake projects while studying
The next step to becoming a computer hardware engineer is earning a bachelor's degree. Most employers prefer hiring computer hardware engineers with a BTech or B.E. in computer science or electrical engineering. Instead of diverting all your efforts to good grades, invest time in developing projects that get the attention of future recruiters. This way, you can build your portfolio and create an example of your project development skills while studying. Some project ideas are hardware remodelling for a CPU (central processing unit) and PCB (printed circuit board) design for a computer.
4. Complete an internship
Either during undergraduate studies or immediately after graduation, you can benefit from completing an internship. An internship is often required by your collegiate program, but you can take one voluntarily as well. Here, you can get direct experience working with computer hardware, learn more about developing hardware in a monitored setting and gain important networking contacts you can use to find a job.
5. Pursue an advanced degree
While not generally required, some larger companies may prefer candidates to have a master's degree in computer hardware engineering. A master's degree is also recommended if you want to advance to management positions in the field. During the course of these studies, you can learn to work on systems like broadcasting, navigation and communication, as working within these industries also typically requires an advanced degree. Getting a doctorate is also an option. While master's degrees and doctorates usually both come with pay increases, a doctorate allows you to teach at the university level.
What kind of education do you need to be a computer hardware engineer?
To apply for computer hardware engineering jobs, you typically need a bachelor's degree in computer science. Many companies also hire hardware engineers if they have an electronics engineering degree. If you already have a degree, consider adding a few relevant hardware engineering courses to your resume. This can help you stand out from other applicants.
When hiring for senior positions, many employers prefer candidates with a master's degree in computer engineering. If you have years of work experience but not a master's degree, you may still be eligible to apply for senior positions.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1988 2023-12-08 00:05:45
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1990) Dietician
Gist
A dietician is an expert in the field of food and nutrition. A dietician is like a physician for your diet.
People who study food in a scientific way are dieticians — they are experts on food and its effects. Dieticians study nutrition, which is the science that looks at what good and bad things various foods do to your body. If you need to change what you eat because of a health problem, like diabetes or obesity, you should consult a dietician. It’s also spelled dietitian.
Summary
Dietitians are qualified and regulated health professionals that assess, diagnose and treat dietary and nutritional problems at an individual and wider public-health level.
They use the most up-to-date public health and scientific research on food, health and disease which they translate into practical guidance to enable people to make appropriate lifestyle and food choices.
They work in the NHS and in private clinics. They work with healthy and sick people in a variety of settings. They can work in the food industry, workplace, catering, education, sport and the media. Other care pathways they work in include mental health, learning disabilities, community, acute settings and public health.
They often work as integral members of multi-disciplinary teams to treat complex clinical conditions such as diabetes, food allergy and intolerance, IBS syndrome, eating disorders, chronic fatigue, malnutrition, kidney failure and bowel disorders. They advise and influence food and health policy across the spectrum from government, to local communities and individuals.
Why might you see a dietitian?
Finding and accessing the services of a dietitian can be achieved in several ways, but why choose one in the first place? You may be referred by a GP or request a referral to address a specific medical/health need or condition. Find out how a dietitian can help you.
Alternatively, you may choose to seek out the services of a freelancer. Here are some examples of where they, working on a one-to-one basis or part of a wider health team, can help improve your health and lifestyle:
* you suffer with digestive problems
* you have been diagnosed with a medical condition, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, coeliac, HIV etc
* you have oral, enteral or parenteral nutrition requirements
* your child, or looked after child, has specialised nutritional requirements
* you are wanting or needing to lose weight in a safe and sensible way
* you need to put weight on following a spell of ill-health or as the result of a medical condition
* you are considering surgery to lose weight
* you want to improve your athletic performance or general fitness levels
* you want advice about breastfeeding and weaning
* you think you have an allergy or intolerance to a certain food
* you would like advice about eating disorders
* you are a carer and want credible and practical advice to ensure the person/s you are caring for is/are getting the appropriate nutrition in their diet/s.
While dietitians work with individuals, as the above examples explain, in the NHS and on a freelance basis, they also work across the board wherever food and nutrition is present.
Details
A dietitian, medical dietitian, or dietician is an expert in identifying and treating disease-related malnutrition and in conducting medical nutrition therapy, for example designing an enteral tube feeding regimen or mitigating the effects of cancer cachexia. Many dietitians work in hospitals and usually see specific patients where a nutritional assessment and intervention has been requested by a doctor or nurse, for example if a patient has lost their ability to swallow or requires artificial nutrition due to intestinal failure. Dietitians are regulated healthcare professionals licensed to assess, diagnose, and treat such problems. In the United Kingdom, dietitian is a 'protected title', meaning identifying yourself as a dietitian without appropriate education and registration is prohibited by law.
A registered dietitian (RD) (UK/USA) or registered dietitian nutritionist (RDN) (USA) meets all of a set of special academic and professional requirements, including the completion of a bachelor's and/or master's degree in nutrition and dietetics (or equivalent). One or more internships (USA) or clinical placements (UK) must also be completed. These may be allocated and monitored by the university as part of the structured degree programme (UK) or may be applied for separately (USA).
Roughly half of all RD(N)s hold graduate degrees and many have certifications in specialized fields such as nutrition support, sports, paediatrics, renal, oncological, food-allergy, or gerontological nutrition. Although assessment priorities differ depending on the specialist area, a patient's medical and surgical history, biochemistry, diet history, eating and exercise habits usually form the basis of assessment. The RD(N) negotiates a treatment plan with the patient which may include prescriptions, and follow-up visits often focus on maintenance and monitoring progress.
Most RDs work in the treatment and prevention of disease (administering medical nutrition therapy, as part of medical teams), often in hospitals, health-maintenance organizations, private practices, or other health-care facilities. In addition, many registered dietitians work in community and public-health settings, and/or in academia and research. A growing number of dietitians work in the food industry, journalism, sports nutrition, corporate wellness programs, and other non-traditional dietetics settings.
The spellings "dietitian" and "dietician"
As explained by the American Heritage and Merriam-Webster's dictionaries, the cause of the confusion is that the spelling with "-tian" is an irregular alteration of the ending "-cian", which is otherwise exclusively used to refer to specialists and practitioners of other professions. These and other American dictionaries also list the spelling with "c" but list the spelling with "t" first because this spelling is more common in the United States. Nevertheless, the American publisher McGraw-Hill exclusively uses the spelling with "c" in the 2003 edition of the McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms and the 2002 edition of the McGraw-Hill Concise Dictionary of Modern Medicine.
The spelling with "t" is the one preferred by the profession itself internationally, but the spelling with "c" is used often enough in texts not written by members of the profession to be considered a valid variant by both American and British dictionaries. In fact, British dictionaries list the spelling with "c" first and list the spelling with "t" as a variant. American dictionaries list the spelling with "t" first and the spelling with "c" as a variant.
As explained in a 2010 newsletter of the International Confederation of Dietetic Associations:
The spelling of the term "dietitian" has been debated for a long time by dietitians. In the early 1960s dietetic associations, under the auspices of the International Committee of Dietetic Associations (ICDA), worked together to standardize information about dietitians under the International Standard Classification of Occupations. When the International Labour Office confirmed the dietetic profession's classification in 1967, it also adopted the spelling "dietitian" at the request of the international dietetic community. This information can be found in the documentation held by ICDA and by the International Labour Office (ILO).
ILO has however also issued new documents using the spelling "dietician".
World Health Organization classification
Dietitians supervise the preparation and service of food, develop modified diets, participate in research, and educate individuals and groups on good nutritional habits. The goals of dietitians are to provide medical nutritional intervention, and to obtain, safely prepare, serve and advise on flavorsome, attractive, and nutritious food for patients, groups and communities. Dietary modification to address medical issues involving dietary intake is a major part of dietetics (the study of nutrition as it relates to health). For example, working in consultation with physicians and other health care providers, a dietitian may provide specific artificial nutritional needs to patients unable to consume food normally. Professional dietitians may also provide specialist services such as in diabetes, obesity, oncology, osteoporosis, pediatrics, renal disease, and micronutrient research.
Different professional terms are used in different countries and employment settings, for example, clinical dietitian, community dietitian, dietetic educator, food-service dietitian, registered dietitian, public health dietitian, therapeutic dietitian, or research dietitian. In many countries, only people who have specified educational credentials and other professional requirements can call themselves "dietitians"—the title is legally protected. The term "nutritionist" is also widely used; however, the terms "dietitian" and "nutritionist" should not be considered interchangeable—the training, regulation and scope of practice of the two professional titles can be very different across individuals and jurisdictions.
In many countries, the majority of dietitians are clinical or therapeutic dietitians, such as the case of the United States, the United Kingdom, and much of Africa. In other countries they are mostly foodservice dietitians, such as in Japan and many European countries.
Dietitians in practice:
Clinical dietitians
Clinical dietitians work in hospitals, outpatient clinics, nursing care facilities and other health care facilities to provide nutrition therapy to patients with a variety of health conditions, and provide dietary consultations to patients and their families. They confer with other health care professionals to review patients' medical charts and develop individual plans to meet nutritional requirements. Some clinical dietitians will also create or deliver outpatient or public education programs in health and nutrition. Clinical dietitians may provide specialized services in areas of nourishment and diets, tube feedings (called enteral nutrition), and intravenous feedings (called parenteral nutrition) such as total parenteral nutrition (TPN) or peripheral parenteral nutrition (PPN). They work as a team with the physicians, physician assistants, physical therapists, occupational therapists, recreational therapists, pharmacists, speech therapists, social workers, nurses, dietetic technicians, psychologists and other specialists to provide care to patients. Some clinical dietitians have dual responsibilities with patient nutrition therapy and in food service or research.
Community dietitians
Community dietitians work with wellness programs, public health agencies, home care agencies, and health maintenance organizations. These dietitians apply and distribute knowledge about food and nutrition to individuals and groups of specific categories, life-styles and geographic areas in order to promote health. They often focus on the needs of the elderly, children, or other individuals with special needs or limited access to healthy food. Some community dietitians conduct home visits for patients who are too physically ill to attend consultations in health facilities in order to provide care and instruction on grocery shopping and food preparation.
Foodservice dietitians
Foodservice dietitians or managers are responsible for large-scale food planning and service. They coordinate, assess and plan foodservice processes in health care facilities, school food-service programs, prisons, restaurants, and company cafeterias. These dietitians may perform audits of their departments to ensure quality control and food safety standards, and launch new menus and various programs within their institution to meet health and nutritional requirements. They train and supervise other food service workers such as kitchen staff, delivery staff, and dietary assistants or aides.
Gerontological dietitians
Gerontological dietitians are specialists in nutrition and aging. They work in nursing homes, community-based aged care agencies, government agencies in aging policy, and in higher education in the field of gerontology (the study of aging).
Neonatal dietitians
Neonatal dietitians provide individualized medical nutrition therapy for critically ill premature newborns. They are considered a part of the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit's medical team. The neonatal dietitian performs clinical assessment of patients, designs nutrition protocols and quality improvement initiatives with the medical team, develops enteral and parenteral regimens, helps establish and promote lactation/breastfeeding guidelines and often oversees the management of infection prevention in the handling, storage, and delivery of nutritional products.
Pediatric dietitians
Pediatric dietitians provide nutrition and health advice for infants, children, and adolescents. They focus on early nutritional needs, and often work closely with doctors, school health services, clinics, hospitals and government agencies, in developing and implementing treatment plans for children with eating disorders, food allergies, or any condition where a child's diet factors into the equation, such as childhood obesity.
Research dietitians
Research dietitians may focus on social sciences or health services research, for example, investigate the impact of health policies or behaviour change, or evaluate program effectiveness. They may survey food-service systems management in order to guide quality improvement. Some research dietitians study the biochemical aspects of nutrient interaction within the body. In universities, they also may have teaching responsibilities. Some clinical dietitians' roles involve research in addition to their patients care workload.
Administrative dietitians
Administrative or management dietitians oversee and direct all aspects of clinical dietetics service, food policy and/or large-scale meal service operations in hospitals, government agencies, company cafeterias, prisons, and schools. They recruit, train and supervise employees of dietetics departments including dietitians and other personnel. They set department goals, policies and procedures; procurement, equipment and supplies; ensure safety and sanitation standards in foodservice; and administer budget management.
Business dietitians
Business dietitians serve as resource people in food and nutrition through business, marketing and communications. Dietitians' expertise in nutrition is often solicited in the media—for example for expert guest opinions on television and radio news or cooking shows, columns for a newspaper or magazine, or resources for restaurants on recipe development and critique. Business dietitians may author books or corporate newsletters on nutrition and wellness. They also work as sales representatives for food manufacturing companies that provide nutritional supplements and tube feeding supplies.
Consultant dietitians
Consultant dietitians are those who are in private practice or practice on a contractual basis with health care facilities or corporations, such as used in Australia, Canada and the United States. Consultant dietitians contract independently to provide nutrition or health related consultation and educational programs to individuals and health care facilities as well as sports teams, fitness clubs, and other health related businesses and corporations.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1989 2023-12-09 00:14:44
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1991) Computer Network
Gist
Basics building blocks of a Computer network are Nodes and Links. A Network Node can be illustrated as Equipment for Data Communication like a Modem, Router, etc., or Equipment of a Data Terminal like connecting two computers or more. Link in Computer Networks can be defined as wires or cables or free space of wireless networks.
The working of Computer Networks can be simply defined as rules or protocols which help in sending and receiving data via the links which allow Computer networks to communicate. Each device has an IP Address, that helps in identifying a device.
Basic Terminologies of Computer Networks
Network: A network is a collection of computers and devices that are connected together to enable communication and data exchange.
Nodes: Nodes are devices that are connected to a network. These can include computers, Servers, Printers, Routers, Switches, and other devices.
Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules and standards that govern how data is transmitted over a network. Examples of protocols include TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP.
Topology: Network topology refers to the physical and logical arrangement of nodes on a network. The common network topologies include bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree.
Service Provider Networks: These types of Networks give permission to take Network Capacity and Functionality on lease from the Provider. Service Provider Networks include Wireless Communications, Data Carriers, etc.
IP Address: An IP address is a unique numerical identifier that is assigned to every device on a network. IP addresses are used to identify devices and enable communication between them.
DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS) is a protocol that is used to translate human-readable domain names into IP addresses that computers can understand.
Firewall: A firewall is a security device that is used to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewalls are used to protect networks from unauthorized access and other security threats.
Summary
Computer network is two or more computers that are connected with one another for the purpose of communicating data electronically. Besides physically connecting computer and communication devices, a network system serves the important function of establishing a cohesive architecture that allows a variety of equipment types to transfer information in a near-seamless fashion. Two popular architectures are ISO Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) and IBM’s Systems Network Architecture (SNA).
Two basic network types are local-area networks (LANs) and wide-area networks (WANs). LANs connect computers and peripheral devices in a limited physical area, such as a business office, laboratory, or college campus, by means of links (wires, Ethernet cables, fibre optics, Wi-Fi) that transmit data rapidly. A typical LAN consists of two or more personal computers, printers, and high-capacity disk-storage devices called file servers, which enable each computer on the network to access a common set of files. LAN operating system software, which interprets input and instructs networked devices, allows users to communicate with each other; share the printers and storage equipment; and simultaneously access centrally located processors, data, or programs (instruction sets). LAN users may also access other LANs or tap into WANs. LANs with similar architectures are linked by “bridges,” which act as transfer points. LANs with different architectures are linked by “gateways,” which convert data as it passes between systems.
WANs connect computers and smaller networks to larger networks over greater geographic areas, including different continents. They may link the computers by means of cables, optical fibres, or satellites, but their users commonly access the networks via a modem (a device that allows computers to communicate over telephone lines). The largest WAN is the Internet, a collection of networks and gateways linking billions of computer users on every continent.
Details
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. Computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.
The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialized or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes and are rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol.
Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications protocols to organize network traffic, the network size, the topology, traffic control mechanisms, and organizational intent.
Computer networks support many applications and services, such as access to the World Wide Web, digital video and audio, shared use of application and storage servers, printers and fax machines, and use of email and instant messaging applications.
Use
Computer networks extend interpersonal communications by electronic means with various technologies, such as email, instant messaging, online chat, voice and video telephone calls, and video conferencing. A network allows sharing of network and computing resources. Users may access and use resources provided by devices on the network, such as printing a document on a shared network printer or use of a shared storage device. A network allows sharing of files, data, and other types of information giving authorized users the ability to access information stored on other computers on the network. Distributed computing uses computing resources across a network to accomplish tasks.
Network packet
Most modern computer networks use protocols based on packet-mode transmission. A network packet is a formatted unit of data carried by a packet-switched network.
Packets consist of two types of data: control information and user data (payload). The control information provides data the network needs to deliver the user data, for example, source and destination network addresses, error detection codes, and sequencing information. Typically, control information is found in packet headers and trailers, with payload data in between.
With packets, the bandwidth of the transmission medium can be better shared among users than if the network were circuit switched. When one user is not sending packets, the link can be filled with packets from other users, and so the cost can be shared, with relatively little interference, provided the link is not overused. Often the route a packet needs to take through a network is not immediately available. In that case, the packet is queued and waits until a link is free.
The physical link technologies of packet networks typically limit the size of packets to a certain maximum transmission unit (MTU). A longer message may be fragmented before it is transferred and once the packets arrive, they are reassembled to construct the original message.
Network topology
The physical or geographic locations of network nodes and links generally have relatively little effect on a network, but the topology of interconnections of a network can significantly affect its throughput and reliability. With many technologies, such as bus or star networks, a single failure can cause the network to fail entirely. In general, the more interconnections there are, the more robust the network is; but the more expensive it is to install. Therefore, most network diagrams are arranged by their network topology which is the map of logical interconnections of network hosts.
Common topologies are:
* Bus network: all nodes are connected to a common medium along this medium. This was the layout used in the original Ethernet, called 10BASE5 and 10BASE2. This is still a common topology on the data link layer, although modern physical layer variants use point-to-point links instead, forming a star or a tree.
* Star network: all nodes are connected to a special central node. This is the typical layout found in a small switched Ethernet LAN, where each client connects to a central network switch, and logically in a wireless LAN, where each wireless client associates with the central wireless access point.
* Ring network: each node is connected to its left and right neighbor node, such that all nodes are connected and that each node can reach each other node by traversing nodes left- or rightwards. Token ring networks, and the Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), made use of such a topology.
* Mesh network: each node is connected to an arbitrary number of neighbors in such a way that there is at least one traversal from any node to any other.
* Fully connected network: each node is connected to every other node in the network.
* Tree network: nodes are arranged hierarchically. This is the natural topology for a larger Ethernet network with multiple switches and without redundant meshing.
The physical layout of the nodes in a network may not necessarily reflect the network topology. As an example, with FDDI, the network topology is a ring, but the physical topology is often a star, because all neighboring connections can be routed via a central physical location. Physical layout is not completely irrelevant, however, as common ducting and equipment locations can represent single points of failure due to issues like fires, power failures and flooding.
Overlay network
An overlay network is a virtual network that is built on top of another network. Nodes in the overlay network are connected by virtual or logical links. Each link corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links, in the underlying network. The topology of the overlay network may (and often does) differ from that of the underlying one. For example, many peer-to-peer networks are overlay networks. They are organized as nodes of a virtual system of links that run on top of the Internet.
Overlay networks have been around since the invention of networking when computer systems were connected over telephone lines using modems before any data network existed.
The most striking example of an overlay network is the Internet itself. The Internet itself was initially built as an overlay on the telephone network. Even today, each Internet node can communicate with virtually any other through an underlying mesh of sub-networks of wildly different topologies and technologies. Address resolution and routing are the means that allow mapping of a fully connected IP overlay network to its underlying network.
Another example of an overlay network is a distributed hash table, which maps keys to nodes in the network. In this case, the underlying network is an IP network, and the overlay network is a table (actually a map) indexed by keys.
Overlay networks have also been proposed as a way to improve Internet routing, such as through quality of service guarantees achieve higher-quality streaming media. Previous proposals such as IntServ, DiffServ, and IP multicast have not seen wide acceptance largely because they require modification of all routers in the network. On the other hand, an overlay network can be incrementally deployed on end-hosts running the overlay protocol software, without cooperation from Internet service providers. The overlay network has no control over how packets are routed in the underlying network between two overlay nodes, but it can control, for example, the sequence of overlay nodes that a message traverses before it reaches its destination.
For example, Akamai Technologies manages an overlay network that provides reliable, efficient content delivery (a kind of multicast). Academic research includes end system multicast, resilient routing and quality of service studies, among others.
.jpg)
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1990 2023-12-09 20:06:30
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1992) Computer Numerical Control
Gist
Computer numerical control (CNC) is a manufacturing method that automates the control, movement and precision of machine tools through the use of preprogrammed computer software, which is embedded inside the tools. CNC is commonly used in manufacturing for machining metal and plastic parts.
Summary
A computer numerical control machine (CNC) is a machining tool that forms stock material to a desired shape that will fulfill manufacturing directives and component requirements. CNC machines use pre-programmed software to control the movements of complex machinery, including grinders, lathes, mills and other cutting tools used to remove material.
These computer-aided manufacturing techniques can perform a wide range of complex and precise CNC machining tasks to create manufactured products and specifically designed parts for the automotive, defense and aerospace industries.
Although 3D printing and other additive manufacturing processes take center stage in the 21st-century production of components made with soft materials, most everyday items are still the result of highly automated subtractive machining techniques.
Plastic water bottles are produced from molds using the CNC die sinking technique, and individual drive system components of any car on the road are milled to accurate dimensions to allow all moving gears to fit together seamlessly for optimal mechanical performance.
"Chances are, nearly everything you touch in your day-to-day life was at some point touched by a machine tool," says University of Tennessee Knoxville engineering professor Tony Schmitz. "If you've ever traveled in an airplane — a Boeing 747, for example — over a million separate components were machined and then assembled to get that plane off the ground."
CNC machine tools are as versatile and dynamic as the multitude of items they create. However, most CNC machinery works within two frameworks: An open-loop or closed-loop system.
In open-loop CNC systems, the operator will develop the computer numerical control for the task at hand and generate the g-code or work file using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The computer then relays the proper steps to the controller and its connected servo motors.
These motors manipulate cutting tools, like lathes or grinders, along at least two axes (X and Y), although high-end CNC machines can increase versatility and accuracy by moving CNC mills and other accessories around several additional axes.
Closed-loop CNC systems provide feedback data to the monitor to address inconsistencies while CNC machines move around the material. This motor-monitor communication allows closed-loop systems to alter the velocity, position and feed rate of turning machines and other CNC machine tools in real time.
Details
In machining, numerical control, also called computer numerical control (CNC), is the automated control of tools by means of a computer. It is used to operate tools such as drills, lathes, mills, grinders, routers and 3D printers. CNC transforms a piece of material (metal, plastic, wood, ceramic, stone, or composite) into a specified shape by following coded programmed instructions and without a manual operator directly controlling the machining operation.
A CNC machine is a motorized maneuverable tool and often a motorized maneuverable platform, which are both controlled by a computer, according to specific input instructions. Instructions are delivered to a CNC machine in the form of a sequential program of machine control instructions such as G-code and M-code, and then executed. The program can be written by a person or, far more often, generated by graphical computer-aided design (CAD) or computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. In the case of 3D printers, the part to be printed is "sliced" before the instructions (or the program) are generated. 3D printers also use G-Code.
CNC offers greatly increased productivity over non-computerized machining for repetitive production, where the machine must be manually controlled (e.g. using devices such as hand wheels or levers) or mechanically controlled by pre-fabricated pattern guides (see pantograph mill). However, these advantages come at significant cost in terms of both capital expenditure and job setup time. For some prototyping and small batch jobs, a good machine operator can have parts finished to a high standard whilst a CNC workflow is still in setup.
In modern CNC systems, the design of a mechanical part and its manufacturing program are highly automated. The part's mechanical dimensions are defined using CAD software and then translated into manufacturing directives by CAM software. The resulting directives are transformed (by "post processor" software) into the specific commands necessary for a particular machine to produce the component and then are loaded into the CNC machine.
Since any particular component might require the use of several different tools – drills, saws, etc. – modern machines often combine multiple tools into a single "cell". In other installations, several different machines are used with an external controller and human or robotic operators that move the component from machine to machine. In either case, the series of steps needed to produce any part is highly automated and produces a part that meets every specification in the original CAD drawing, where each specification includes a tolerance.
Description
Motion is controlling multiple axes, normally at least two (X and Y), and a tool spindle that moves in the Z (depth). The position of the tool is driven by direct-drive stepper motors or servo motors to provide highly accurate movements, or in older designs, motors through a series of step-down gears. Open-loop control works as long as the forces are kept small enough and speeds are not too great. On commercial metalworking machines, closed-loop controls are standard and required to provide the accuracy, speed, and repeatability demanded.
Parts description
As the controller hardware evolved, the mills themselves also evolved. One change has been to enclose the entire mechanism in a large box as a safety measure (with safety glass in the doors to permit the operator to monitor the machine's function), often with additional safety interlocks to ensure the operator is far enough from the working piece for safe operation. Most new CNC systems built today are 100% electronically controlled.
CNC-like systems are used for any process that can be described as movements and operations. These include laser cutting, welding, friction stir welding, ultrasonic welding, flame and plasma cutting, bending, spinning, hole-punching, pinning, gluing, fabric cutting, sewing, tape and fiber placement, routing, picking and placing, and sawing.
History
The first CNC machines were built in the 1940s and 1950s, based on existing tools that were modified with motors that moved the tool or part to follow points fed into the system on punched tape. These early servomechanisms were rapidly augmented with analog and digital computers, creating the modern CNC machine tools that have revolutionized machining processes.
Today
Now the CNC in the processing manufacturing field has been very extensive, not only the traditional milling and turning, other machines and equipment are also installed with the corresponding CNC, which makes the manufacturing industry in its support, greatly improving the quality and efficiency. Of course, the latest trend in CNC is to combine traditional subtractive manufacturing with additive manufacturing (3D printing) to create a new manufacturing method - hybrid additive subtractive manufacturing (HASM). Another trend is the combination of AI, using a large number of sensors, with the goal of achieving flexible manufacturing.
Tool/machine crashing
In CNC, a "crash" occurs when the machine moves in such a way that is harmful to the machine, tools, or parts being machined, sometimes resulting in bending or breakage of cutting tools, accessory clamps, vises, and fixtures, or causing damage to the machine itself by bending guide rails, breaking drive screws, or causing structural components to crack or deform under strain. A mild crash may not damage the machine or tools but may damage the part being machined so that it must be scrapped. Many CNC tools have no inherent sense of the absolute position of the table or tools when turned on. They must be manually "homed" or "zeroed" to have any reference to work from, and these limits are just for figuring out the location of the part to work with it and are no hard motion limit on the mechanism. It is often possible to drive the machine outside the physical bounds of its drive mechanism, resulting in a collision with itself or damage to the drive mechanism. Many machines implement control parameters limiting axis motion past a certain limit in addition to physical limit switches. However, these parameters can often be changed by the operator.
Many CNC tools also do not know anything about their working environment. Machines may have load sensing systems on spindle and axis drives, but some do not. They blindly follow the machining code provided and it is up to an operator to detect if a crash is either occurring or about to occur, and for the operator to manually abort the active process. Machines equipped with load sensors can stop axis or spindle movement in response to an overload condition, but this does not prevent a crash from occurring. It may only limit the damage resulting from the crash. Some crashes may not ever overload any axis or spindle drives.
If the drive system is weaker than the machine's structural integrity, then the drive system simply pushes against the obstruction, and the drive motors "slip in place". The machine tool may not detect the collision or the slipping, so for example the tool should now be at 210mm on the X-axis, but is, in fact, at 32mm where it hit the obstruction and kept slipping. All of the next tool motions will be off by −178mm on the X-axis, and all future motions are now invalid, which may result in further collisions with clamps, vises, or the machine itself. This is common in open-loop stepper systems but is not possible in closed-loop systems unless mechanical slippage between the motor and drive mechanism has occurred. Instead, in a closed-loop system, the machine will continue to attempt to move against the load until either the drive motor goes into an overload condition or a servo motor fails to get to the desired position.
Collision detection and avoidance are possible, through the use of absolute position sensors (optical encoder strips or disks) to verify that motion occurred, or torque sensors or power-draw sensors on the drive system to detect abnormal strain when the machine should just be moving and not cutting, but these are not a common component of most hobby CNC tools. Instead, most hobby CNC tools simply rely on the assumed accuracy of stepper motors that rotate a specific number of degrees in response to magnetic field changes. It is often assumed the stepper is perfectly accurate and never missteps, so tool position monitoring simply involves counting the number of pulses sent to the stepper over time. An alternate means of stepper position monitoring is usually not available, so crash or slip detection is not possible.
Commercial CNC metalworking machines use closed-loop feedback controls for axis movement. In a closed-loop system, the controller monitors the actual position of each axis with an absolute or incremental encoder. Proper control programming will reduce the possibility of a crash, but it is still up to the operator and programmer to ensure that the machine is operated safely. However, during the 2000s and 2010s, the software for machining simulation has been maturing rapidly, and it is no longer uncommon for the entire machine tool envelope (including all axes, spindles, chucks, turrets, tool holders, tailstocks, fixtures, clamps, and stock) to be modeled accurately with 3D solid models, which allows the simulation software to predict fairly accurately whether a cycle will involve a crash. Although such simulation is not new, its accuracy and market penetration are changing considerably because of computing advancements.
Numerical precision and equipment backlash
Within the numerical systems of CNC programming, the code generator can assume that the controlled mechanism is always perfectly accurate, or that precision tolerances are identical for all cutting or movement directions. This is not always a true condition of CNC tools. CNC tools with a large amount of mechanical backlash can still be highly precise if the drive or cutting mechanism is only driven to apply cutting force from one direction, and all driving systems are pressed tightly together in that one cutting direction. However, a CNC device with high backlash and a dull cutting tool can lead to cutter chatter and possible workpiece gouging. The backlash also affects the precision of some operations involving axis movement reversals during cutting, such as the milling of a circle, where axis motion is sinusoidal. However, this can be compensated for if the amount of backlash is precisely known by linear encoders or manual measurement.
The high backlash mechanism itself is not necessarily relied on to be repeatedly precise for the cutting process, but some other reference object or precision surface may be used to zero the mechanism, by tightly applying pressure against the reference and setting that as the zero references for all following CNC-encoded motions. This is similar to the manual machine tool method of clamping a micrometer onto a reference beam and adjusting the Vernier dial to zero using that object as the reference.
Positioning control system
In numerical control systems, the position of the tool is defined by a set of instructions called the part program. Positioning control is handled using either an open-loop or a closed-loop system. In an open-loop system, communication takes place in one direction only: from the controller to the motor. In a closed-loop system, feedback is provided to the controller so that it can correct for errors in position, velocity, and acceleration, which can arise due to variations in load or temperature. Open-loop systems are generally cheaper but less accurate. Stepper motors can be used in both types of systems, while servo motors can only be used in closed systems.
Cartesian coordinates
The G & M code positions are all based on a three-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. This system is a typical plane often seen in mathematics when graphing. This system is required to map out the machine tool paths and any other kind of actions that need to happen in a specific coordinate. Absolute coordinates are what are generally used more commonly for machines and represent the (0,0,0) point on the plane. This point is set on the stock material to give a starting point or "home position" before starting the actual machining.
Additional Information
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a manufacturing process in which pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of factory tools and machinery. The process can be used to control a range of complex machinery, from grinders and lathes to mills and CNC routers. With CNC machining, three-dimensional cutting tasks can be accomplished in a single set of prompts.
The CNC process runs in contrast to — and thereby supersedes — the limitations of manual control, where live operators are needed to prompt and guide the commands of machining tools via levers, buttons and wheels. To the onlooker, a CNC system might resemble a regular set of computer components, but the software programs and consoles employed in CNC machining distinguish it from all other forms of computation.
If you’re interested in utilizing CNC manufacturing to produce various products, find out more about how CNC machining and CNC programming works. You might also want to know about the main types of CNC machinery and the kind of work it can do to see if it can meet your needs.
What is CNC Machining?
When a CNC system is activated, the desired cuts are programmed into the software and dictated to corresponding tools and machinery, which carry out the dimensional tasks as specified, much like a robot.
In CNC programming, the code generator within the numerical system will often assume mechanisms are flawless, despite the possibility of errors, which is greater whenever a CNC machine is directed to cut in more than one direction simultaneously. The placement of a tool in a numerical control system is outlined by a series of inputs known as the part program.
With a numerical control machine, programs are inputted via punch cards. By contrast, the programs for CNC machines are fed to computers through small keyboards. CNC programming is retained in a computer’s memory. The code itself is written and edited by programmers. Therefore, CNC systems offer far more expansive computational capacity. Best of all, CNC systems are by no means static since newer prompts can be added to pre-existing programs through revised code.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1991 2023-12-10 18:33:04
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1993) Mason
Gist
A mason is a person who is skilled at making things or building things with stone. In American English, masons are people who work with stone or bricks. 2. countable noun. A Mason is the same as a Freemason.
Details:
Stonemasonry
Stonemasonry or stonecraft is the creation of buildings, structures, and sculpture using stone as the primary material. Stonemasonry is the craft of shaping and arranging stones, often together with mortar and even the ancient lime mortar, to wall or cover formed structures.
The basic tools, methods and skills of the banker mason have existed as a trade for thousands of years. It is one of the oldest activities and professions in human history. Many of the long-lasting, ancient shelters, temples, monuments, artifacts, fortifications, roads, bridges, and entire cities were built of stone. Famous works of stonemasonry include Göbekli Tepe, the Egyptian pyramids, the Taj Mahal, Cusco's Incan Wall, Easter Island's statues, Angkor Wat, Borobudur, Tihuanaco, Tenochtitlan, Persepolis, the Parthenon, Stonehenge, the Great Wall of China, the Mesoamerican pyramids, Chartres Cathedral, and the Stari Most.
While stone was important traditionally, it fell out of use in the modern era, in favor of brick and steel-reinforced concrete. This is despite the advantages of stone over concrete. Those advantages include: (1) many types of stone are stronger than concrete in compression; (2) stone uses much less energy to produce, and hence its production emits less carbon dioxide than either brick or concrete, and (3) stone is widely considered aesthetically pleasing, while concrete is often painted or clad. Modern stonemasonry is in the process of reinventing itself for automation, modern load-bearing stone construction, innovative reinforcement techniques, and integration with other sustainable materials, like wood.
Stonemasonry disciplines
* A quarryman splits or cuts rock in the quarry, and extracts the resulting blocks of stone. The cut or split pieces are collected and transported away from the extraction surface for further refinement.
* A sawyer stonemason cuts these stone blocks into dimension stone, to required size with saws. The resulting block if ordered for a specific component is known as sawn six sides (SSS). A sawyer mason is similar to a banker mason in that they work with rough pieces of stone and shape them according to certain standards. The main difference between a sawyer mason and a banker mason is the size of the stone they work with – a sawyer mason typically works with much larger pieces and uses diamond-coated tools. Sawyer masons may work in quarries or be found in tile or flooring stores, possessing a range of specific skills, such as examining grain patterns to determine cleavage, creating smaller stones from larger pieces, and carving precise outlines and drilling holes using various tools like chisels.
* A banker mason, sometimes referred to as a bank mason, is workshop-based, and specializes in working the stones into the shapes required by a building's design, this set out on templets and a bed mould. A banker mason uses various hand and power tools to cut, carve, and shape stone. They can produce anything from stones with simple chamfers to tracery windows, detailed mouldings and the more classical architectural building masonry. When working a stone from a sawn block, the mason ensures that the stone is bedded in the right way, so the finished work sits in the building in the same orientation as it was formed on the ground. Occasionally though some stones need to be oriented correctly for the application; this includes voussoirs, jambs, copings, and cornices. The stone's size and shape are usually predetermined by builders or other parties involved in a project, and the banker mason works according to a brief or a set of designs provided for that project. Once the stone has been crafted to the required specifications, it is transported to the construction site or another location for use in a building or other structure.
* Fixer mason specializes in the fixing of stones onto buildings, using lifting tackle, and traditional lime mortars and grouts. Sometimes modern cements, mastics, and epoxy resins are used, usually on specialist applications such as stone cladding. Metal fixings, from simple dowels and cramps to specialized single application fixings, are also used. The precise tolerances necessarily make this a highly skilled job. This type of masons has specialized into fixing the stones onto the buildings. A fixer mason is responsible for traveling to a job site to fit and lay pre-prepared stone or cladding for buildings. They might do this with grouts, mortars, and lifting tackle. They might also use things like single application specialized fixings, simple cramps, and dowels as well as stone cladding with things like epoxy resins, mastics, and modern cements.
* Memorial mason or monumental mason carve gravestones and inscriptions.
* Carver mason crosses the line from craft to art. They use their artistic ability to carve stone into foliage, figures, animals or abstract designs. Carver masons are the artists of stonemasonry, responsible for creating designs and/or patterns from stone, as well as on stones. This work can include stone sculptures of figures or animals, or other projects of a similar nature. Throughout history, carver masons have been renowned for their exceptional skills in crafting beautiful pieces from stone.
Classical stonemasonry techniques
Stone has been used in construction for thousands of years, in many contexts. Listed below are six types of classical stonemasonry techniques, some of which still see widespread use.
* Ashlar masonry. Stone masonry using dressed (cut) stones is known as ashlar masonry.
* Trabeated systems. One of the oldest forms of stone construction uses a lintel (beam) laid across stone posts or columns. This method predates Stonehenge, and refined versions were used by the Egyptians, Persians, Greeks, and Romans.
* Arch masonry. Also called "arcuated systems" in contrast with trabeated systems, which are two ancient methods for creating a void below a stone span (either a lintel or an arch). Note that the Wikipedia page on stone arches is about stone-arch bridges exclusively, and the arch page is about all arches, including non-stone.
* Rubble masonry. Use of rubble in masonry: antonymous to ashlar masonry. Can be infill in an ashlar wall, used in cyclopean concrete, and other contexts. The term is antonymous to "ashlar".
* Dry stone. Stone walls built without mortar, using the shape of the stones, compression, and friction for stability. This technique encompasses cyclopean masonry and other mortar-less methods, but is conventionally used to describe agricultural walls used to mark boundaries, contain livestock, and retain soil.
* Cyclopean masonry. Dry wall construction using massive boulders that may have been shaped to fit together. Polygonal masonry is a subtype of cyclopean masonry where the boulders are shaped into polygonal profiles.
Modern stonemasonry systems
In the modern era, stone has been largely relegated as a cosmetic element of buildings, often used as decorative cladding on steel-reinforced concrete. This is despite its wide historical use in large compressive structures: 50-m bridges and colosseums in Roman times, ~65-m tall cathedrals since the middle ages, and 12-story apartment buildings built in the 1690s.
* Stone veneer is used as a protective and decorative covering for interior or exterior walls and surfaces. The veneer is typically 1 in (25.4 mm) thick and must weigh less than 15 lb per square foot (73 kg m^{−2}) so that no additional structural supports are required. The structural wall is put up first, and thin, flat stones are mortared onto the face of the wall. Metal tabs in the structural wall are mortared between the stones to tie everything together, to prevent the stonework from separating from the wall.
* Massive precut stone. Also known as "prefabricated stone", "massive stone", "pre-sized stone", or "pré-taille" stone.
* Formwork stone. "Pierre banchée" in French. Uses stone tiles or ashlars as shuttering for pouring concrete. These are left in place after the concrete sets. This is the inverse procedure to stone cladding, where the stone tiles are attached to the concrete after the temporary shuttering has been removed. Developed by Fernand Pouillon to accelerate construction. Formwork stone is distinct from cyclopean concrete in that the former uses rectilinear tiles, while the latter uses boulders and/or cobblestone.
* Post-tensioned stone. A high-performance composite construction material consisting of stone held in compression with tension elements. The tension elements can be connected to the outside of the stone, but more typically uses tendons threaded internally through a duct formed from aligned drilled holes.
* Pre-tensioned stone. Using an epoxy shear connector, early experiments have shown that it is possible to pre-tension stone, maintaining the tendon under tension while the liquid epoxy is injected and allowed to set.
* Cyclopean concrete. This method uses a combination of cyclopean masonry and rubble masonry: boulders and or rubble are placed in a form (or in a ditch), and concrete is poured on top to bind the stones together before removing the form. Variations of this include Frank Lloyd Wright's 'desert masonry' and Institut Balear de l'Habitatge's cyclopean concrete blocks, which are cast in a large slab and precisely sawn for use as prefabricated masonry in the massive precut stone system.
* Slipform stonemasonry is a variation of Cyclopean concrete stone-wall construction that uses formwork to contain the rocks and mortar while keeping the walls straight. Short forms, up to two feet tall, are placed on both sides of the wall to serve as a guide for the stonework. Stones are placed inside the forms with the good faces against the formwork. Concrete is poured behind the rocks. Rebar is added for strength, to make a wall that is approximately half reinforced concrete and half stonework. The wall can be faced with stone on one side or both sides.
* Digital stereotomy. Using CAD and computer models of load, modern designers are able to cut complex vaults, arches, and other arrangements of precisely cut ashlars. Antecedents to this discipline include curved vaults, and also flat vaults that use a concentric flat arch vault and the Abeille flat vault. Using digital design and machining, such compression structures can be shapes into complex compressive structures.
* Trabeated stone exoskeleton. In the modern era, post-and-lintel construction was adapted use as a stone exoskeleton in the design of 15 Clerkenwell Close. The stone exoskeleton method is a variant of the massive precut stone method: the ends of the posts and lintels are precisely precut offsite prior to assembly by crane. At least two more trabeated stone exoskeleton high-rise buildings are underway, one in London, and another in Bristol.
* Stone bricks. Small stone ashlars that are cut by the quarry to brick sizing to allow their use in standardized brick-laying workflows. Cost is similar to clay composite bricks, but with greatly reduced carbon emissions.
Tools
Stonemasons use a wide variety of tools to handle and shape stone blocks (ashlar) and slabs into finished articles. The basic tools for shaping the stone are a mallet, chisels, and a metal straight edge. With these one can make a flat surface – the basis of all stonemasonry.
Chisels come in a variety of sizes and shapes, dependent upon the function for which they are being used and have many different names depending on locality. There are different chisels for different materials and sizes of material being worked, for removing large amounts of material and for putting a fine finish on the stone. A drove chisel is used for smoothing off roughly finished stones.
Mixing mortar is normally done today with mortar mixers which usually use a rotating drum or rotating paddles to mix the mortar.
The masonry trowel is used for the application of the mortar between and around the stones as they are set into place. Filling in the gaps (joints) with mortar is referred to as pointing. Pointing in smaller joints can be accomplished using tuck pointers, pointing trowels, and margin trowels, among other tools.
A mason's hammer has a long thin head and is called a Punch Hammer. It would be used with a chisel or splitter for a variety of purposes
A walling hammer (catchy hammer) can be used in place of a hammer and chisel or pincher to produce rubble or pinnings or snecks.
Stonemasons use a lewis together with a crane or block and tackle to hoist building stones into place.
Today power tools such as compressed-air chisels, abrasive spinners, and angle grinders are much used: these save time and money, but are hazardous and require just as much skill as the hand tools that they augment. But many of the basic tools of stonemasonry have remained virtually the same throughout vast amounts of time, even thousands of years, for instance when comparing chisels that can be bought today with chisels found at the pyramids of Giza the common sizes and shapes are virtually unchanged.
Training
Traditionally medieval stonemasons served a seven-year apprenticeship. A similar system still operates today.
A modern apprenticeship lasts three years. This combines on-site learning through personal experience, the experience of the tradesmen, and college work where apprentices are given an overall experience of the building, hewing and theory work involved in masonry. In some areas, colleges offer courses which teach not only the manual skills but also related fields such as drafting and blueprint reading or construction conservation. Electronic Stonemasonry training resources enhance traditional delivery techniques. Hands-on workshops are a good way to learn about stonemasonry also. Those wishing to become stonemasons should have little problem working at heights, possess reasonable hand-eye coordination, be moderately physically fit, and have basic mathematical ability. Most of these things can be developed while learning.
The modern stonemason undergoes comprehensive training, both in the classroom and in the working environment. Hands-on skill is complemented by an intimate knowledge of each stone type, its application, and best uses, and how to work and fix each stone in place. The mason may be skilled and competent to carry out one or all of the various branches of stonemasonry. In some areas, the trend is towards specialization, in other areas towards adaptability.
Today's stonemasons undergo training that is quite comprehensive and is done both in the work environment and in the classroom. It isn't enough to have hands-on skills only. One must also have knowledge of the types of stones as well as its best uses and how to work it as well as how to fix it in place.
Additional Information
What is Stone Masonry?
Stone masonry is the construction of stones cemented together with mortar. Where stones are plentiful, cutting and dressing them to the right shape makes it cost-effective to construct numerous building components such as walls, columns, tooting, arches, beams, etc. Piers, docks, dams, lighthouses, and other sea construction built with stone masonry, stronger, more robust, and more weather-resistant than brick masonry.
Materials Used for Stone Masonry:
The materials used for stone masonry are:
1. Stones:
The stones used in masonry must be robust, durable, and free of cracks, sand holes, and voids. The availability of the stone and the construction’s relevance decide the stone’s selection for a given project. Limestone, sandstone, granite, marble, laterite, and other stones are utilized in masonry construction.
2. Mortar:
Mortar is the binding medium used in masonry construction. Masonry mortar consists of cement or lime, sand, and water. In nature, the resulting mixture is uniform. The following are the most important aspects to consider while choosing masonry mortar:
i) Strength is needed.
ii) The stone’s color
iii) The loads placed on the structure
Uses of Stone Masonry:
i) The base of the building, walls, piers, and pillars, as well as the architectural work.
ii) Roofing materials and roof coverings
iii) The process of cladding is carried out.
iv) Dams, lighthouses, and other colossal constructions are examples of this.
v) Careers in paving
vi) Ballast, blackboards, and an electrical switch building are part of the railway system.
vii) Lintels, beams, beams, arches, domes, and other architectural elements.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1992 2023-12-11 17:37:43
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1994) Marine Engineering
Gist
Marine Engineering is the discipline that deals with matters related to the design, innovation, construction and maintenance of seagoing vessels and navigation equipment.
Summary
Marine Engineering is the discipline that deals with matters related to the design, innovation, construction and maintenance of seagoing vessels and navigation equipment. Marine Engineering focuses primarily on the development and production of internal systems of boats, ships, or submarines. Marine Engineering prepares students who can design propulsion systems, auxiliary power machinery and operation equipment. Technical responsibilities also include working on-board and maintaining these systems.
Marine Engineering is closely related to other fields such as naval architecture, nautical sciences, oceanographic engineering, or automotive and mechanical engineering. These study areas require very good knowledge of physics, and more specifically fluid mechanics, propulsion, applied mathematics, control engineering, and computer-aided design (CAD).
Students of Marine Engineering have the opportunity to specialise in certain areas including hydrodynamics, naval operations, design and logistics, resources and aquaculture and technology management. A graduate of Marine Engineering possesses good knowledge of mechanics, hydraulics, materials science and specialised computer software.
Marine Engineering professionals work in many different settings and industries, from marine engineering firms and the naval forces, to offshore oil and gas industries and mineral extraction companies, and marine consultancy and survey agencies. Typical job roles include ship engineer, travelling service engineer, sales engineer, port engineer, consultant in maritime accidents, casualties and claims.
Details
Marine engineering is the engineering of boats, ships, submarines, and any other marine vessel. Here it is also taken to include the engineering of other ocean systems and structures – referred to in certain academic and professional circles as “ocean engineering.”
Marine engineering applies a number of engineering sciences, including mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, electronic engineering, and computer science, to the development, design, operation and maintenance of watercraft propulsion and ocean systems. It includes but is not limited to power and propulsion plants, machinery, piping, automation and control systems for marine vehicles of any kind, as well as coastal and offshore structures.
History
Archimedes is traditionally regarded as the first marine engineer, having developed a number of marine engineering systems in antiquity. Modern marine engineering dates back to the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (early 1700s).
In 1807, Robert Fulton successfully used a steam engine to propel a vessel through the water. Fulton's ship used the engine to power a small wooden paddle wheel as its marine propulsion system. The integration of a steam engine into a watercraft to create a marine steam engine was the start of the marine engineering profession. Only twelve years after Fulton’s Clermont had her first voyage, the Savannah marked the first sea voyage from America to Europe. Around 50 years later the steam powered paddle wheels had a peak with the creation of the Great Eastern, which was as big as one of the cargo ships of today, 700 feet in length, weighing 22,000 tons. Paddle steamers would become the front runners of the steamship industry for the next thirty years till the next type of propulsion came around.
Relevance and Scope
Here are many ways to become a Marine Engineer, but all include a university or college degree. Primarily, training includes a Bachelor of Engineering (B.Eng. or B.E.), Bachelor of Science (B.Sc. or B.S.), Bachelor of Technology (B.Tech.) or Bachelor of Applied Science (B.A.Sc.) in Marine Engineering. Depending on the country and jurisdiction, to be licensed as a Marine engineer, a Master's degree; Master of Engineering (M.Eng.), Master of Science (M.Sc or M.S.) or Master of Applied Science (M.A.Sc.) may be required. There are also Marine engineers who have come from other disciplines, e.g., from engineering fields like Mechanical Engineering, Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Geomatics Engineering, Environmental Engineering or from science fields like Geology, Geophysics, Physics, Geomatics, Earth Science, Mathematics, However, this path requires taking a graduate degree such as M.Eng, M.S., M.Sc. or M.A.Sc. in Marine Engineering after graduating from a different quantitative undergraduate program to be qualified as a Marine engineer.
The fundamental subjects of Marine engineering study usually include:
* Mathematics; Calculus, Algebra, Differential Equations, Numerical Analysis
* Geoscience; Geochemistry, Geophysics, Mineralogy, Geomatics
* Mechanics; Rock mechanics, Soil Mechanics, Geomechanics
* Thermodynamics; Heat Transfer, Work (thermodynamics), Mass Transfer
* Hydrogeology
* Fluid Mechanics; Fluid statics, Fluid Dynamics
* Geostatistics; Spatial Analysis, Statistics
* Control Engineering; Control Theory, Instrumentation
* Surface Mining; Open-pit mining.
Related Fields
Naval architecture
In the engineering of seagoing vessels, naval architecture is concerned with the overall design of the ship and its propulsion through the water, while marine engineering ensures that the ship systems function as per the design. Although they have distinctive disciplines, naval architects and marine engineers often work side-by-side.
Ocean engineering (and combination with Marine engineering)
Ocean engineering is concerned with other structures and systems in or adjacent to the ocean, including offshore platforms, coastal structures such as piers and harbors, and other ocean systems such as ocean wave energy conversion and underwater life-support systems. This in fact makes ocean engineering a distinctive field from marine engineering, which is concerned with the design and application of shipboard systems specifically. However, on account of its similar nomenclature and multiple overlapping core disciplines (e.g. hydrodynamics, hydromechanics, and materials science), “ocean engineering” sometimes operates under the umbrella term of “marine engineering,” especially in industry and academia outside of the U.S.
Oceanography
Oceanography is a scientific field concerned with the acquisition and analysis of data to characterize the ocean. Although separate disciplines, marine engineering and oceanography are closely intertwined: marine engineers often use data gathered by oceanographers to inform their design and research, and oceanographers use tools designed by marine engineers (more specifically, oceanographic engineers) to advance their understanding and exploration of the ocean.
Mechanical engineering
Marine engineering incorporates many aspects of mechanical engineering. One manifestation of this relationship lies in the design of shipboard propulsion systems. Mechanical engineers design the main propulsion plant, the powering and mechanization aspects of the ship functions such as steering, anchoring, cargo handling, heating, ventilation, air conditioning interior and exterior communication, and other related requirements. Electrical power generation and electrical power distribution systems are typically designed by their suppliers; the only design responsibility of the marine engineering is installation.
Furthermore, an understanding of mechanical engineering topics such as fluid dynamics, fluid mechanics, linear wave theory, strength of materials, structural mechanics, and structural dynamics is essential to a marine engineer's repertoire of skills. These and other mechanical engineering subjects serve as an integral component of the marine engineering curriculum.
Civil Engineering
Civil engineering concepts play in an important role in many marine engineering projects such as the design and construction of ocean structures, ocean bridges and tunnels, and port/harbor design.
Coastal engineering
Coastal engineering is a branch of civil engineering concerned with the specific demands posed by constructing at or near the coast, as well as the development of the coast itself.
The hydrodynamic impact of especially waves, tides, storm surges and tsunamis and (often) the harsh environment of salt seawater are typical challenges for the coastal engineer – as are the morphodynamic changes of the coastal topography, caused both by the autonomous development of the system and man-made changes. The areas of interest in coastal engineering include the coasts of the oceans, seas, marginal seas, estuaries and big lakes.
Besides the design, building and maintenance of coastal structures, coastal engineers are often interdisciplinary involved in integrated coastal zone management, also because of their specific knowledge of the hydro- and morphodynamics of the coastal system. This may include providing input and technology for e.g. environmental impact assessment, port development, strategies for coastal defense, land reclamation, offshore wind farms and other energy-production facilities, etc.
Electronics and Robotics
Marine engineering often deals in the fields of electrical engineering and robotics, especially in applications related to employing deep-sea cables and UUVs.
Deep-sea cables
A series of transoceanic fiber optic cables are responsible for connecting much of the world’s communication via the internet, carrying as much as 99 percent of total global internet and signal traffic. These cables must be engineered to withstand deep-sea environments that are remote and often unforgiving, with extreme pressures and temperatures as well as potential interference by fishing, trawling, and sea life.
UUV autonomy and networks
The use of unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) stands to benefit from the use of autonomous algorithms and networking. Marine engineers aim to learn how advancements in autonomy and networking can be used to enhance existing UUV technologies and facilitate the development of more capable underwater vehicles.
Petroleum Engineering
A knowledge of marine engineering proves useful in the field of petroleum engineering, as hydrodynamics and seabed integration serve as key elements in the design and maintenance of offshore oil platforms.
Marine construction
Marine construction is the process of building structures in or adjacent to large bodies of water, usually the sea. These structures can be built for a variety of purposes, including transportation, energy production, and recreation. Marine construction can involve the use of a variety of building materials, predominantly steel and concrete. Some examples of marine structures include ships, offshore platforms, moorings, pipelines, cables, wharves, bridges, tunnels, breakwaters and docks.
Additional Information:
Marine Engineering Job Description
A marine engineer is a professional who has studied marine engineering (sometimes also called maritime engineering) and is responsible for the operation, maintenance and repair of all major mechanical and engineered equipment onboard a ship.
There are several mechanical systems that help in the operations of any vessel like the propulsion mechanics, electricity and power generation system, lubrication, fuel systems, water distillation, lighting and air conditioning system etc.
These are all included in the technical responsibilities of a marine engineer.
Duties of Marine Engineers
Some of the important duties that people who have done marine engineering (maritime engineering) perform are:
Monitoring and maintenance of mechanical systems – Engineers of each rank on board ship is allocated specific machinery and systems for maintenance and monitoring purpose.
Machinery systems are divided among all engineers and it is the duty of each engineer to ensure his/her machinery is running at all times. Marine engineers are also required to look after the machinery on deck.
Proper record-keeping and planning maintenance – The engine room department works as a team to ensure the maintenance of all machinery systems is carried out according to the planned maintenance system. Precise record-keeping of various parameters is carried out for official paperwork and reporting.
Fuel oil bunkering – Marine engineers also handle the transfer of fuel oil to the ship from a bunker station or barge. It is usually the duty of the 4th engineer, who also takes regular soundings of the fuel oil tanks and report it to the chief engineer for planning bunkering operations.
Emergency breakdown and repair – The study of marine engineering also teaches how to deal with major maintenance and breakdown of machinery systems at sea. Though marine engineers are quite capable of the same, there are times when there might be a need for experts. In such cases, marine engineers are required to work with the experts to repair and resolve the issue.
Apart from the above-mentioned duties, a marine engineer on ships is required to follow all the instructions of the chief engineer, the head of the engine room department on the ship.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1993 2023-12-12 01:33:54
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1995) Import
Gist
Imports is to buy goods, etc. from a foreign country and bring them into your own country.
Summary:
What Is an Import?
An import is a good or service bought in one country that was produced in another. Imports and exports are the components of international trade. If the value of a country's imports exceeds the value of its exports, the country has a negative balance of trade, also known as a trade deficit.
The United States has run a trade deficit since 1975. The deficit stood at $576.86 billion in 2019, according to the U.S. Census Bureau.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
An import is a product or service produced abroad and purchased in your home country.
Imported goods or services are attractive when domestic industries cannot produce similar goods and services cheaply or efficiently.
Free trade agreements and tariff schedules often dictate which goods and materials are less expensive to import.
Economists and policy analysts disagree on the positive and negative impacts of imports.
The Basics of an Import
Countries are most likely to import goods or services that their domestic industries cannot produce as efficiently or cheaply as the exporting country. Countries may also import raw materials or commodities that are not available within their borders. For example, many countries import oil because they cannot produce it domestically or cannot produce enough to meet demand.
Free trade agreements and tariff schedules often dictate which goods and materials are less expensive to import. With globalization and the increasing prevalence of free-trade agreements between the United States, other countries and trading blocks, U.S. imports of goods and services increased from $580.14 billion in 1989 to $3.1 trillion as of 2019.
Free-trade agreements and a reliance on imports from countries with cheaper labor often seem responsible for a large portion of the decline in manufacturing jobs in the importing nation. Free trade opens the ability to import goods and materials from cheaper production zones and reduces reliance on domestic goods. The impact on manufacturing jobs was evident between 2000 and 2007, and it was further exacerbated by the Great Recession and the slow recovery afterward.
Details
An import is the receiving country in an export from the sending country. Importation and exportation are the defining financial transactions of international trade.
In international trade, the importation and exportation of goods are limited by import quotas and mandates from the customs authority. The importing and exporting jurisdictions may impose a tariff (tax) on the goods. In addition, the importation and exportation of goods are subject to trade agreements between the importing and exporting jurisdictions.
History:
Definition
Imports consist of transactions in goods and services to a resident of a jurisdiction (such as a nation) from non-residents. The exact definition of imports in national accounts includes and excludes specific "borderline" cases. Importation is the action of buying or acquiring products or services from another country or another market other than own. Imports are important for the economy because they allow a country to supply nonexistent, scarce, high cost, or low-quality certain products or services, to its market with products from other countries.
A general delimitation of imports in national accounts is given below:
* An import of a good occurs when there is a change of ownership from a non-resident to a resident; this does not necessarily imply that the good in question physically crosses the frontier. However, in specific cases, national accounts impute changes of ownership even though in legal terms no change of ownership takes place (e.g. cross border financial leasing, cross border deliveries between affiliates of the same enterprise, goods crossing the border for significant processing to order or repair). Also, smuggled goods must be included in the import measurement.
* Imports of services consist of all services rendered by non-residents to residents. In national accounts any direct purchases by residents outside the economic territory of a country are recorded as imports of services; therefore all expenditure by tourists in the economic territory of another country are considered part of the imports of services. Also, international flows of illegal services must be included.
Basic trade statistics often differ in terms of definition and coverage from the requirements in the national accounts:
* Data on international trade in goods are mostly obtained through declarations to custom services. If a country applies the general trade system, all goods entering the country are recorded as imports. If the special trade system (e.g. extra-EU trade statistics) is applied goods that are received into customs warehouses are not recorded in external trade statistics unless they subsequently go into free circulation of the importing country.
* A special case is the intra-EU trade statistics. Since goods move freely between the member states of the EU without customs controls, statistics on trade in goods between the member states must be obtained through surveys. To reduce the statistical burden on the respondent's small-scale traders are excluded from the reporting obligation.
* Statistical recording of trade in services is based on declarations by banks to their central banks or by surveys of the main operators. In a globalized economy where services can be rendered via electronic means (e.g. internet) the related international flows of services are difficult to identify.
Basic statistics on international trade normally do not record smuggled goods or international flows of illegal services. A small fraction of the smuggled goods and illegal services may nevertheless be included in official trade statistics through dummy shipments or dummy declarations that serve to conceal the illegal nature of the activities.
Balance of trade
A country has demand for an import when the price of the good (or service) on the world market is less than the price on the domestic market.
The balance of trade, usually denoted NX, is the difference between the value of all the goods (and services) a country exports and the value of the goods the country imports. A trade deficit occurs when imports are larger than exports. Imports are impacted principally by a country's income and its productive resources. For example, the US imports oil from Canada even though the US has oil and Canada uses oil. However, consumers in the US are willing to pay more for the marginal barrel of oil than Canadian consumers are, because there is more oil demanded in the US than there is oil produced.
In macroeconomic theory, the value of imports can be modeled as a function of domestic absorption (spending on everything, regardless of source) and the real exchange rate. These are the two most important factors affecting imports and they both affect imports positively.
Types of import
There are two basic types of import:
* Industrial and consumer goods
* Intermediate goods and services
Companies import goods and services to supply to the domestic market at a cheaper price and better quality than competing goods manufactured in the domestic market. Companies import products that are not available in the local market.
There are three broad types of importers:
* Those looking for any product around the world to import and sell
* Those looking for foreign sourcing to get their products at the cheapest price
* Those who using foreign sourcing as part of their global supply chain
* Direct-import refers to a type of business importation involving a major retailer (e.g. Wal-Mart) and an overseas manufacturer. A retailer typically purchases products designed by local companies that can be manufactured overseas. In a direct-import program, the retailer bypasses the local supplier (colloquial: "middle-man") and buys the final product directly from the manufacturer, possibly saving in added cost data on the value of imports and their quantities often broken down by detailed lists of products are available in statistical collections on international trade published by the statistical services of intergovernmental organisations (e.g. UNSD, FAOSTAT, OECD), supranational statistical institutes (e.g. Eurostat) and national statistical institutes.
Import of goods
Importation and declaration and payment of customs duties is done by the importer of record, which may be the owner of the goods, the purchaser, or a licensed customs broker.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1994 2023-12-13 00:04:09
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1996) Chemical Engineering
Gist
Chemical engineering involves the production and manufacturing of products through chemical processes. This includes designing equipment, systems, and processes for refining raw materials and for mixing, compounding, and processing chemicals.
Summary
Chemical engineering is the development of processes and the design and operation of plants in which materials undergo changes in their physical or chemical state. Applied throughout the process industries, it is founded on the principles of chemistry, physics, and mathematics.
The laws of physical chemistry and physics govern the practicability and efficiency of chemical engineering operations. Energy changes, deriving from thermodynamic considerations, are particularly important. Mathematics is a basic tool in optimization and modeling. Optimization means arranging materials, facilities, and energy to yield as productive and economical an operation as possible. Modeling is the construction of theoretical mathematical prototypes of complex process systems, commonly with the aid of computers.
History
Chemical engineering is as old as the process industries. Its heritage dates from the fermentation and evaporation processes operated by early civilizations. Modern chemical engineering emerged with the development of large-scale, chemical-manufacturing operations in the second half of the 19th century. Throughout its development as an independent discipline, chemical engineering has been directed toward solving problems of designing and operating large plants for continuous production.
Manufacture of chemicals in the mid-19th century consisted of modest craft operations. Increase in demand, public concern at the emission of noxious effluents, and competition between rival processes provided the incentives for greater efficiency. This led to the emergence of combines with resources for larger operations and caused the transition from a craft to a science-based industry. The result was a demand for chemists with knowledge of manufacturing processes, known as industrial chemists or chemical technologists. The term chemical engineer was in general use by about 1900. Despite its emergence in traditional chemicals manufacturing, it was through its role in the development of the petroleum industry that chemical engineering became firmly established as a unique discipline. The demand for plants capable of operating physical separation processes continuously at high levels of efficiency was a challenge that could not be met by the traditional chemist or mechanical engineer.
A landmark in the development of chemical engineering was the publication in 1901 of the first textbook on the subject, by George E. Davis, a British chemical consultant. This concentrated on the design of plant items for specific operations. The notion of a processing plant encompassing a number of operations, such as mixing, evaporation, and filtration, and of these operations being essentially similar, whatever the product, led to the concept of unit operations. This was first enunciated by the American chemical engineer Arthur D. Little in 1915 and formed the basis for a classification of chemical engineering that dominated the subject for the next 40 years. The number of unit operations—the building blocks of a chemical plant—is not large. The complexity arises from the variety of conditions under which the unit operations are conducted.
In the same way that a complex plant can be divided into basic unit operations, so chemical reactions involved in the process industries can be classified into certain groups, or unit processes (e.g., polymerizations, esterifications, and nitrations), having common characteristics. This classification into unit processes brought rationalization to the study of process engineering.
The unit approach suffered from the disadvantage inherent in such classifications: a restricted outlook based on existing practice. Since World War II, closer examination of the fundamental phenomena involved in the various unit operations has shown these to depend on the basic laws of mass transfer, heat transfer, and fluid flow. This has given unity to the diverse unit operations and has led to the development of chemical engineering science in its own right; as a result, many applications have been found in fields outside the traditional chemical industry.
Study of the fundamental phenomena upon which chemical engineering is based has necessitated their description in mathematical form and has led to more sophisticated mathematical techniques. The advent of digital computers has allowed laborious design calculations to be performed rapidly, opening the way to accurate optimization of industrial processes. Variations due to different parameters, such as energy source used, plant layout, and environmental factors, can be predicted accurately and quickly so that the best combination can be chosen.
Chemical engineering functions
Chemical engineers are employed in the design and development of both processes and plant items. In each case, data and predictions often have to be obtained or confirmed with pilot experiments. Plant operation and control is increasingly the sphere of the chemical engineer rather than the chemist. Chemical engineering provides an ideal background for the economic evaluation of new projects and, in the plant construction sector, for marketing.
Branches of chemical engineering
The fundamental principles of chemical engineering underlie the operation of processes extending well beyond the boundaries of the chemical industry, and chemical engineers are employed in a range of operations outside traditional areas. Plastics, polymers, and synthetic fibres involve chemical-reaction engineering problems in their manufacture, with fluid flow and heat transfer considerations dominating their fabrication. The dyeing of a fibre is a mass-transfer problem. Pulp and paper manufacture involve considerations of fluid flow and heat transfer. While the scale and materials are different, these again are found in modern continuous production of foodstuffs. The pharmaceuticals industry presents chemical engineering problems, the solutions of which have been essential to the availability of modern drugs. The nuclear industry makes similar demands on the chemical engineer, particularly for fuel manufacture and reprocessing. Chemical engineers are involved in many sectors of the metals processing industry, which extends from steel manufacture to separation of rare metals.
Further applications of chemical engineering are found in the fuel industries. In the second half of the 20th century, considerable numbers of chemical engineers have been involved in space exploration, from the design of fuel cells to the manufacture of propellants. Looking to the future, it is probable that chemical engineering will provide the solution to at least two of the world’s major problems: supply of adequate fresh water in all regions through desalination of seawater and environmental control through prevention of pollution.
Details
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials into useful products. Chemical engineering uses principles of chemistry, physics, mathematics, biology, and economics to efficiently use, produce, design, transport and transform energy and materials. The work of chemical engineers can range from the utilization of nanotechnology and nanomaterials in the laboratory to large-scale industrial processes that convert chemicals, raw materials, living cells, microorganisms, and energy into useful forms and products. Chemical engineers are involved in many aspects of plant design and operation, including safety and hazard assessments, process design and analysis, modeling, control engineering, chemical reaction engineering, nuclear engineering, biological engineering, construction specification, and operating instructions.
Chemical engineers typically hold a degree in Chemical Engineering or Process Engineering. Practicing engineers may have professional certification and be accredited members of a professional body. Such bodies include the Institution of Chemical Engineers (IChemE) or the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE). A degree in chemical engineering is directly linked with all of the other engineering disciplines, to various extents.
Concepts
Chemical engineering involves the application of several principles. Key concepts are presented below.
Plant design and construction
Chemical engineering design concerns the creation of plans, specifications, and economic analyses for pilot plants, new plants, or plant modifications. Design engineers often work in a consulting role, designing plants to meet clients' needs. Design is limited by several factors, including funding, government regulations, and safety standards. These constraints dictate a plant's choice of process, materials, and equipment.
Plant construction is coordinated by project engineers and project managers, depending on the size of the investment. A chemical engineer may do the job of project engineer full-time or part of the time, which requires additional training and job skills or act as a consultant to the project group. In the USA the education of chemical engineering graduates from the Baccalaureate programs accredited by ABET do not usually stress project engineering education, which can be obtained by specialized training, as electives, or from graduate programs. Project engineering jobs are some of the largest employers for chemical engineers.
Process design and analysis
A unit operation is a physical step in an individual chemical engineering process. Unit operations (such as crystallization, filtration, drying and evaporation) are used to prepare reactants, purifying and separating its products, recycling unspent reactants, and controlling energy transfer in reactors. On the other hand, a unit process is the chemical equivalent of a unit operation. Along with unit operations, unit processes constitute a process operation. Unit processes (such as nitration, hydrogenation, and oxidation involve the conversion of materials by biochemical, thermochemical and other means. Chemical engineers responsible for these are called process engineers.
Process design requires the definition of equipment types and sizes as well as how they are connected and the materials of construction. Details are often printed on a Process Flow Diagram which is used to control the capacity and reliability of a new or existing chemical factory.
Education for chemical engineers in the first college degree 3 or 4 years of study stresses the principles and practices of process design. The same skills are used in existing chemical plants to evaluate the efficiency and make recommendations for improvements.
Transport phenomena
Modeling and analysis of transport phenomena is essential for many industrial applications. Transport phenomena involve fluid dynamics, heat transfer and mass transfer, which are governed mainly by momentum transfer, energy transfer and transport of chemical species, respectively. Models often involve separate considerations for macroscopic, microscopic and molecular level phenomena. Modeling of transport phenomena, therefore, requires an understanding of applied mathematics.
Applications and practice
Chemical engineers "develop economic ways of using materials and energy". Chemical engineers use chemistry and engineering to turn raw materials into usable products, such as medicine, petrochemicals, and plastics on a large-scale, industrial setting. They are also involved in waste management and research. Both applied and research facets could make extensive use of computers.
Chemical engineers may be involved in industry or university research where they are tasked with designing and performing experiments, by scaling up theoretical chemical reactions, to create better and safer methods for production, pollution control, and resource conservation. They may be involved in designing and constructing plants as a project engineer. Chemical engineers serving as project engineers use their knowledge in selecting optimal production methods and plant equipment to minimize costs and maximize safety and profitability. After plant construction, chemical engineering project managers may be involved in equipment upgrades, troubleshooting, and daily operations in either full-time or consulting roles.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1995 2023-12-14 00:03:05
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1997) Export
Gist
Exports are goods and services that are produced in one country and sold to buyers in another. Exports, along with imports, make up international trade.
Summary
Exports are goods and services that are produced in one country and sold to buyers in another. Exports, along with imports, make up international trade. Instead of confining itself within its geographical borders, countries often intentionally seek external markets around the world for commerce, allowing greater revenue and transactional opportunities.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
* Export refers to a product or service produced in one country but sold to a buyer abroad.
* Exports are one of the oldest forms of economic transfer and occur on a large scale between nations.
* Exporting can increase sales and profits if they reach new markets, and they may even present an opportunity to capture significant global market share.
* Companies that export heavily are typically exposed to a higher degree of financial risk.
* In 2021, the world exported nearly $28 trillion of goods and services, led by China ($3.5 trillion of exports).
Understanding Exports
Exports are incredibly important to modern economies because they offer people and firms many more markets for their goods. One of the core functions of diplomacy and foreign policy between governments is to foster economic trade, encouraging exports and imports for the benefit of all trading parties.
Export agreements are often heavily strategic, with countries exchanging agreements to ensure their own country can not only receive the goods they need via export but can distribute goods for more domestic revenue via imports. Also, consider how governments may use exports as leverage over political situations. In response to the war in Ukraine, the White House issued an executive order prohibiting both the importation and exportation of certain goods from Russia.
Companies often measure their net exports which is their total exports minus their total imports. Net exports is a component of measuring a country's gross domestic product (GDP), so exports play a factor in determining a country's financial and economic well-being.
Good may be sent via direct exporting or indirect exporting. Direct exporting entails working directly with the importer. The exporting company will handle all of the client communication; as a result, they do not pay a middleman fee. Because the direct export method may require teams with specialized knowledge, many companies opt to contract out a middle party to facilitate an indirect export.
Details
An export in international trade is a good produced in one country that is sold into another country or a service provided in one country for a national or resident of another country. The seller of such goods or the service provider is an exporter; the foreign buyers is an importer. Services that figure in international trade include financial, accounting and other professional services, tourism, education as well as intellectual property rights.
Exportation of goods often requires the involvement of customs authorities.
Firms
For any firm, Global expansion strategies may include:
* Franchising,
* Turn Key Project,
* Export,
* Joint Venture,
* Licensing,
* Creating an owned subsidiary,
* Acquisition,
* Merger, etc.
Exporting is mostly a strategy used by product based companies. Many manufacturing firms begin their global expansion as exporters and only later switch to another mode for serving a foreign market.
Barriers
There are four main types of export barriers: motivational, informational, operational/resource-based, and knowledge.
Trade barriers are laws, regulations, policy, or practices that protect domestically made products from foreign competition. While restrictive business practices sometimes have a similar effect, they are not usually regarded as trade barriers. The most common foreign trade barriers are government-imposed measures and policies that restrict, prevent, or impede the international exchange of goods and services.
Strategic
International agreements limit trade-in and the transfer of certain types of goods and information, e.g., goods associated with weapons of mass destruction, advanced telecommunications, arms and torture and also some art and archaeological artifacts. For example:
* Nuclear Suppliers Group limits trade in nuclear weapons and associated goods (45 countries participate).
* The Australia Group limits trade in chemical and biological weapons and associated goods (39 countries).
* Missile Technology Control Regime limits trade in the means of delivering weapons of mass destruction (35 countries).
* The Wassenaar Arrangement limits trade in conventional arms and technological developments (40 countries).
Although the outbreak of COVID-19 sufficiently changed the world economy, people started doing business, so international trade is a key for economic growth. Armenia's economy is dependent on international flows, tourism, and inner production. Competitive export Industries were established which helped the growth of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to generate financial resources. The market shifted to more efficient exporters, which is the effect of trade liberalization on aggregate productivity. Due to the increase of the number of international business activities through a multilateral trading system, RA Government Program, which was approved in February 2019, the government policy became the objective of economic growth. The period established for the program was 2019-2024. Export quality is developed by developing the export volumes and services.
Tariffs
Tariffs, a tax on a specific good or category of goods exported from or imported to a country, is an economic barrier to trade. A tariff increases the cost of imported or exported goods, and may be used when domestic producers are having difficulty competing with imports. Tariffs may also be used to protect an industry viewed as being of national security concern. Some industries receive protection that has a similar effect to subsidies; tariffs reduce the industry's incentives to produce goods quicker, cheaper, and more efficiently, becoming ever less competitive.
The third basis for a tariff involves dumping. When a producer exports at a loss, its competitors may term this dumping. Another case is when the exporter prices a good lower in the export market than in its domestic market. The purpose and expected outcome of a tariff is to encourage spending on domestic goods and services rather than their imported equivalents.
Tariffs may create tension between countries, such as the United States steel tariff in 2002, and when China placed a 14% tariff on imported auto parts. Such tariffs may lead to a complaint with the World Trade Organization (WTO) which sets rules and attempts to resolve trade disputes. If that is unsatisfactory, the exporting country may choose to put a tariff of its own on imports from the other country.
Advantages
Exporting avoids the cost of establishing manufacturing operations in the target country.
Exporting may help a company achieve experience curve effects and location economies in their home country. Ownership advantages include the firm's assets, international experience, and the ability to develop either low-cost or differentiated products. The locational advantages of a particular market are a combination of costs, market potential and investment risk. Internationalization advantages are the benefits of retaining a core competence within the company and threading it though the value chain rather than to license, outsource, or sell it.
In relation to the eclectic paradigm, companies with meager ownership advantages do not enter foreign markets. If the company and its products are equipped with ownership advantage and internalization advantage, they enter through low-risk modes such as exporting. Exporting requires significantly less investment than other modes, such as direct investment. Export's lower risk typically reduces the rate of return on sales versus other modes. Exporting allows managers to exercise production control, but does not provide them the option to exercise as much marketing control. An exporter enlists various intermediaries to manage marketing management and marketing activities. Exports also has effect on the Economy. Businesses export goods and services where they have a competitive advantage. This means they are better than any other country at providing that product or have a natural ability to produce either due to their climate or geographical location etc.
Disadvantages
Exporting may not be viable unless appropriate locations can be found abroad.
High transport costs can make exporting uneconomical, particularly for bulk products.
Another drawback is that trade barriers can make exporting uneconomical and risky.
For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with fewer than 250 employees, export is generally more difficult than serving the domestic market. The lack of knowledge of trade regulations, cultural differences, different languages and foreign-exchange situations, as well as the strain of resources and staff, complicate the process. Two-thirds of SME exporters pursue only one foreign market.
Another disadvantage is the dependency on almost unpredictable exchange rates. The depreciation of foreign currency badly affects exporters. For example, Armenia exports different things - from foodstuff to software. In 2022, the country had an enormous number of Russian visitors and tourists because of the military situation in Russia. This resulted in a change in exchange rates and the appreciation of the Armenian dram. At first, it may seem that Armenia’s economy is growing. In fact, the GDP growth is expected to hit 7% by the IMF. However, exporters, who export products and get paid mostly in dollars, suffer because of the depreciation of the dollar against the Armenian dram. Moreover, Armenia’s other exporting bright spot is the IT industry, since a lot of companies and individuals work for US-based companies and get paid in US dollars. Because of the drastic change in the exchange rates, these people and companies who export their service to the US or other countries and get paid in US dollars, make around 25% less revenue.
Exports could also devalue a local currency to lower export prices. It could also lead to imposition of tariffs on imported goods.
Motivations
The variety of export motivators can lead to selection bias. Size, knowledge of foreign markets, and unsolicited orders motivate firms to along specific dimensions (research, external, reactive).
Macroeconomics
In macroeconomics, net exports (exports minus imports) are a component of gross domestic product, along with domestic consumption, physical investment, and government spending. Foreign demand for a country's exports depends positively on income in foreign countries and negatively on the strength of the producing country's currency (i.e., on how expensive it is for foreign customers to buy the producing country's currency in the foreign exchange market).
Additional Information
Exports are the goods and services that a country produces domestically, or within the borders of its own country, and sells to buyers in a foreign country. The opposite of exports are imports, which are goods and services that buyers in a country purchase from sellers in a foreign country. Exports and imports are components of international trade, which is the exchange of goods and services between countries. Trade barriers such as tariffs, taxes on imports, and subsidies, funding given to domestic businesses, can affect a country's flow of exports.
A country's trade balance is the difference between the values of its exports and imports. In macroeconomics, which is the study of global economies, the value of a country's exports minus its imports is its gross domestic product (GDP). If a country's exports outweigh its imports, it has a trade surplus. If its imports outweigh its exports, it has a trade deficit. A country's GDP or trade balance can measure the fiscal health of a country because it represents the value of a country's goods and services produced in a certain time period.
Typically, a country has a competitive advantage on its exports. This means that it has the natural ability to produce certain goods and services in a high quality and quantity, often based on its climate and geographic region. For example, because of the tropical climate of Brazil, its largest export is sugarcane.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1996 2023-12-15 00:07:58
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1998) Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
Gist
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid found in cold-water, fatty fish, such as salmon. It is also found in fish oil supplements, along with eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Vegetarian sources of DHA come from seaweed.
Summary
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that is found along with eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in cold-water fish, including tuna and salmon.
DHA plays a key role in the development of eye and nerve tissues. DHA might also reduce the risk of heart and circulatory disease by decreasing the thickness of the blood, reducing swelling (inflammation), and lowering blood levels of triglycerides.
People commonly use DHA for high levels of cholesterol or other fats in the blood. It is also used for boosting memory and thinking skills, for helping infant and child development, for certain eye disorders, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support many of these uses.
Don't confuse DHA with EPA. They are both in fish oil, but they are not the same. DHA can be converted into EPA in the body in very small amounts.
Details
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a primary structural component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina. In physiological literature, it is given the name 22:6(n-3). It can be synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid or obtained directly from maternal milk (breast milk), fatty fish, fish oil, or algae oil.
DHA's structure is a carboxylic acid (-oic acid) with a 22-carbon chain (docosa- derives from the Ancient Greek for 22) and six (hexa-) cis double bonds (-en-); with the first double bond located at the third carbon from the omega end. Its trivial name is cervonic acid (from the Latin word cerebrum for "brain"), its systematic name is all-cis-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexa-enoic acid, and its shorthand name is 22:6(n−3) in the nomenclature of fatty acids.
Most of the docosahexaenoic acid in fish and multi-cellular organisms with access to cold-water oceanic foods originates from photosynthetic and heterotrophic microalgae, and becomes increasingly concentrated in organisms the further they are up the food chain. DHA is also commercially manufactured from microalgae: Crypthecodinium cohnii and another of the genus Schizochytrium.
In organisms that do not eat algae containing DHA nor animal products containing DHA, DHA is instead produced internally from α-linolenic acid, a shorter omega-3 fatty acid manufactured by plants (and also occurring in animal products as obtained from plants). Limited amounts of eicosapentaenoic and docosapentaenoic acids are possible products of α-linolenic acid metabolism in young women and men. DHA in breast milk is important for the developing infant. Rates of DHA production in women are 15% higher than in men.
DHA is a major fatty acid in brain phospholipids and the retina. Research into the potential role or benefit of DHA in various pathologies is ongoing, with significant focus on its mechanism in Alzheimer's disease and cardiovascular disease.
Central nervous system constituent
DHA is the most abundant omega-3 fatty acid in the brain and retina. DHA comprises 40% of the polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in the brain and 60% of the PUFAs in the retina. Fifty percent of a neuronal plasma membrane is composed of DHA. DHA modulates the carrier-mediated transport of choline, glycine, and taurine, the function of delayed rectifier potassium channels, and the response of rhodopsin contained in the synaptic vesicles.
Phosphatidylserine (PS) – which contains high DHA content – has roles in neuronal signaling and neurotransmitter synthesis, and DHA deficiency is associated with cognitive decline. DHA levels are reduced in the brain tissue of severely depressed people.
Metabolic synthesis
In humans, DHA is either obtained from the diet or may be converted in small amounts from eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, 20:5, ω-3) via docosapentaenoic acid (DPA, 22:5 ω-3) as an intermediate. This synthesis had been thought to occur through an elongation step followed by the action of Δ4-desaturase. It is now considered more likely that DHA is biosynthesized via a C24 intermediate followed by beta oxidation in peroxisomes. Thus, EPA is twice elongated, yielding 24:5 ω-3, then desaturated to 24:6 ω-3, then shortened to DHA (22:6 ω-3) via beta oxidation. This pathway is known as "Sprecher's shunt".
In organisms such as microalgae, mosses and fungi, biosynthesis of DHA usually occurs as a series of desaturation and elongation reactions, catalyzed by the sequential action of desaturase and elongase enzymes. One known pathway in these organisms involves:
* a desaturation at the sixth carbon of alpha-linolenic acid by a Δ6 desaturase to produce stearidonic acid,
elongation of the stearidonic acid by a Δ6 elongase to produce to eicosatetraenoic acid,
* desaturation at the fifth carbon of eicosatetraenoic acid by a Δ5 desaturase to produce eicosapentaenoic acid,
elongation of eicosapentaenoic acid by a Δ5 elongase to produce docosapentaenoic acid, and
* desaturation at the fourth carbon of docosapentaenoic acid by a Δ4 desaturase to produce DHA.[20]
Metabolism
DHA can be metabolized into DHA-derived specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs), DHA epoxides, electrophilic oxo-derivatives (EFOX) of DHA, neuroprostanes, ethanolamines, acylglycerols, docosahexaenoyl amides of amino acids or neurotransmitters, and branched DHA esters of hydroxy fatty acids, among others.
The enzyme CYP2C9 metabolizes DHA to epoxydocosapentaenoic acids (EDPs; primarily 19,20-epoxy-eicosapentaenoic acid isomers [i.e. 10,11-EDPs]).
Additional Information
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is essential for the growth and functional development of the brain in infants. DHA is also required for maintenance of normal brain function in adults. The inclusion of plentiful DHA in the diet improves learning ability, whereas deficiencies of DHA are associated with deficits in learning. DHA is taken up by the brain in preference to other fatty acids. The turnover of DHA in the brain is very fast, more so than is generally realized. The visual acuity of healthy, full-term, formula-fed infants is increased when their formula includes DHA. During the last 50 years, many infants have been fed formula diets lacking DHA and other omega-3 fatty acids. DHA deficiencies are associated with foetal alcohol syndrome, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, cystic fibrosis, phenylketonuria, unipolar depression, aggressive hostility, and adrenoleukodystrophy. Decreases in DHA in the brain are associated with cognitive decline during aging and with onset of sporadic Alzheimer disease. The leading cause of death in western nations is cardiovascular disease. Epidemiological studies have shown a strong correlation between fish consumption and reduction in sudden death from myocardial infarction. The reduction is approximately 50% with 200 mg day(-1)of DHA from fish. DHA is the active component in fish. Not only does fish oil reduce triglycerides in the blood and decrease thrombosis, but it also prevents cardiac arrhythmias. The association of DHA deficiency with depression is the reason for the robust positive correlation between depression and myocardial infarction. Patients with cardiovascular disease or Type II diabetes are often advised to adopt a low-fat diet with a high proportion of carbohydrate. A study with women shows that this type of diet increases plasma triglycerides and the severity of Type II diabetes and coronary heart disease. DHA is present in fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel) and mother's milk. DHA is present at low levels in meat and eggs, but is not usually present in infant formulas. EPA, another long-chain n-3 fatty acid, is also present in fatty fish. The shorter chain n-3 fatty acid, alpha-linolenic acid, is not converted very well to DHA in man. These longchain n-3 fatty acids (also known as omega-3 fatty acids) are now becoming available in some foods, especially infant formula and eggs in Europe and Japan. Fish oil decreases the proliferation of tumour cells, whereas arachidonic acid, a longchain n-6 fatty acid, increases their proliferation. These opposite effects are also seen with inflammation, particularly with rheumatoid arthritis, and with asthma. DHA has a positive effect on diseases such as hypertension, arthritis, atherosclerosis, depression, adult-onset diabetes mellitus, myocardial infarction, thrombosis, and some cancers.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1997 2023-12-16 00:03:08
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
1999) Relational Database Management System
Gist
RDBMS stands for Relational Database Management System. RDBMS is a program used to maintain a relational database. RDBMS is the basis for all modern database systems such as MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and Microsoft Access. RDBMS uses SQL queries to access the data in the database.
Summary
A relational database is a (most commonly digital) database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and updating the database.
History
The term "relational database" was first defined by E. F. Codd at IBM in 1970. Codd introduced the term in his research paper "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks". In this paper and later papers, he defined what he meant by "relational". One well-known definition of what constitutes a relational database system is composed of Codd's 12 rules. However, no commercial implementations of the relational model conform to all of Codd's rules, so the term has gradually come to describe a broader class of database systems, which at a minimum:
* Present the data to the user as relations (a presentation in tabular form, i.e. as a collection of tables with each table consisting of a set of rows and columns);
* Provide relational operators to manipulate the data in tabular form.
In 1974, IBM began developing System R, a research project to develop a prototype RDBMS. The first system sold as an RDBMS was Multics Relational Data Store (June 1976). Oracle was released in 1979 by Relational Software, now Oracle Corporation. Ingres and IBM BS12 followed. Other examples of an RDBMS include IBM Db2, SAP Sybase ASE, and Informix. In 1984, the first RDBMS for Macintosh began being developed, code-named Silver Surfer, and was released in 1987 as 4th Dimension and known today as 4D.
The first systems that were relatively faithful implementations of the relational model were from:
* University of Michigan – Micro DBMS (1969)
* Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1971)
* IBM UK Scientific Centre at Peterlee – IS1 (1970–72) and its successor, PRTV (1973–79)
The most common definition of an RDBMS is a product that presents a view of data as a collection of rows and columns, even if it is not based strictly upon relational theory. By this definition, RDBMS products typically implement some but not all of Codd's 12 rules.
A second school of thought argues that if a database does not implement all of Codd's rules (or the current understanding on the relational model, as expressed by Christopher J. Date, Hugh Darwen and others), it is not relational. This view, shared by many theorists and other strict adherents to Codd's principles, would disqualify most DBMSs as not relational. For clarification, they often refer to some RDBMSs as truly-relational database management systems (TRDBMS), naming others pseudo-relational database management systems (PRDBMS).
As of 2009, most commercial relational DBMSs employ SQL as their query language.
Alternative query languages have been proposed and implemented, notably the pre-1996 implementation of Ingres QUEL.
Relational model
A relational model organizes data into one or more tables (or "relations") of columns and rows, with a unique key identifying each row. Rows are also called records or tuples. Columns are also called attributes. Generally, each table/relation represents one "entity type" (such as customer or product). The rows represent instances of that type of entity (such as "Lee" or "chair") and the columns represent values attributed to that instance (such as address or price).
For example, each row of a class table corresponds to a class, and a class corresponds to multiple students, so the relationship between the class table and the student table is "one to many".
Keys
Each row in a table has its own unique key. Rows in a table can be linked to rows in other tables by adding a column for the unique key of the linked row (such columns are known as foreign keys). Codd showed that data relationships of arbitrary complexity can be represented by a simple set of concepts.
Part of this processing involves consistently being able to select or modify one and only one row in a table. Therefore, most physical implementations have a unique primary key (PK) for each row in a table. When a new row is written to the table, a new unique value for the primary key is generated; this is the key that the system uses primarily for accessing the table. System performance is optimized for PKs. Other, more natural keys may also be identified and defined as alternate keys (AK). Often several columns are needed to form an AK (this is one reason why a single integer column is usually made the PK). Both PKs and AKs have the ability to uniquely identify a row within a table. Additional technology may be applied to ensure a unique ID across the world, a globally unique identifier, when there are broader system requirements.
The primary keys within a database are used to define the relationships among the tables. When a PK migrates to another table, it becomes a foreign key in the other table. When each cell can contain only one value and the PK migrates into a regular entity table, this design pattern can represent either a one-to-one or one-to-many relationship. Most relational database designs resolve many-to-many relationships by creating an additional table that contains the PKs from both of the other entity tables – the relationship becomes an entity; the resolution table is then named appropriately and the two FKs are combined to form a PK. The migration of PKs to other tables is the second major reason why system-assigned integers are used normally as PKs; there is usually neither efficiency nor clarity in migrating a bunch of other types of columns.
Relationships
Relationships are a logical connection between different tables (entities), established on the basis of interaction among these tables. These relationships can be modelled as an entity-relationship model.
Details
A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a collection of programs and capabilities that enable IT teams and others to create, update, administer and otherwise interact with a relational database. RDBMSes store data in the form of tables, with most commercial relational database management systems using Structured Query Language (SQL) to access the database. However, since SQL was invented after the initial development of the relational model, it is not necessary for RDBMS use.
The RDBMS is the most popular database system among organizations across the world. It provides a dependable method of storing and retrieving large amounts of data while offering a combination of system performance and ease of implementation.
RDBMS vs. DBMS
In general, databases store sets of data that can be queried for use in other applications. A database management system supports the development, administration and use of database platforms.
An RDBMS is a type of database management system (DBMS) that stores data in a row-based table structure which connects related data elements. An RDBMS includes functions that maintain the security, accuracy, integrity and consistency of the data. This is different than the file storage used in a DBMS.
Other differences between database management systems and relational database management systems include:
* Number of allowed users. While a DBMS can only accept one user at a time, an RDBMS can operate with multiple users.
* Hardware and software requirements. A DBMS needs less software and hardware than an RDBMS.
* Amount of data. RDBMSes can handle any amount of data, from small to large, while a DBMS can only manage small amounts.
* Database structure. In a DBMS, data is kept in a hierarchical form, whereas an RDBMS utilizes a table where the headers are used as column names and the rows contain the corresponding values.
* ACID implementation. DBMSes do not use the atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability (ACID) model for storing data. On the other hand, RDBMSes base the structure of their data on the ACID model to ensure consistency.
* Distributed databases. While an RDBMS offers complete support for distributed databases, a DBMS will not provide support.
* Types of programs managed. While an RDBMS helps manage the relationships between its incorporated tables of data, a DBMS focuses on maintaining databases that are present within the computer network and system hard disks.
* Support of database normalization. An RDBMS can be normalized, but a DBMS cannot.
Key differences between a DBMS and an RDBMS
Features of relational database management systems
Elements of the relational database management system that overarch the basic relational database are so intrinsic to operations that it is hard to dissociate the two in practice.
The most basic RDBMS functions are related to create, read, update and delete operations -- collectively known as CRUD. They form the foundation of a well-organized system that promotes consistent treatment of data.
The RDBMS typically provides data dictionaries and metadata collections that are useful in data handling. These programmatically support well-defined data structures and relationships. Data storage management is a common capability of the RDBMS, and this has come to be defined by data objects that range from binary large object -- or blob -- strings to stored procedures. Data objects like this extend the scope of basic relational database operations and can be handled in a variety of ways in different RDBMSes.
The most common means of data access for the RDBMS is SQL. Its main language components comprise data manipulation language and data definition language statements. Extensions are available for development efforts that pair SQL use with common programming languages, such as the Common Business-Oriented Language (COBOL), Java and .NET.
RDBMSes use complex algorithms that support multiple concurrent user access to the database while maintaining data integrity. Security management, which enforces policy-based access, is yet another overlay service that the RDBMS provides for the basic database as it is used in enterprise settings.
RDBMSes support the work of database administrators (DBAs) who must manage and monitor database activity. Utilities help automate data loading and database backup. RDBMSes manage log files that track system performance based on selected operational parameters. This enables measurement of database usage, capacity and performance, particularly query performance. RDBMSes provide graphical interfaces that help DBAs visualize database activity.
While not limited solely to the RDBMS, ACID compliance is an attribute of relational technology that has proved important in enterprise computing. These capabilities have particularly suited RDBMSes for handling business transactions.
As RDBMSes have matured, they have achieved increasingly higher levels of query optimization, and they have become key parts of reporting, analytics and data warehousing applications for businesses as well. RDBMSes are intrinsic to operations of a variety of enterprise applications and are at the center of most master data management systems.
How RDBMS works
As mentioned before, an RDBMS will store data in the form of a table. Each system will have varying numbers of tables with each table possessing its own unique primary key. The primary key is then used to identify each table.
Within the table are rows and columns. The rows are known as records or horizontal entities; they contain the information for the individual entry. The columns are known as vertical entities and possess information about the specific field.
Before creating these tables, the RDBMS must check the following constraints:
* Primary keys -- this identifies each row in the table. One table can only contain one primary key. The key must be unique and without null values.
* Foreign keys -- this is used to link two tables. The foreign key is kept in one table and refers to the primary key associated with another table.
* Not null -- this ensures that every column does not have a null value, such as an empty cell.
* Check -- this confirms that each entry in a column or row satisfies a precise condition and that every column holds unique data.
* Data integrity -- the integrity of the data must be confirmed before the data is created.
Assuring the integrity of data includes several specific tests, including entity, domain, referential and user-defined integrity. Entity integrity confirms that the rows are not duplicated in the table. Domain integrity makes sure that data is entered into the table based on specific conditions, such as file format or range of values. Referential integrity ensures that any row that is re-linked to a different table cannot be deleted. Finally, user-defined integrity confirms that the table will satisfy all user-defined conditions.
Advantages of relational database management system
The use of an RDBMS can be beneficial to most organizations; the systematic view of raw data helps companies better understand and execute the information while enhancing the decision-making process. The use of tables to store data also improves the security of information stored in the databases. Users are able to customize access and set barriers to limit the content that is made available. This feature makes the RDBMS particularly useful to companies in which the manager decides what data is provided to employees and customers.
Furthermore, RDBMSes make it easy to add new data to the system or alter existing tables while ensuring consistency with the previously available content.
Other advantages of the RDBMS include:
* Flexibility -- updating data is more efficient since the changes only need to be made in one place.
* Maintenance -- database administrators can easily maintain, control and update data in the database. Backups also become easier since automation tools included in the RDBMS automate these tasks.
* Data structure -- the table format used in RDBMSes is easy to understand and provides an organized and structural manner through which entries are matched by firing queries.
On the other hand, relational database management systems do not come without their disadvantages. For example, in order to implement an RDBMS, special software must be purchased. This introduces an additional cost for execution. Once the software is obtained, the setup process can be tedious since it requires millions of lines of content to be transferred into the RDBMS tables. This process may require the additional help of a programmer or a team of data entry specialists. Special attention must be paid to the data during entry to ensure sensitive information is not placed into the wrong hands.
Some other drawbacks of the RDBMS include the character limit placed on certain fields in the tables and the inability to fully understand new forms of data -- such as complex numbers, designs and images.
Furthermore, while isolated databases can be created using an RDBMS, the process requires large chunks of information to be separated from each other. Connecting these large amounts of data to form the isolated database can be very complicated.
Uses of RDBMS
Relational database management systems are frequently used in disciplines such as manufacturing, human resources and banking. The system is also useful for airlines that need to store ticket service and passenger documentation information as well as universities maintaining student databases.
Some examples of specific systems that use RDBMS include IBM, Oracle, MySQL, Microsoft SQLServer and PostgreSQL.
RDBMS product history
Many vying relational database management systems arose as news spread in the early 1970s of the relational data model. This and related methods were originally theorized by IBM researcher E.F. Codd, who proposed a database schema, or logical organization, that was not directly associated with physical organization, as was common at the time.
Codd's work was based around a concept of data normalization, which saved file space on storage disk drives at a time when such machinery could be prohibitively expensive for businesses.
File systems and database management systems preceded what could be called the RDBMS era. Such systems ran primarily on mainframe computers. While RDBMSes also ran on mainframes -- IBM's DB2 being a pointed example -- much of their ascendance in the enterprise was in UNIX midrange computer deployments. The RDBMS was a linchpin in the distributed architecture of client-server computing, which connected pools of stand-alone personal computers to file and database servers.
Numerous RDBMSes arose along with the use of client-server computing. Among the competitors were Oracle, Ingres, Informix, Sybase, Unify, Progress and others. Over time, three RDBMSes came to dominate in commercial implementations. Oracle, IBM's DB2 and Microsoft's SQL Server, which was based on a design originally licensed from Sybase, found considerable favor throughout the client-server computing era, despite repeated challenges by competing technologies.
As the 20th century drew to an end, lower-cost, open source versions of RDBMSes began to find use, particularly in web applications.
Eventually, as distributed computing took greater hold, and as cloud architecture became more prominently employed, RDBMSes met competition in the form of NoSQL systems. Such systems were often specifically designed for massive distribution and high scalability in the cloud, sometimes forgoing SQL-style full consistency for so-called eventual consistency of data. But, even in the most diverse and complex cloud systems, the need for some guaranteed data consistency requires RDBMSes to appear in some way, shape or form. Moreover, versions of RDBMSes have been significantly restructured for cloud parallelization and replication.
It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1998 2023-12-17 00:02:28
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
2000) Talc
Gist
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate, with the chemical formula Mg 3Si 4O 10(OH)2.
Summary
Talc, common silicate mineral that is distinguished from almost all other minerals by its extreme softness (it has the lowest rating on the Mohs scale of hardness). Its soapy or greasy feel accounts for the name soapstone given to compact aggregates of talc and other rock-forming minerals. Dense aggregates of high-purity talc are called steatite.
Since ancient times, soapstones have been employed for carvings, ornaments, and utensils; Assyrian cylinder seals, Egyptian scarabs, and Chinese statuary are notable examples. Soapstones are resistant to most reagents and to moderate heat; thus, they are especially suitable for sinks and countertops. Talc is also used in lubricants, leather dressings, toilet and dusting powders, and certain marking pencils. It is used as a filler in ceramics, paint, paper, roofing materials, plastic, and rubber; as a carrier in insecticides; and as a mild abrasive in the polishing of cereal grains such as rice and corn.
Talc is found as a metamorphic mineral in veins, in foliated masses, and in certain rocks. It is often associated with serpentine, tremolite, forsterite, and almost always with carbonates (calcite, dolomite, or magnesite) in the lower metamorphic facies. It also occurs as an alteration product, as from tremolite or forsterite.
One of the remarkable features of talc is its simple, almost constant composition; talc is a basic magnesium silicate, Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Unlike other silicates, even closely related ones, talc appears to be unable to accept iron or aluminum into its structure to form chemical-replacement series, even though an iron analog of talc is known, and the structurally related chlorite forms at least a partial series between iron and magnesium end-members. Talc is distinguishable from pyrophyllite chemically and optically.
Details
Talc, or talcum, is a clay mineral composed of hydrated magnesium silicate, with the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thickening agent and lubricant. It is an ingredient in ceramics, paints, and roofing material. It is a main ingredient in many cosmetics. It occurs as foliated to fibrous masses, and in an exceptionally rare crystal form. It has a perfect basal cleavage and an uneven flat fracture, and it is foliated with a two-dimensional platy form.
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 1 as the hardness of talc, the softest mineral. When scraped on a streak plate, talc produces a white streak; though this indicator is of little importance, because most silicate minerals produce a white streak. Talc is translucent to opaque, with colors ranging from whitish grey to green with a vitreous and pearly luster. Talc is not soluble in water, and is slightly soluble in dilute mineral acids.
Soapstone is a metamorphic rock composed predominantly of talc.
Talc is also found as a diagenetic mineral in sedimentary rocks where it can form from the transformation of metastable hydrated magnesium-clay precursors such as kerolite, sepiolite, or stevensite that can precipitate from marine and lake water in certain conditions.
In this reaction, the ratio of talc and kyanite depends on aluminium content, with more aluminous rocks favoring production of kyanite. This is typically associated with high-pressure, low-temperature minerals such as phengite, garnet, and glaucophane within the lower blueschist facies. Such rocks are typically white, friable, and fibrous, and are known as whiteschist.
Talc is a trioctahedral layered mineral; its structure is similar to pyrophyllite, but with magnesium in the octahedral sites of the composite layers. The crystal structure of talc is described as TOT, meaning that it is composed of parallel TOT layers weakly bonded to each other by weak van der Waals forces. The TOT layers in turn consist of two tetrahedral sheets (T) strongly bonded to the two faces of a single trioctahedral sheet (O). It is the weak bonding between TOT layers that gives talc its perfect basal cleavage and softness.
The tetrahedral sheets consist of silica tetrahedra, which are silicon ions surrounded by four oxygen ions. The tetrahedra each share three of their four oxygen ions with neighboring tetrahedra to produce a hexagonal sheet. The remaining oxygen ion (the apical oxygen ion) is available to bond with the trioctahedral sheet.
The trioctahedral sheet has the structure of a sheet of the mineral brucite. Apical oxygens take the place of some of the hydroxyl ions that would be present in a brucite sheet, bonding the tetrahedral sheets tightly to the trioctahedral sheet.
Tetrahedral sheets have a negative charge, since their bulk composition is Si4O104-. The trioctahedral sheet has an equal positive charge, since its bulk composition is Mg3(OH)24+ The combined TOT layer thus is electrically neutral.
Because the hexagons in the T and O sheets are slightly different in size, the sheets are slightly distorted when they bond into a TOT layer. This breaks the hexagonal symmetry and reduces it to monoclinic or triclinic symmetry. However, the original hexahedral symmetry is discernible in the pseudotrigonal character of talc crystals.
Occurrence
Talc is a common metamorphic mineral in metamorphic belts that contain ultramafic rocks, such as soapstone (a high-talc rock), and within whiteschist and blueschist metamorphic terranes. Prime examples of whiteschists include the Franciscan Metamorphic Belt of the western United States, the western European Alps especially in Italy, certain areas of the Musgrave Block, and some collisional orogens such as the Himalayas, which stretch along Pakistan, India, Nepal, and Bhutan.
Talc carbonate ultramafics are typical of many areas of the Archaean cratons, notably the komatiite belts of the Yilgarn Craton in Western Australia. Talc-carbonate ultramafics are also known from the Lachlan Fold Belt, eastern Australia, from Brazil, the Guiana Shield, and from the ophiolite belts of Turkey, Oman, and the Middle East.
China is the key world talc and steatite-producing country with an output of about 2.2M tonnes(2016), which accounts for 30% of total global output. The other major producers are Brazil (12%), India (11%), the U.S. (9%), France (6%), Finland (4%), Italy, Russia, Canada, and Austria (2%, each).
Notable economic talc occurrences include the Mount Seabrook talc mine, Western Australia, formed upon a polydeformed, layered ultramafic intrusion. The France-based Luzenac Group is the world's largest supplier of mined talc. Its largest talc mine at Trimouns near Luzenac in southern France produces 400,000 tonnes of talc per year.
Uses
The structure of talc is composed of Si2O5 sheets with magnesium sandwiched between sheets in octahedral sites.
Talc is used in many industries, including paper making, plastic, paint and coatings (e.g. for metal casting molds), rubber, food, electric cable, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and ceramics. A coarse grayish-green high-talc rock is soapstone or steatite, used for stoves, sinks, electrical switchboards, etc. It is often used for surfaces of laboratory table tops and electrical switchboards because of its resistance to heat, electricity, and acids.
In finely ground form, talc finds use as a cosmetic (talcum powder), as a lubricant, and as a filler in paper manufacture. It is used to coat the insides of inner tubes and rubber gloves during manufacture to keep the surfaces from sticking. Talcum powder, with heavy refinement, has been used in baby powder, an astringent powder used to prevent diaper rash (nappy rash). The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that parents avoid using baby powder because it poses a risk of respiratory problems, including breathing trouble and serious lung damage if inhaled. The small size of the particles makes it difficult to keep them out of the air while applying the powder. Zinc oxide-based ointments are a much safer alternative.
Soapstone (massive talc) is often used as a marker for welding or metalworking.
Talc is also used as food additive or in pharmaceutical products as a glidant. In medicine, talc is used as a pleurodesis agent to prevent recurrent pleural effusion or pneumothorax. In the European Union, the additive number is E553b.
Talc may be used in the processing of white rice as a buffing agent in the polishing stage.
Due to its low shear strength, talc is one of the oldest known solid lubricants. Also, limited use is made of talc as a friction-reducing additive in lubricating oils.
Talc is widely used in the ceramics industry in both bodies and glazes. In low-fire art-ware bodies, it imparts whiteness and increases thermal expansion to resist crazing. In stonewares, small percentages of talc are used to flux the body and therefore improve strength and vitrification. It is a source of MgO flux in high-temperature glazes (to control melting temperature). It is also employed as a matting agent in earthenware glazes and can be used to produce magnesia mattes at high temperatures.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#1999 2023-12-17 23:14:21
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
2001) Gums
Gist
Your gums (gingivae) are tissues that surround the base of your teeth and help keep them in place. It’s important to protect your gums from periodontal disease that can damage your gums, leading to tooth and bone loss. Good oral hygiene, like brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily and seeing a dentist twice a year, is the best way to have healthy gums.
Summary
Gum, in anatomy, is connective tissue covered with mucous membrane, attached to and surrounding the necks of the teeth and adjacent alveolar bone. Before the erupting teeth enter the mouth cavity, gum pads develop; these are slight elevations of the overlying oral mucous membrane. When tooth eruption is complete, the gum embraces the neck region of each tooth. As well as being attached to adjacent alveolar bone, gum is connected to the cement of each tooth and to the tooth enamel.
Healthy gums are pink, stippled, and tough and have a limited sensibility to pain, temperature, and pressure. The gums are separated from the alveolar mucosa, which is red, by a scalloped line that approximately follows the contours of the teeth. The edges of the gums around the teeth are free and extend as small wedges into the spaces between the teeth (interdental papillae). Internally, fibres of the periodontal membrane enter the gum and hold it tightly against the teeth. Changes in colour, loss of stippling, or abnormal sensitivity are early signs of gum inflammation, or gingivitis (q.v.).
Details
When you think about dental health, the focus is likely to be on preventing cavities in your teeth. But it's important to pay attention to your gums, too. Gums play a major role not only in your dental health, but in your overall well-being.
In many instances, swollen and bleeding gums are a sign of gum disease. However, there are a number of other things that could be causing your gum problems. Whatever the cause of sore, painful gums, there are steps you can take to minimize gum damage and discomfort.
Gums and Brushing Technique
In the quest to keep teeth clean, you might be tempted to brush teeth as vigorously as you can. Gums are made of delicate tissue, though, so brushing the wrong way could damage them.
Whether you opt for a manual or electric toothbrush, choose one with soft nylon bristles that have blunted ends. Even though you can find brushes with medium or hard bristles, they may damage the enamel on your teeth or cause red and swollen gums.
When you brush, make sure you use gentle, circular motions to massage and clean the teeth and gums. While many people use a back-and-forth motion, this motion can irritate and damage your gums, making them sore and more likely to bleed or recede.
Gums and Flossing Technique
We all know the importance of flossing every day to help remove plaque from places where your toothbrush can't reach. To make sure that your healthy habit isn't causing swollen or bleeding gums, be gentle when you floss. Rather than forcing the floss between your teeth, carefully slide it up and down, following the curve of each tooth.
Gum Disease
According to the CDC, 47.2% of Americans 30 and older have some form of periodontal (gum) disease. While most people with gum disease have the less severe form, called gingivitis, between 5% and 15% have a much more serious type of gum disease known as periodontitis.
When people don't practice proper dental hygiene, bacteria in the mouth forms plaque on the teeth. These bacteria may cause your gums to become inflamed, which results in red, swollen, or bleeding gums. For many people with gingivitis, this inflammation is not painful. If you catch gingivitis early, it can be reversed and healed with proper oral hygiene. But left untreated, gingivitis can worsen and ultimately lead to tooth loss. Be sure to seek medical attention if you have the following symptoms, even if you don't have any discomfort:
* changes in the way teeth fit together on biting, or in the fit of partial dentures
* formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
* gums that bleed during and after toothbrushing
* loose or shifting teeth
* persistent bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
* receding gums
* red, swollen, or tender gums
When gingivitis progresses, it develops into periodontitis, a condition in which the gums and bone that hold the teeth in place can be severely weakened. The bacteria on the teeth release toxic substances that harm your gums and cause them to become infected. The infection and the inflammation that result when your body attacks the bacteria can degrade your gums and the bone in your jaw even further. You may have exceptionally swollen, painful gums that are likely to bleed. If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth loss.
Gums and Canker Sores
Common culprits behind painful gums are canker sores, or mouth ulcers. These painful sores can develop anywhere inside the mouth, including on the gums, and often have a whitish center with red edges. You may have one canker sore at a time, making only one area on your gums sore, or you may have multiple sores at the same time throughout your mouth.
While researchers don't know what causes canker sores, there may be bacterial or viral involvement. People with certain autoimmune diseases may also be more likely to have gum problems caused by canker sores. Canker sores often come back over time and are not contagious.
Gums and Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can have a number of unpleasant side effects, including painful, swollen, and bleeding gums. Many people undergoing treatment for cancer contend with stomatitis, which causes the development of painful sores and ulcers on the gums and throughout the mouth.
Gums and Tobacco Products
Using cigarettes and other tobacco products can be extremely damaging to your gums. People who smoke are far more likely to develop gum disease. You may find that your smoking habit gives you a number of gum problems, from sensitive gums that bleed to painful sores.
Gums and Hormones
Some women find they have gum problems during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. The rise in hormones during puberty can heighten blood flow to the gums, making them red, swollen, and sensitive. For women with menstrual gingivitis, the gums become red, swollen, and more likely to bleed shortly before each menstrual period. These problems typically subside after the period begins. Pregnancy gingivitis typically starts in the second or third month of pregnancy and continues through the eighth month, causing sore, swollen, and bleeding gums. The use of oral birth control products may cause similar gum problems. Though uncommon, some women going through menopause may find that their gums become extremely dry and therefore sore and likely to bleed.
Additional Information
The gums or gingiva (pl.: gingivae) consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation.
Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, both in health and disease. When gum tissue is not healthy, it can provide a gateway for periodontal disease to advance into the deeper tissue of the periodontium, leading to a poorer prognosis for long-term retention of the teeth. Both the type of periodontal therapy and homecare instructions given to patients by dental professionals and restorative care are based on the clinical conditions of the tissue.
The gums are divided anatomically into marginal, attached and interdental areas.
Marginal gums
The marginal gum is the edge of the gums surrounding the teeth in collar-like fashion. In about half of individuals, it is demarcated from the adjacent, attached gums by a shallow linear depression, the free gingival groove. This slight depression on the outer surface of the gum does not correspond to the depth of the gingival sulcus but instead to the apical border of the junctional epithelium. This outer groove varies in depth according to the area of the oral cavity. The groove is very prominent on mandibular anteriors and premolars.
The marginal gum varies in width from 0.5 to 2.0 mm from the free gingival crest to the attached gingiva. The marginal gingiva follows the scalloped pattern established by the contour of the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) of the teeth. The marginal gingiva has a more translucent appearance than the attached gingiva, yet has a similar clinical appearance, including pinkness, dullness, and firmness. In contrast, the marginal gingiva lacks the presence of stippling, and the tissue is mobile or free from the underlying tooth surface, as can be demonstrated with a periodontal probe. The marginal gingiva is stabilized by the gingival fibers that have no bony support. The gingival margin, or free gingival crest, at the most superficial part of the marginal gingiva, is also easily seen clinically, and its location should be recorded on a patient's chart.
Attached gum
The attached gums are continuous with the marginal gum. It is firm, resilient, and tightly bound to the underlying periosteum of alveolar bone. The facial aspect of the attached gum extends to the relatively loose and movable alveolar mucosa, from which it is demarcated by the mucogingival junction. Attached gum may present with surface stippling. The tissue when dried is dull, firm, and immobile, with varying amounts of stippling. The width of the attached gum varies according to its location. The width of the attached gum on the facial aspect differs in different areas of the mouth. It is generally greatest in the incisor region (3.5 to 4.5 mm in the maxilla and 3.3 to 3.9 mm in the mandible) and less in the posterior segments, with the least width in the first premolar area (1.9 mm in the maxilla and 1.8 mm in the mandible). However, certain levels of attached gum may be necessary for the stability of the underlying root of the tooth.
Interdental gum
The interdental gum lies between the teeth. They occupy the gingival embrasure, which is the interproximal space beneath the area of tooth contact. The interdental papilla can be pyramidal or have a "col" shape. Attached gums are resistant to the forces of chewing and covered in keratin.
The col varies in depth and width, depending on the expanse of the contacting tooth surfaces. The epithelium covering the col consists of the marginal gum of the adjacent teeth, except that it is nonkeratinized. It is mainly present in the broad interdental gingiva of the posterior teeth, and generally is not present with those interproximal tissue associated with anterior teeth because the latter tissue is narrower. In the absence of contact between adjacent teeth, the attached gum extends uninterrupted from the facial to the lingual aspect. The col may be important in the formation of periodontal disease but is visible clinically only when teeth are extracted.

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline
#2000 2023-12-19 00:03:57
- Jai Ganesh
- Administrator

- Registered: 2005-06-28
- Posts: 50,869
Re: Miscellany
2002) Carpenter
Gist
A carpenter a worker who builds or repairs wooden structures or their structural parts.
Summary
A carpenter is a person who works with wood. They can make cabinets, build houses, or do other things with wood.
Carpenters usually make very good foremen (people who watch over a job) on larger jobs as they deal with so much of the project from ground up. Carpenters are always adding to their tools and always learning how to use the new tools, materials, and ways of working with wood.
Many carpenters will choose to focus their skills in one of two broad ranging categories. Rough carpenters will focus on building things that need to be simple and structural. This includes framing for houses, or crates for shipping. Finish carpenters will focus on things that are detailed and artistic. For example, they can be furniture builders, cabinet makers or toy makers. Wood carvers are sometimes counted as carpenters.
Details
Carpentry is a skilled trade and a craft in which the primary work performed is the cutting, shaping and installation of building materials during the construction of buildings, ships, timber bridges, concrete formwork, etc. Carpenters traditionally worked with natural wood and did rougher work such as framing, but today many other materials are also used and sometimes the finer trades of cabinetmaking and furniture building are considered carpentry. In the United States, 98.5% of carpenters are male, and it was the fourth most male-dominated occupation in the country in 1999. In 2006 in the United States, there were about 1.5 million carpentry positions. Carpenters are usually the first tradesmen on a job and the last to leave. Carpenters normally framed post-and-beam buildings until the end of the 19th century; now this old-fashioned carpentry is called timber framing. Carpenters learn this trade by being employed through an apprenticeship training—normally four years—and qualify by successfully completing that country's competence test in places such as the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Switzerland, Australia and South Africa. It is also common that the skill can be learned by gaining work experience other than a formal training program, which may be the case in many places.
Carpentry covers various services, such as furniture design and construction, door and window installation or repair, flooring installation, trim and molding installation, custom woodworking, stair construction, structural framing, wood structure and furniture repair, and restoration.
Etymology
The word "carpenter" is the English rendering of the Old French word carpentier (later, charpentier) which is derived from the Latin carpentarius [artifex], "(maker) of a carriage." The Middle English and Scots word (in the sense of "builder") was wright (from the Old English wryhta, cognate with work), which could be used in compound forms such as wheelwright or boatwright.
In the United Kingdom
In the UK, carpentry is used to describe the skill involved in first fixing of timber items such as construction of roofs, floors and timber framed buildings, i.e. those areas of construction that are normally hidden in a finished building. An easy way to envisage this is that first fix work is all that is done before plastering takes place. The second fix is done after plastering takes place. Second fix work, the installation of items such as skirting boards, architraves, doors, and windows are generally regarded as carpentry, however, the off-site manufacture and pre-finishing of the items is regarded as joinery. Carpentry is also used to construct the formwork into which concrete is poured during the building of structures such as roads and highway overpasses. In the UK, the skill of making timber formwork for poured or in situ concrete is referred to as shuttering.
In the United States
Carpentry in the United States is historically defined similarly to the United Kingdom as the "heavier and stronger" work distinguished from a joiner "...who does lighter and more ornamental work than that of a carpenter..." although the "...work of a carpenter and joiner are often combined." Joiner is less common than the terms finish carpenter or cabinetmaker. The terms housewright and barnwright were used historically and are now occasionally used by carpenters who work using traditional methods and materials. Someone who builds custom concrete formwork is a form carpenter.
History
Along with stone, wood is among the oldest building materials. The ability to shape it into tools, shelter, and weapons improved with technological advances from the Stone Age to the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. Some of the oldest archaeological evidence of carpentry are water well casings. These include an oak and hazel structure dating from 5256 BC, found in Ostrov, Czech Republic, and one built using split oak timbers with mortise and tenon and notched corners excavated in eastern Germany, dating from about 7,000 years ago in the early Neolithic period.
Relatively little history of carpentry was preserved before written language. Knowledge and skills were simply passed down over the generations. Even the advent of cave painting and writing recorded little. The oldest surviving complete architectural text is Vitruvius' ten books collectively titled De architectura, which discuss some carpentry.[citation needed] It was only with the invention of the printing press in the 15th century that this began to change, albeit slowly, with builders finally beginning to regularly publish guides and pattern books in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Some of the oldest surviving wooden buildings in the world are temples in China such as the Nanchan Temple built-in 782, Greensted Church in England, parts of which are from the 11th century, and the stave churches in Norway from the 12th and 13th centuries.
Europe
By the 16th century, sawmills were coming into use in Europe. The founding of America was partly based on a desire to extract resources from the new continent including wood for use in ships and buildings in Europe. In the 18th century part of the Industrial Revolution was the invention of the steam engine and cut nails. These technologies combined with the invention of the circular saw led to the development of balloon framing which was the beginning of the decline of traditional timber framing.
The 19th century saw the development of electrical engineering and distribution which allowed the development of hand-held power tools, wire nails, and machines to mass-produce screws. In the 20th century, portland cement came into common use and concrete foundations allowed carpenters to do away with heavy timber sills. Also, drywall (plasterboard) came into common use replacing lime plaster on wooden lath. Plywood, engineered lumber, and chemically treated lumber also came into use.
For types of carpentry used in America see American historic carpentry.
Training
Carpentry requires training which involves both acquiring knowledge and physical practice. In formal training a carpenter begins as an apprentice, then becomes a journeyperson, and with enough experience and competency can eventually attain the status of a master carpenter. Today pre-apprenticeship training may be gained through non-union vocational programs such as high school shop classes and community colleges.
Informally a laborer may simply work alongside carpenters for years learning skills by observation and peripheral assistance. While such an individual may obtain journeyperson status by paying the union entry fee and obtaining a journeyperson's card (which provides the right to work on a union carpentry crew) the carpenter foreperson will, by necessity, dismiss any worker who presents the card but does not demonstrate the expected skill level.
Carpenters may work for an employer or be self-employed. No matter what kind of training a carpenter has had, some U.S. states require contractors to be licensed which requires passing a written test and having minimum levels of insurance.
Schools and programs
Formal training in the carpentry trade is available in seminars, certificate programs, high-school programs, online classes, in the new construction, restoration, and preservation carpentry fields. Sometimes these programs are called pre-apprenticeship training.
In the modern British construction industry, carpenters are trained through apprenticeship schemes where general certificates of secondary education (GCSE) in Mathematics, English, and Technology help but are not essential. However, this is deemed the preferred route, as young people can earn and gain field experience whilst training towards a nationally recognized qualification.
There are two main divisions of training: construction-carpentry and cabinetmaking. During pre-apprenticeship, trainees in each of these divisions spend 30 hours a week for 12 weeks in classrooms and indoor workshops learning mathematics, trade terminology, and skill in the use of hand and power tools. Construction-carpentry trainees also participate in calisthenics to prepare for the physical aspect of the work.
Upon completion of pre-apprenticeship, trainees who have successfully passed the graded curriculum (taught by highly experienced journeyperson carpenters) are assigned to a local union and to union carpentry crews at work on construction sites or in cabinet shops as First Year Apprentices. Over the next four years, as they progress in status to Second Year, Third Year, and Fourth Year Apprentice, apprentices periodically return to the training facility every three months for a week of more detailed training in specific aspects of the trade.
In the United States, fewer than 5% of carpenters identify as female. A number of schools in the U.S. appeal to non-traditional tradespeople by offering carpentry classes for and taught by women, including Hammerstone: Carpentry for Women in Ithaca, NY, Yestermorrow in Waitsfield, VT and Oregon Tradeswomen in Portland, OR.
Apprenticeships and journeyperson
Tradesmen in countries such as Germany and Australia are required to fulfill formal apprenticeships (usually three to four years) to work as professional carpenters. Upon graduation from the apprenticeship, they are known as journeyperson carpenters.
Up through the 19th and even the early 20th century, the journeyperson traveled to another region of the country to learn the building styles and techniques of that area before (usually) returning home. In modern times, journeypeople are not required to travel, and the term now refers to a level of proficiency and skill. Union carpenters in the United States, that is, members of the United Brotherhood of Carpenters and Joiners of America, are required to pass a skills test to be granted official journeyperson status, but uncertified professional carpenters may also be known as journeypersons based on their skill level, years of experience, or simply because they support themselves in the trade and not due to any certification or formal woodworking education.
Professional status as a journeyperson carpenter in the United States may be obtained in a number of ways. Formal training is acquired in a four-year apprenticeship program administered by the United Brotherhood of Carpenters and Joiners of America, in which journeyperson status is obtained after successful completion of twelve weeks of pre-apprenticeship training, followed by four years of on-the-job field training working alongside journeyperson carpenters. The Timber Framers Guild also has a formal apprenticeship program for traditional timber framing. Training is also available in groups like the Kim Bồng woodworking village in Vietnam where apprentices live and work to learn woodworking and carpentry skills.
In Canada, each province sets its own standards for apprenticeship. The average length of time is four years and includes a minimum number of hours of both on-the-job training and technical instruction at a college or other institution. Depending on the number of hours of instruction an apprentice receives, they can earn a Certificate of Proficiency, making them a journeyperson, or a Certificate of Qualification, which allows them to practice a more limited amount of carpentry. Canadian carpenters also have the option of acquiring an additional Interprovincial Red Seal that allows them to practice anywhere in Canada. The Red Seal requires the completion of an apprenticeship and an additional examination.
Master carpenter
After working as a journeyperson for a while, a carpenter may go on to study or test as a master carpenter. In some countries, such as Germany, Iceland and Japan, this is an arduous and expensive process, requiring extensive knowledge (including economic and legal knowledge) and skill to achieve master certification; these countries generally require master status for anyone employing and teaching apprentices in the craft. In others, like the United States, 'master carpenter' can be a loosely used term to describe any skilled carpenter.
Fully trained carpenters and joiners will often move into related trades such as shop fitting, scaffolding, bench joinery, maintenance and system installation.
Materials
Carpenters traditionally worked with natural wood which has been prepared by splitting (riving), hewing, or sawing with a pit saw or sawmill called lumber (American English) or timber (British English). Today natural and engineered lumber and many other building materials carpenters may use are typically prepared by others and delivered to the job site. In 2013 the carpenters union in America used the term carpenter for a catch-all position. Tasks performed by union carpenters include installing "...flooring, windows, doors, interior trim, cabinetry, solid surface, roofing, framing, siding, flooring, insulation, ...acoustical ceilings, computer-access flooring, metal framing, wall partitions, office furniture systems, and both custom or factory-produced materials, ...trim and molding,... ceiling treatments, ... exposed columns and beams, displays, mantels, staircases...metal studs, metal lath, and drywall..."
Health and safety:
United States
Carpentry is often hazardous work. Types of woodworking and carpentry hazards include: machine hazards, flying materials, tool projection, fire and explosion, electrocution, noise, vibration, dust, and chemicals. In the United States the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) tries to prevent illness, injury, and fire through regulations. However, self-employed workers are not covered by the OSHA act. OSHA claims that "Since 1970, workplace fatalities have been reduced by more than 65 percent and occupational injury and illness rates have declined by 67 percent. At the same time, U.S. employment has almost doubled." The leading cause of overall fatalities, called the "fatal four," are falls, followed by struck by object, electrocution, and caught-in/between. In general construction "employers must provide working conditions that are free of known dangers. Keep floors in work areas in a clean and, so far as possible, dry condition. Select and provide required personal protective equipment at no cost to workers. Train workers about job hazards in a language that they can understand." Examples of how to prevent falls includes placing railings and toe-boards at any floor opening which cannot be well covered and elevated platforms and safety harness and lines, safety nets, stair railings, and handrails.
Safety is not just about the workers on the job site. Carpenters' work needs to meet the requirements in the Life Safety Code such as in stair building and building codes to promote long-term quality and safety for the building occupants.
Types
* Cabinetmaker is a carpenter who does fine and detailed work specializing in the making of cabinets made from wood, wardrobes, dressers, storage chests, and other furniture designed for storage.
* Carpenter and joiner has broad skill sets ranging from joinery, finish carpentry, framing, and formwork.
* Conservation carpenter works in architectural conservation, known in the U.S. as a "preservation" or "restoration"; a carpenter who works in historic preservation, maintaining structures as they were built or restoring them to that condition.
* Cooper, a barrel maker.
* Finish carpenter (North America), also trim carpenter, specializes in installing molding and trim, such as door and window casings, mantels, crown mouldings, baseboards, and other types of ornamental work. Finish carpenters pick up where framing ends off, including hanging doors and installing cabinets.
* Formwork carpenter creates the shuttering and falsework used in concrete construction, and reshores as necessary.
* Framer is a carpenter who builds the skeletal structure or wooden framework of buildings, most often in the platform framing method. A framer who specializes in building with timbers and traditional joints rather than studs is known as a timber framer.
* Log builder builds structures of stacked horizontal logs with limited joints.
* Joiner (a traditional name now rare in North America), is one who does cabinetry, furniture making, fine woodworking, model building, instrument making, parquetry, joinery, or other carpentry where exact joints and minimal margins of error are important.
* Luthier is someone who makes or repairs stringed instruments. The word luthier comes from the French word for lute, "luth".
* Restoration carpenter
* Set carpenter builds and dismantles temporary scenery and sets in film-making, television, and the theater.
* Ship's carpenter specializes in maintenance, repair techniques, and carpentry specific to vessels afloat. Such a carpenter patrols the vessel's carpenter's walk to examine the hull for leaks.
* Shipwright builds wooden ships on land.
Other
* Japanese carpentry, daiku is the simple term for carpenter, a Miya-daiku (temple carpenter) performs the work of both architect and builder of shrines and temples, and a sukiya-daiku works on teahouse construction and houses. Sashimono-shi build furniture and tateguya do interior finishing work.
*Green carpentry specializes in the use of environmentally friendly, energy-efficient and sustainable sources of building materials for use in construction projects. They also practice building methods that require using less material and material that has the same structural soundness.
*Recycled (reclaimed, repurposed) carpentry is carpentry that uses scrap wood and parts of discarded or broken furniture to build new wood products

It appears to me that if one wants to make progress in mathematics, one should study the masters and not the pupils. - Niels Henrik Abel.
Nothing is better than reading and gaining more and more knowledge - Stephen William Hawking.
Offline